| title | description | keywords | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2577. 在网格图中访问一个格子的最少时间 |
LeetCode 2577. 在网格图中访问一个格子的最少时间题解,Minimum Time to Visit a Cell In a Grid,包含解题思路、复杂度分析以及完整的 JavaScript 代码实现。 |
|
🔴 Hard 🔖 广度优先搜索 图 数组 矩阵 最短路 堆(优先队列) 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
You are given a m x n matrix grid consisting of non-negative integers
where grid[row][col] represents the minimum time required to be able to
visit the cell (row, col), which means you can visit the cell (row, col)
only when the time you visit it is greater than or equal to grid[row][col].
You are standing in the top-left cell of the matrix in the 0th second,
and you must move to any adjacent cell in the four directions: up, down,
left, and right. Each move you make takes 1 second.
Return theminimum time required in which you can visit the bottom-right
cell of the matrix. If you cannot visit the bottom-right cell, then return
-1.
Example 1:
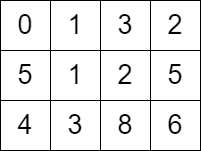
Input: grid = [[0,1,3,2],[5,1,2,5],[4,3,8,6]]
Output: 7
Explanation: One of the paths that we can take is the following:
- at t = 0, we are on the cell (0,0).
- at t = 1, we move to the cell (0,1). It is possible because grid[0][1] <= 1.
- at t = 2, we move to the cell (1,1). It is possible because grid[1][1] <= 2.
- at t = 3, we move to the cell (1,2). It is possible because grid[1][2] <= 3.
- at t = 4, we move to the cell (1,1). It is possible because grid[1][1] <= 4.
- at t = 5, we move to the cell (1,2). It is possible because grid[1][2] <= 5.
- at t = 6, we move to the cell (1,3). It is possible because grid[1][3] <= 6.
- at t = 7, we move to the cell (2,3). It is possible because grid[2][3] <= 7.
The final time is 7. It can be shown that it is the minimum time possible.
Example 2:
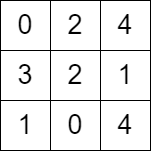
Input: grid = [[0,2,4],[3,2,1],[1,0,4]]
Output: -1
Explanation: There is no path from the top left to the bottom-right cell.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 10^50 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5grid[0][0] == 0
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵 grid ,每个元素都为 非负 整数,其中 grid[row][col] 表示可以访问格子 (row, col) 的 最早 时间。也就是说当你访问格子 (row, col) 时,最少已经经过的时间为 grid[row][col] 。
你从 最左上角 出发,出发时刻为 0 ,你必须一直移动到上下左右相邻四个格子中的 任意
一个格子(即不能停留在格子上)。每次移动都需要花费 1 单位时间。
请你返回 最早 到达右下角格子的时间,如果你无法到达右下角的格子,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
输入: grid = [[0,1,3,2],[5,1,2,5],[4,3,8,6]]
输出: 7
解释: 一条可行的路径为:
- 时刻 t = 0 ,我们在格子 (0,0) 。
- 时刻 t = 1 ,我们移动到格子 (0,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[0][1] <= 1 。
- 时刻 t = 2 ,我们移动到格子 (1,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][1] <= 2 。
- 时刻 t = 3 ,我们移动到格子 (1,2) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][2] <= 3 。
- 时刻 t = 4 ,我们移动到格子 (1,1) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][1] <= 4 。
- 时刻 t = 5 ,我们移动到格子 (1,2) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][2] <= 5 。
- 时刻 t = 6 ,我们移动到格子 (1,3) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[1][3] <= 6 。
- 时刻 t = 7 ,我们移动到格子 (2,3) ,可以移动的原因是 grid[2][3] <= 7 。
最终到达时刻为 7 。这是最早可以到达的时间。
示例 2:
输入: grid = [[0,2,4],[3,2,1],[1,0,4]]
输出: -1
解释: 没法从左上角按题目规定走到右下角。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 10^50 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5grid[0][0] == 0
这是一个 加权图的最短路径问题,使用 优先队列(小顶堆) 来动态选择路径最短的格子。
- 判断是否直接不可行
如果起点的右边 (0, 1) 和下方 (1, 0) 都需要大于 1 的时间才解锁,无法开始任何有效移动,直接返回 -1。
- 使用优先队列动态搜索最短路径
- 队列中存储的是
[时间, 行, 列]格子信息,优先选择时间最短的格子进行扩展。 - 每次从优先队列中取出当前时间最小的状态
(t, r, c)。 - 尝试移动到四个相邻格子
(nr, nc),新的时间newTime取决于:- 如果到达新格子时,时间大于等于其解锁时间
grid[nr][nc],则可以直接移动,newTime等于当前时间t加上移动的时间1。 - 否则,需要在之前的相邻格子内来回移动,直到时间大于等于
grid[nr][nc],且从(r, c)到(nr, nc)所花的时间一定为奇数(2 * 来回移动次数 + 最终移动到(nr, nc)的一步)
const wait = Math.abs(grid[nr][nc] - t) % 2 === 0 ? 1 : 0; const newTime = Math.max(grid[nr][nc] + wait, t + 1);
- 如果到达新格子时,时间大于等于其解锁时间
- 使用访问集合优化
- 用
visited集合记录访问过的格子[r, c],避免重复访问。 - 如果新路径的时间小于已知最短路径,才会重新处理。
- 时间复杂度:
O(m * n * log(m * n)),每个格子最多访问一次,且每次从堆中弹出操作的复杂度为O(log(m * n))。 - 空间复杂度:
O(m * n),需要存储visited集合和优先队列。
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var minimumTime = function (grid) {
// 如果无法从起点有效移动,返回 -1
if (Math.min(grid[0][1], grid[1][0]) > 1) {
return -1;
}
const m = grid.length,
n = grid[0].length;
// 最小优先队列,优先扩展时间最短的路径
const minHeap = new MinPriorityQueue({ priority: (x) => x[0] });
minHeap.enqueue([0, 0, 0]); // 初始状态 [时间, 行, 列]
const visited = new Set();
const directions = [
[1, 0],
[-1, 0],
[0, 1],
[0, -1]
]; // 四个方向
// BFS 遍历
while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) {
const [t, r, c] = minHeap.dequeue().element; // 取出时间最短的格子
// 如果到达终点,返回时间
if (r === m - 1 && c === n - 1) {
return t;
}
// 遍历相邻的四个方向
for (let [dr, dc] of directions) {
const nr = r + dr,
nc = c + dc;
const key = `${nr},${nc}`; // 唯一标识格子
// 跳过越界或已访问的格子
if (nr < 0 || nr >= m || nc < 0 || nc >= n || visited.has(key)) {
continue;
}
// 计算等待时间
const wait = Math.abs(grid[nr][nc] - t) % 2 === 0 ? 1 : 0;
const newTime = Math.max(grid[nr][nc] + wait, t + 1); // 到达时间
minHeap.enqueue([newTime, nr, nc], newTime); // 加入优先队列
visited.add(key); // 标记格子为已访问
}
}
// 如果终点不可达,返回 -1
return -1;
};