gsElasticity is a submodule of G+Smo which has started as a collection of nonlinear elasticity solvers for 2D and 3D solids. Since then, its focus has shifted towards mesh deformation, and now gsElasticity contains isogeometric solvers for nonlinear elasticity and incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, various PDE-based mesh deformations algorithms and a partitioned fluid-structure interaction solver. Additionally, gsElasticity includes numerous application examples and the corresponding NURBS geometries.
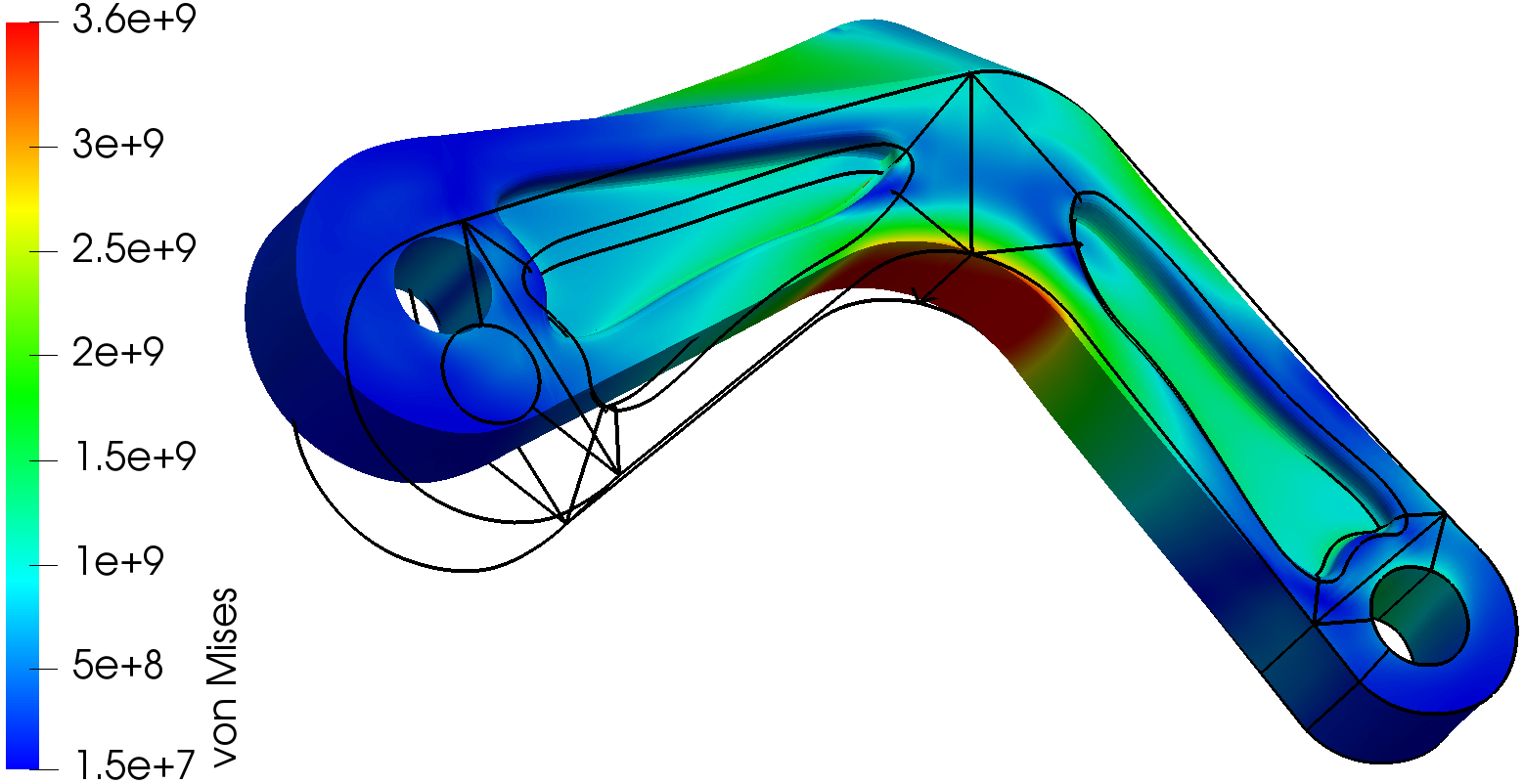
------------------ Nonlinear elastic deformation of a 3D object ----------------------------------------------------
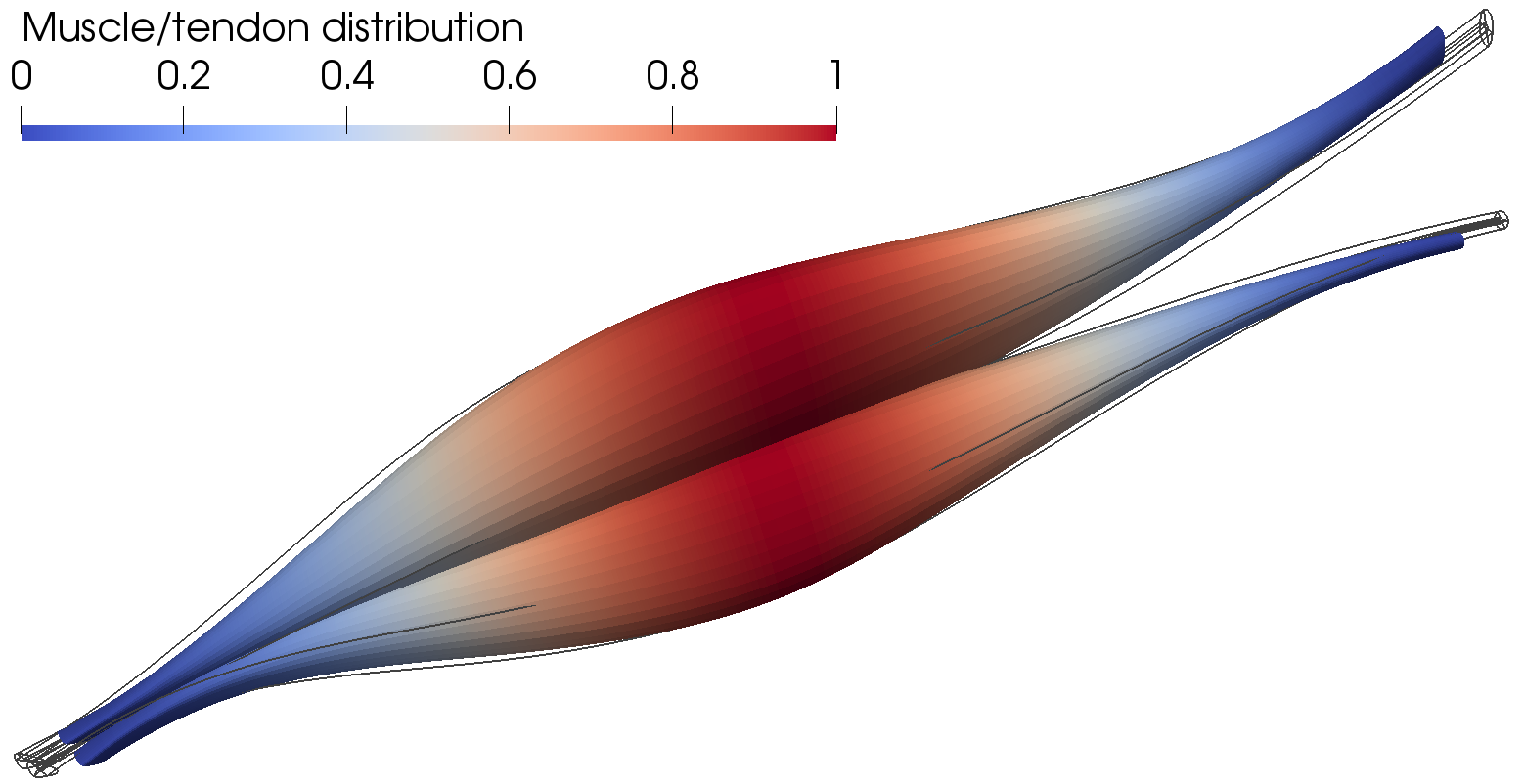
------------------ Active muscle behavior ----------------------------------------------------
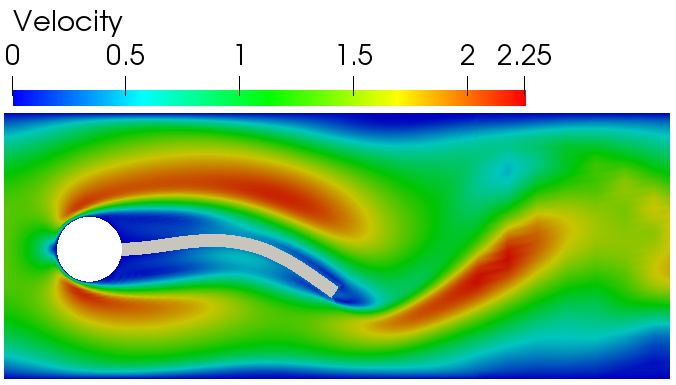
------------------ Fluid-structure interaction in 2D ---------------------------------------------------------------
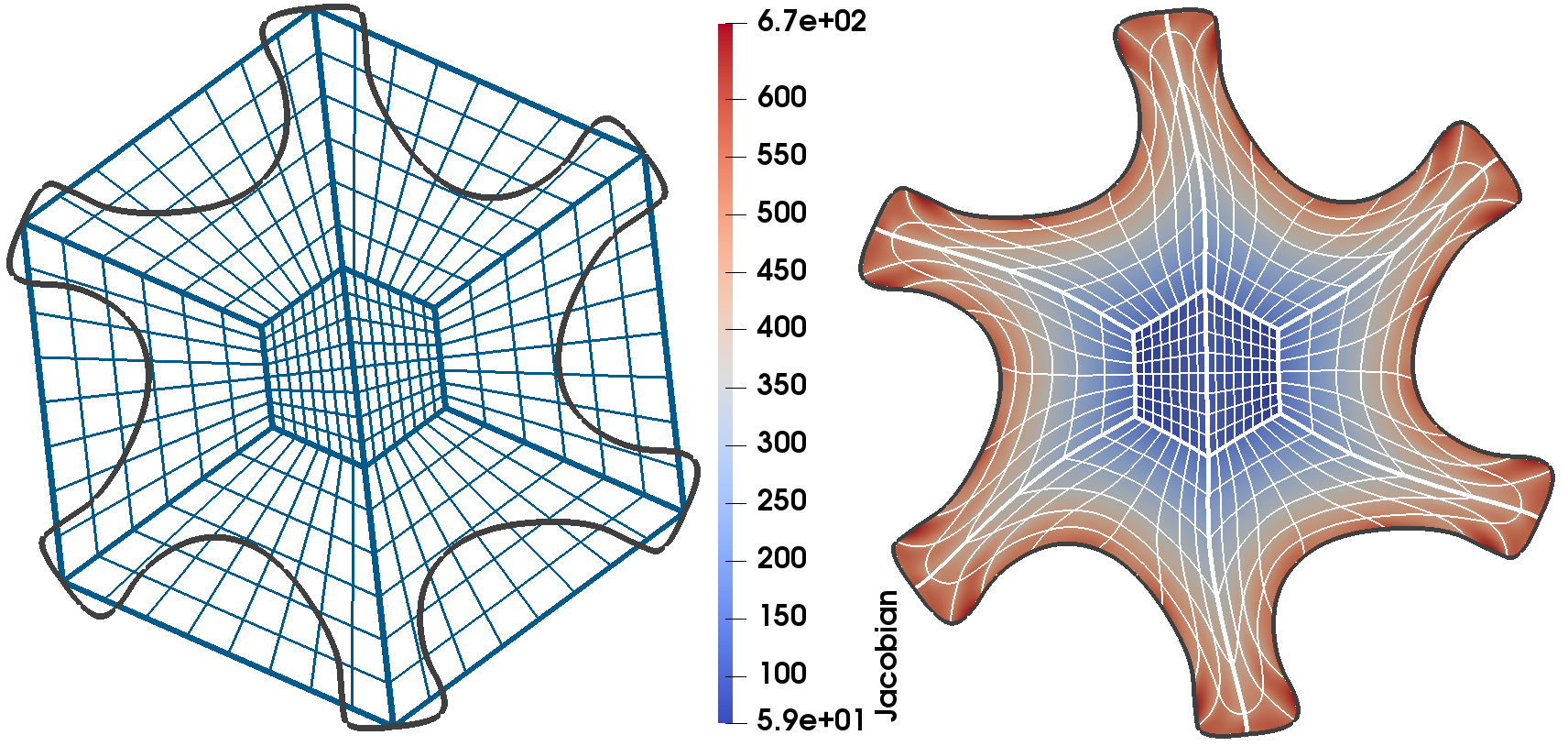
------------------ Mesh deformation for isogeometric domain parametrization -----------------------------------------
gsElasticity currently includes the following solvers for 2D and 3D multi-patch tensor-product NURBS geometries:
- Elasticity solvers
- linear elasticity
- nonlinear elasticity with St.Venant-Kirchhoff and neo-Hookean material laws
- implicit time integration with Newmark method
- pure displacement and mixed displacement-pressure formulations
- thermal expansion
- active muscle behavior
- Incompressible Navier-Stokes solver
- Stokes equation
- stationary INSE
- explicit and implicit time integration with the one-step theta-scheme
- suitable for arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) mappings
SUPG stabilizationturbulence model
- Fluid-structure interaction solver
- partitioned approach
- strong coupling
- Aitken relaxation for convergence speed-up
- Bi-harmonic equation solver in mixed formulation
- Poisson's equation solver
Since gsElasticity is a submodule of G+Smo, you should download G+Smo first:
git clone https://github.com/gismo/gismo.git
Then, configure G+Smo with `-DGISMO_OPTIONAL=";gsElasticity"````:
cd gismo
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. -DGISMO_OPTIONAL="<other submodules>;gsElasticity"
This will trigger a download of gsElasticity from GitHub. Once gsElasticity is downloaded, you can compile G+Smo with gsElasticity:
make
Once complete, you can find the compiled library in /path/to/gismo/build/lib and examples in /path/to/gismo/build/bin.
gsElasticity is an independent .git repository. By default, the procedure described above downloads the version of gsElasticity that is linked to G+Smo. Usually, it is the latest stable version. However, if you want to get other versions/branches of gsElastisity, or even contribute to it, you should access gsElasticity via its .git repository located in /path/to/gismo/extenstions/gsElasticity. For example, to get the latest version of gsElasticity, do
cd /path/to/gismo/extenstion/gsElasticity
git pull
Simulation of time-dependent processes can be rather computationally costly. Although G+Smo and gsElasticity are not suitable for distributed computing, you can achieve significant speed-up by using it with multi-theading on your desktop or laptop. To that end, you should install OpenMP library https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/openmp-introduction-with-installation-guide/. Once you have OpenMP, configure G+Smo with GISMO_WITH_OPENMP=ON:
cd /path/to/gismo/build
cmake .. -DGISMO_OPTIONAL="<other submodules>;gsElasticity" -DGISMO_WITH_OPENMP=ON
By defining the environmental variable OMP_NUM_THREADS, you can choose how many threads your application is going to use
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=<number of threads to use>
With OpenMP included, at least the linear system assebmly is parallelized. This is a big deal in IGA since the high continuity of NURBS inceases the support of each basis function, which in turn increases the number of function evaluations necessary for matrix assembly. However, G+Smo uses Eigen library http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Main_Page as a linear algebra backend, and linear system solvers in Eigen tend to be pretty slow. Luckily, there is a way to significantly speed up your applications - get Pardiso solver https://www.pardiso-project.org/ and compile G+Smo with it included!
There are two options to get Pardiso - either as a stand-alone library from the official page https://www.pardiso-project.org/#download, or as a part of Intel MKL https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl. The former options allows you to get the latest version of Pardiso (which, theoretically, should be faster than the version that Intel MKL uses). Once you register, download the library and get a license, you can configure G+Smo with Pardiso by
cd /path/to/gismo/build
cmake .. -DGISMO_OPTIONAL="<other submodules>;gsElasticity" -DGISMO_WITH_OPENMP=ON -DGISMO_WITH_PARDISO=ON -DPardiso_DIR=/path/to/pardiso
The Intel MKL way to use Pardiso is only viable for machines with an Intel CPU. To that end, you should register at Intel Development Tools https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/free-ipsxe-tools-and-libraries, download and intall Inter C/C++ compiler and Intel MKL library. After that, you can configure G+Smo with Pardiso in the following way:
cd /path/to/gismo/build
source /path/to/intel/compilers_and_libraries/linux/bin/compilervars.sh intel64
cmake .. -DGISMO_OPTIONAL="<other submodules>;gsElasticity" -DGISMO_WITH_OPENMP=ON -DEIGEN_USE_MKL_ALL=ON -DGISMO_WITH_PARDISO=ON -DPARDISO_USE_MKL=ON -DINTEL_ROOT=/path/to/intel -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=icc -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=icpc
Despite an older version of Pardiso used in MKL, Intel optimization often results in faster performance than if a stand-alone library is used.
Final tip: you can speed up the compilation of G+Smo by specifying the number of threads make command uses:
make -j<number of threads to use>
Check out numerous detailed examples in path/to/gismo/extensions/gsElasticity/examples!