| title | description | keywords | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2458. 移除子树后的二叉树高度 |
LeetCode 2458. 移除子树后的二叉树高度题解,Height of Binary Tree After Subtree Removal Queries,包含解题思路、复杂度分析以及完整的 JavaScript 代码实现。 |
|
🔴 Hard 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 数组 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is
assigned a unique value from 1 to n. You are also given an array queries
of size m.
You have to perform m independent queries on the tree where in the ith
query you do the following:
- Remove the subtree rooted at the node with the value
queries[i]from the tree. It is guaranteed thatqueries[i]will not be equal to the value of the root.
Return an arrayanswer of sizem whereanswer[i]is the height of the
tree after performing theith query.
Note :
- The queries are independent, so the tree returns to its initial state after each query.
- The height of a tree is the number of edges in the longest simple path from the root to some node in the tree.
Example 1:
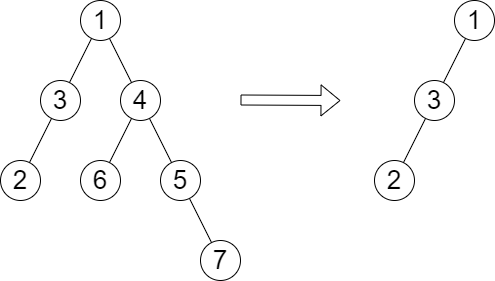
Input: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4]
Output: [2]
Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree after removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4.
The height of the tree is 2 (The path 1 -> 3 -> 2).
Example 2:
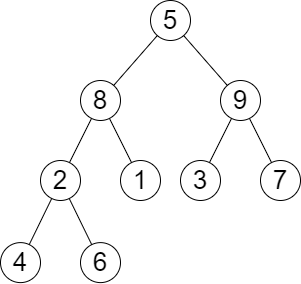
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8]
Output: [3,2,3,2]
Explanation: We have the following queries:
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 3. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 2. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 1).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 4. The height of the tree becomes 3 (The path 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6).
- Removing the subtree rooted at node with value 8. The height of the tree becomes 2 (The path 5 -> 9 -> 3).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 10^51 <= Node.val <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 104)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
给你一棵 二叉树 的根节点 root ,树中有 n 个节点。每个节点都可以被分配一个从 1 到 n 且互不相同的值。另给你一个长度为
m 的数组 queries 。
你必须在树上执行 m 个 独立 的查询,其中第 i 个查询你需要执行以下操作:
- 从树中 移除 以
queries[i]的值作为根节点的子树。题目所用测试用例保证queries[i]不 等于根节点的值。
返回一个长度为 m 的数组 **answer ** ,其中 answer[i] 是执行第 i 个查询后树的高度。
注意:
- 查询之间是独立的,所以在每个查询执行后,树会回到其 初始 状态。
- 树的高度是从根到树中某个节点的 最长简单路径中的边数 。
示例 1:
输入: root = [1,3,4,2,null,6,5,null,null,null,null,null,7], queries = [4]
输出:[2]
解释: 上图展示了从树中移除以 4 为根节点的子树。
树的高度是 2(路径为 1 -> 3 -> 2)。
示例 2:
输入: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], queries = [3,2,4,8]
输出:[3,2,3,2]
解释: 执行下述查询:
- 移除以 3 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 3(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 4)。
- 移除以 2 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 2(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 1)。
- 移除以 4 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 3(路径为 5 -> 8 -> 2 -> 6)。
- 移除以 8 为根节点的子树。树的高度变为 2(路径为 5 -> 9 -> 3)。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目是
n 2 <= n <= 10^51 <= Node.val <= n- 树中的所有值 互不相同
m == queries.length1 <= m <= min(n, 10^4)1 <= queries[i] <= nqueries[i] != root.val
树的高度是指从根节点到叶子节点的最长路径上的边数,使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来计算树的高度。
-
存储节点信息:
- 使用一个哈希表(
heightMap)来存储每个节点的高度和深度,键为节点的值,值为一个数组,包含节点的高度和深度[height, depth]。
- 使用一个哈希表(
-
层级信息的存储:
- 使用另一个哈希表(
levelsMap)来存储每一层的最大高度和第二高的节点,对于每一层,我们需要记录:- 最大高度(max)
- 第二高的高度(second)
- 最大高度节点的值(maxNodeVal)
- 使用另一个哈希表(
-
计算树的高度:
- 通过递归方式遍历树的每个节点,在遍历过程中计算每个节点的高度,并更新
heightMap和levelsMap。
- 通过递归方式遍历树的每个节点,在遍历过程中计算每个节点的高度,并更新
-
处理查询:
- 对于每个查询,首先获取待删除节点的高度和深度。
- 检查该节点是否为其所在层的最大高度节点:
- 如果是,新的树高度为
rootHeight - max + second(即去掉最大高度节点的影响,使用第二高的高度)。 - 如果不是,树的高度保持不变,即
rootHeight。
- 如果是,新的树高度为
-
返回结果:
- 将每个查询的结果存储到数组中,并最终返回该数组。
- 时间复杂度:
O(n + m),其中n为树的节点数,m为查询的数量;- DFS 计算高度和层级信息的时间复杂度为
O(n); - 查询每个节点的高度的时间复杂度为
O(1),总查询复杂度为O(m);
- DFS 计算高度和层级信息的时间复杂度为
- 空间复杂度:
O(n),存储每个节点信息的heightMap和levelsMap的空间复杂度均为O(n);
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number[]} queries
* @return {number[]}
*/
var treeQueries = function (root, queries) {
let heightMap = new Map();
let levelsMap = new Map();
// DFS 计算高度并记录每层的最大和第二高
calculateHeight(root, heightMap, levelsMap, 0);
const res = [];
const rootHeight = heightMap.get(root.val)[0];
for (let num of queries) {
const [height, deep] = heightMap.get(num);
const { max, second, maxNodeVal } = levelsMap.get(deep);
// 检查该节点是否为其所在层的最大高度节点
if (num === maxNodeVal) {
res.push(rootHeight - max + second);
} else {
res.push(rootHeight);
}
}
return res;
};
var calculateHeight = function (node, heightMap, levelsMap, deep) {
if (!node) return -1;
const left = calculateHeight(node.left, heightMap, levelsMap, deep + 1);
const right = calculateHeight(node.right, heightMap, levelsMap, deep + 1);
const height = 1 + Math.max(left, right);
heightMap.set(node.val, [height, deep]);
if (!levelsMap.has(deep)) {
levelsMap.set(deep, { max: height, second: -1, maxNodeVal: node.val });
} else {
const levelInfo = levelsMap.get(deep);
if (height > levelInfo.max) {
levelInfo.second = levelInfo.max;
levelInfo.max = height;
levelInfo.maxNodeVal = node.val;
} else if (height > levelInfo.second) {
levelInfo.second = height;
}
}
return height;
};| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | 二叉树的最大深度 | [✓] | 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 1+ |
🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |