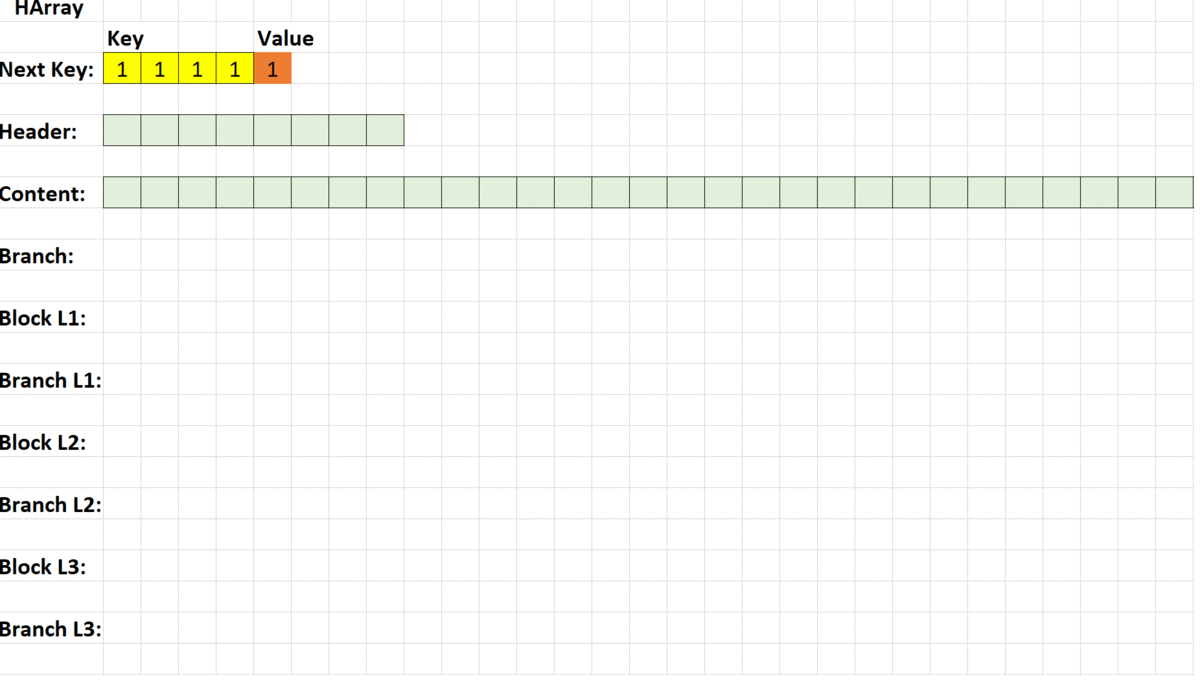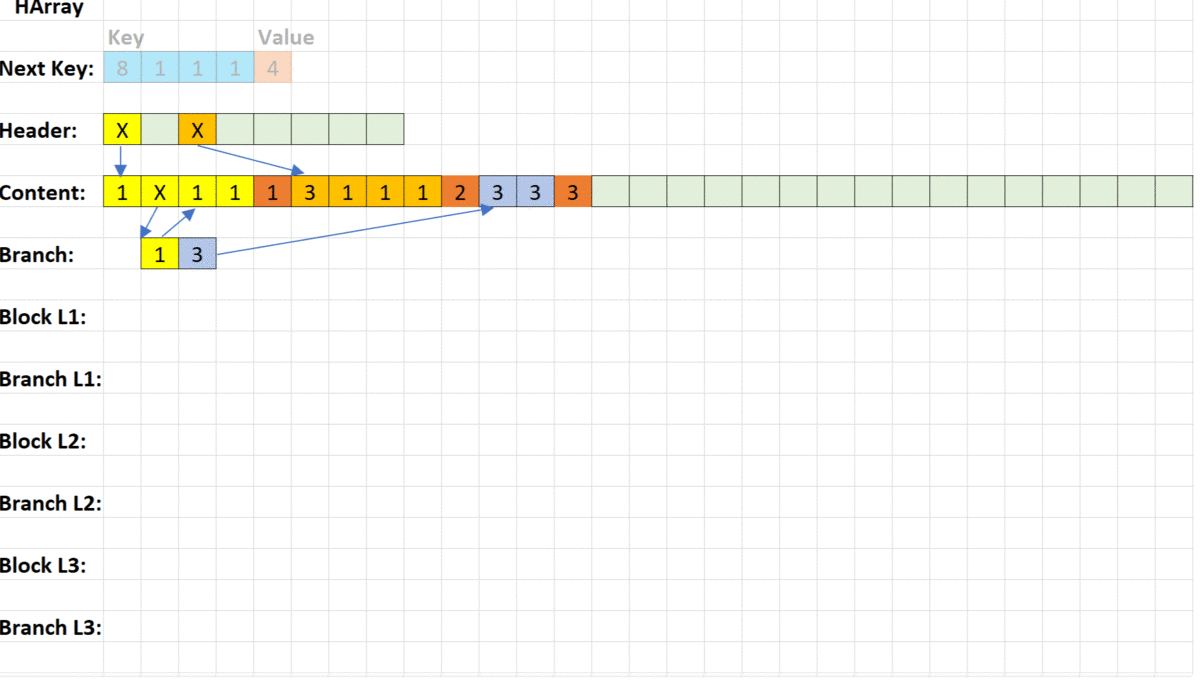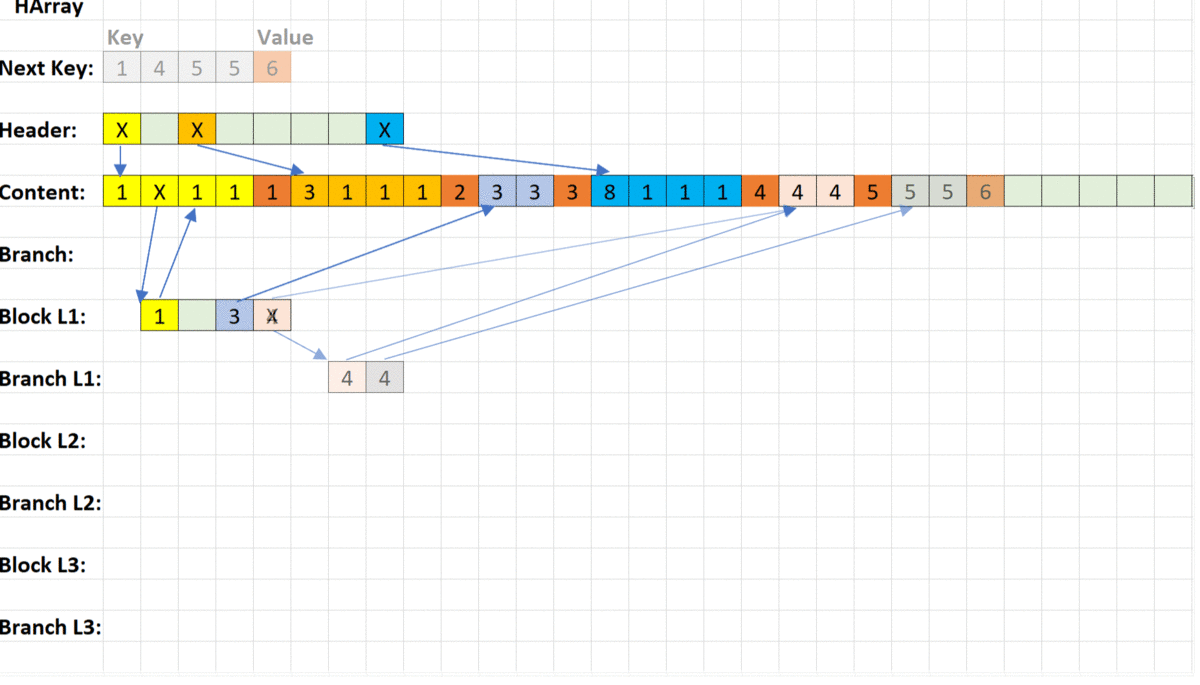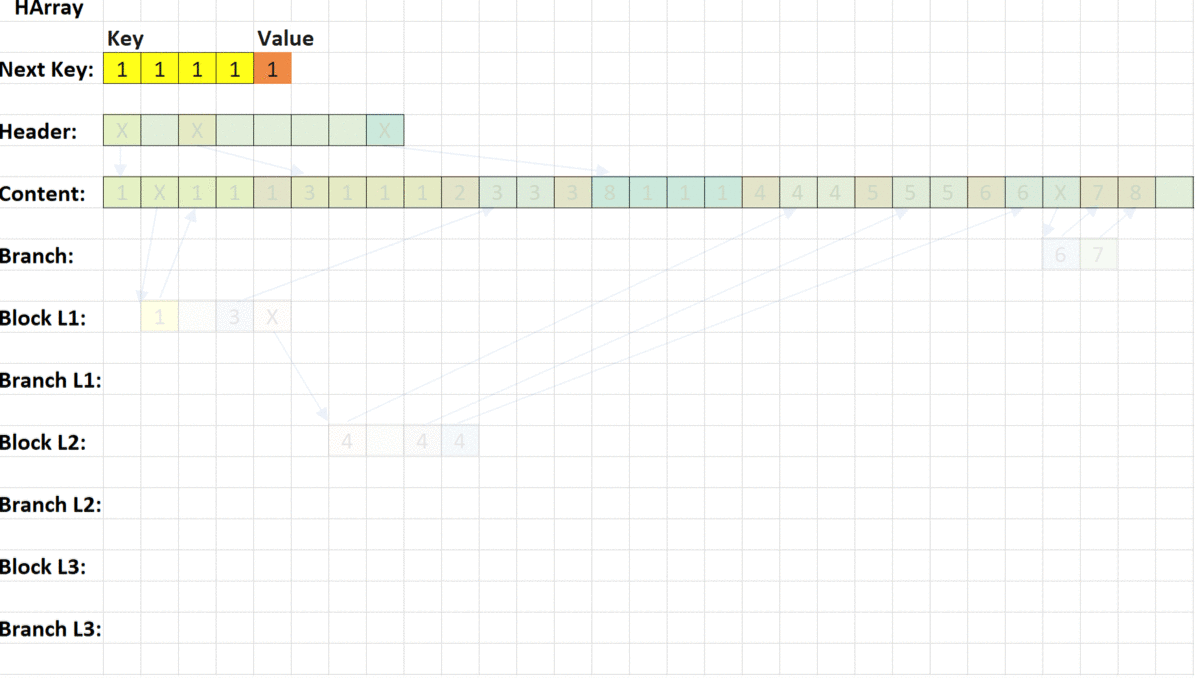
Best way understand difference between associative arrays if you realise how several keys will be arranged inside. We have only three Keys - each with four segments (one segment could be 1 byte or 4 byte or 8 bytes - it doesn't matter in our explanation).
In Hashtable these keys will be arranged in more complex structure as unordered data. Also sometimes it needs more extra space.
In Trie these keys will be arranged as ordered data and sometimes it requires a little bit less space.
In Binary Tree we need find right place in ordered sequence and insert our key there. Sometimes we need split our page to do balancing of tree.
If you have a good hash function in almost cases you just filled new empty space in Address Table. But if you have much data, even with good hash function you will have much collisions. Here illustrated Best Case for Hashtable without any collisions.
If you insert a new key into Trie, you needn't reallocate or balancing data and you can use existing segments as part of your new key.
If you search a key in Binary Tree you need always makes long jumps. If you have 1 million keys these jumps will be about 20.
In Hashtable in Best Case you put your key into hash function and after calculation of address you make one long jump by this address. But this is not enough, when you come by address you need scan your key again to ensure that this address is right. In collision case you need scan all scope of collided keys.
In Trie you always scan key only once. It could costs several long jumps, but maximum amount of jumps always constant. It like a maze - you need find right way.
___