| title | description | keywords | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2415. 反转二叉树的奇数层 |
LeetCode 2415. 反转二叉树的奇数层题解,Reverse Odd Levels of Binary Tree,包含解题思路、复杂度分析以及完整的 JavaScript 代码实现。 |
|
🟠 Medium 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
Given the root of a perfect binary tree, reverse the node values at each
odd level of the tree.
- For example, suppose the node values at level 3 are
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18], then it should become[18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2].
Return the root of the reversed tree.
A binary tree is perfect if all parent nodes have two children and all leaves are on the same level.
The level of a node is the number of edges along the path between it and the root node.
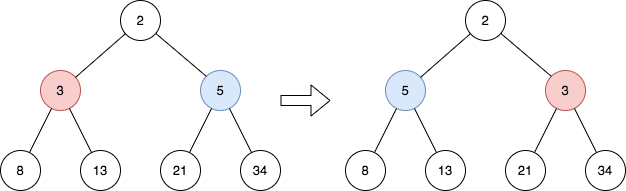
Example 1:
Input: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34]
Output: [2,5,3,8,13,21,34]
Explanation:
The tree has only one odd level.
The nodes at level 1 are 3, 5 respectively, which are reversed and become 5, 3.
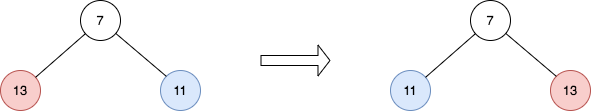
Example 2:
Input: root = [7,13,11]
Output: [7,11,13]
Explanation:
The nodes at level 1 are 13, 11, which are reversed and become 11, 13.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2]
Output: [0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1]
Explanation:
The odd levels have non-zero values.
The nodes at level 1 were 1, 2, and are 2, 1 after the reversal.
The nodes at level 3 were 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, and are 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1 after the reversal.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 214]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10^5rootis a perfect binary tree.
给你一棵 完美 二叉树的根节点 root ,请你反转这棵树中每个 奇数 层的节点值。
- 例如,假设第 3 层的节点值是
[2,1,3,4,7,11,29,18],那么反转后它应该变成[18,29,11,7,4,3,1,2]。
反转后,返回树的根节点。
完美 二叉树需满足:二叉树的所有父节点都有两个子节点,且所有叶子节点都在同一层。
节点的 层数 等于该节点到根节点之间的边数。
示例 1:
输入: root = [2,3,5,8,13,21,34]
输出:[2,5,3,8,13,21,34]
解释:
这棵树只有一个奇数层。
在第 1 层的节点分别是 3、5 ,反转后为 5、3 。
示例 2:
输入: root = [7,13,11]
输出:[7,11,13]
解释:
在第 1 层的节点分别是 13、11 ,反转后为 11、13 。
示例 3:
输入: root = [0,1,2,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2]
输出:[0,2,1,0,0,0,0,2,2,2,2,1,1,1,1]
解释: 奇数层由非零值组成。
在第 1 层的节点分别是 1、2 ,反转后为 2、1 。
在第 3 层的节点分别是 1、1、1、1、2、2、2、2 ,反转后为 2、2、2、2、1、1、1、1 。
提示:
- 树中的节点数目在范围
[1, 214]内 0 <= Node.val <= 10^5root是一棵 完美 二叉树
- 使用队列进行层序遍历。
- 在遍历的过程中:
- 如果是奇数层,反转交换当前层的节点值。
- 将当前层节点的子节点插入队列。
- 将当前层的节点出队。
- 返回修改后的树。
- 时间复杂度:
O(n)- 每个节点访问一次,时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - 反转每一奇数层的值,时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - 总时间复杂度为
O(n)。
- 每个节点访问一次,时间复杂度为
- 空间复杂度:
O(n),队列的最大长度为某一层的节点数,最坏情况下为O(n)。
- 通过递归遍历树。
- 当到达奇数层时,将左子树和右子树对应位置的值交换。
- 对于偶数层,不进行任何操作。
- 递归地同时遍历左子树和右子树。
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),每个节点访问一次。 - 空间复杂度:
O(log n),递归栈的最大深度为树的高度,最坏情况下为O(log n)。
::: code-tabs
@tab 广度优先搜索(BFS)
var reverseOddLevels = function (root) {
if (!root) return root;
let queue = [root]; // 初始化队列
let level = 0; // 当前层数
while (queue.length > 0) {
const n = queue.length;
// 遍历当前层
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前是奇数层,交换两个节点的值
if (level % 2 == 1 && i < n / 2) {
let temp = queue[i].val;
queue[i].val = queue[n - 1 - i].val;
queue[n - 1 - i].val = temp;
}
// 下一层节点入队
if (queue[i].left) queue.push(queue[i].left);
if (queue[i].right) queue.push(queue[i].right);
}
queue = queue.slice(n);
level++; // 进入下一层
}
return root;
};@tab 深度优先搜索(DFS)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var reverseOddLevels = function (root) {
const dfs = (left, right, level) => {
if (!left || !right) return;
// 如果当前是奇数层,交换两个节点的值
if (level % 2 == 0) {
let temp = left.val;
left.val = right.val;
right.val = temp;
}
// 递归下一层
dfs(left.left, right.right, level + 1);
dfs(left.right, right.left, level + 1);
};
// 从第 1 层开始(根节点为第 0 层)
dfs(root.left, root.right, 0);
return root;
};:::
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 226 | 翻转二叉树 | [✓] | 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 1+ |
🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |