| title | description | keywords | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3203. 合并两棵树后的最小直径 |
LeetCode 3203. 合并两棵树后的最小直径题解,Find Minimum Diameter After Merging Two Trees,包含解题思路、复杂度分析以及完整的 JavaScript 代码实现。 |
|
🔴 Hard 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 图 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
There exist two undirected trees with n and m nodes, numbered from 0
to n - 1 and from 0 to m - 1, respectively. You are given two 2D integer
arrays edges1 and edges2 of lengths n - 1 and m - 1, respectively,
where edges1[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes
ai and bi in the first tree and edges2[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that
there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the second tree.
You must connect one node from the first tree with another node from the second tree with an edge.
Return the minimum possible diameter of the resulting tree.
The diameter of a tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in the tree.
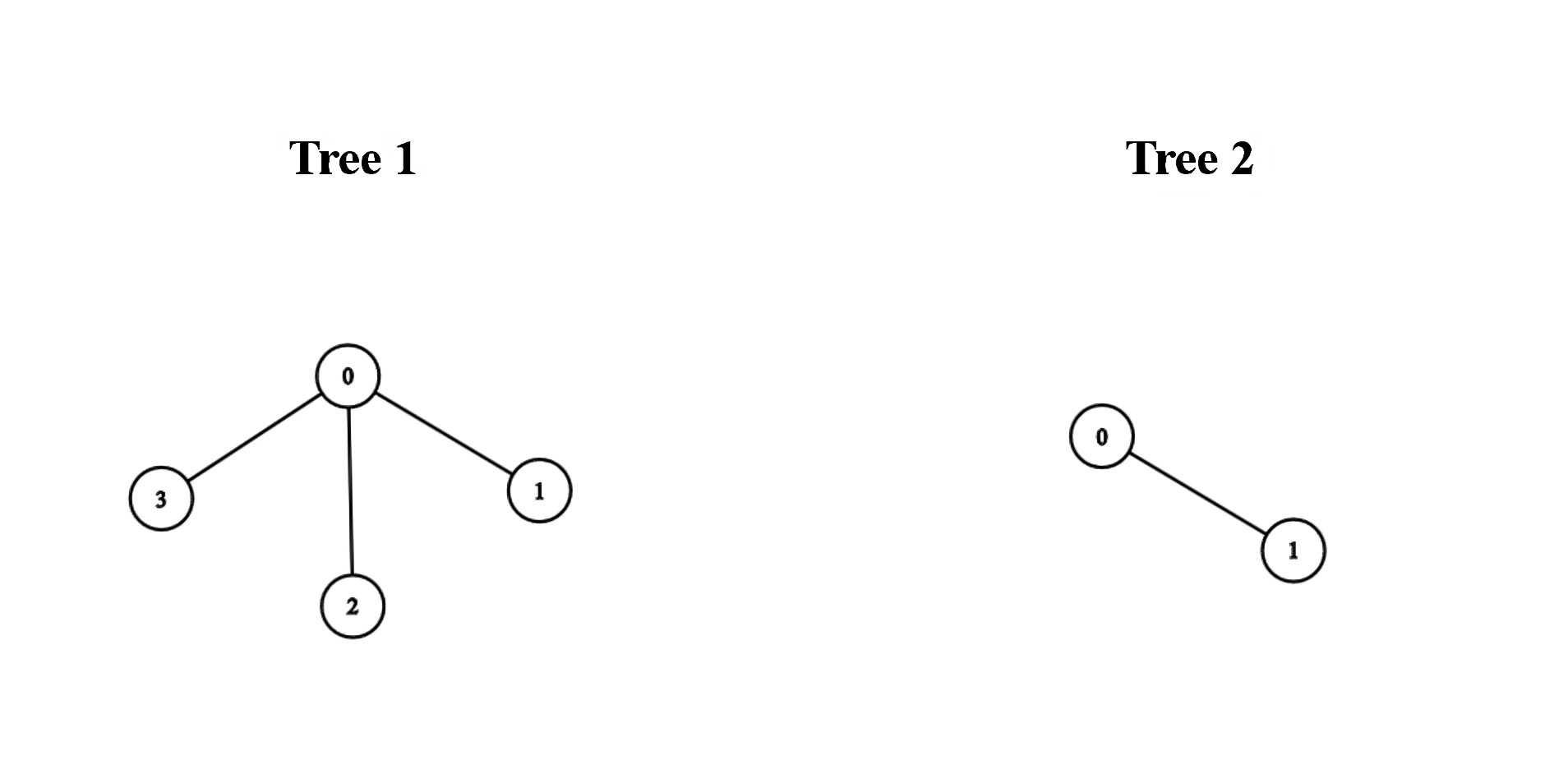
Example 1:
Input:
edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], edges2 = [[0,1]]Output: 3
Explanation:
We can obtain a tree of diameter 3 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with any node from the second tree.
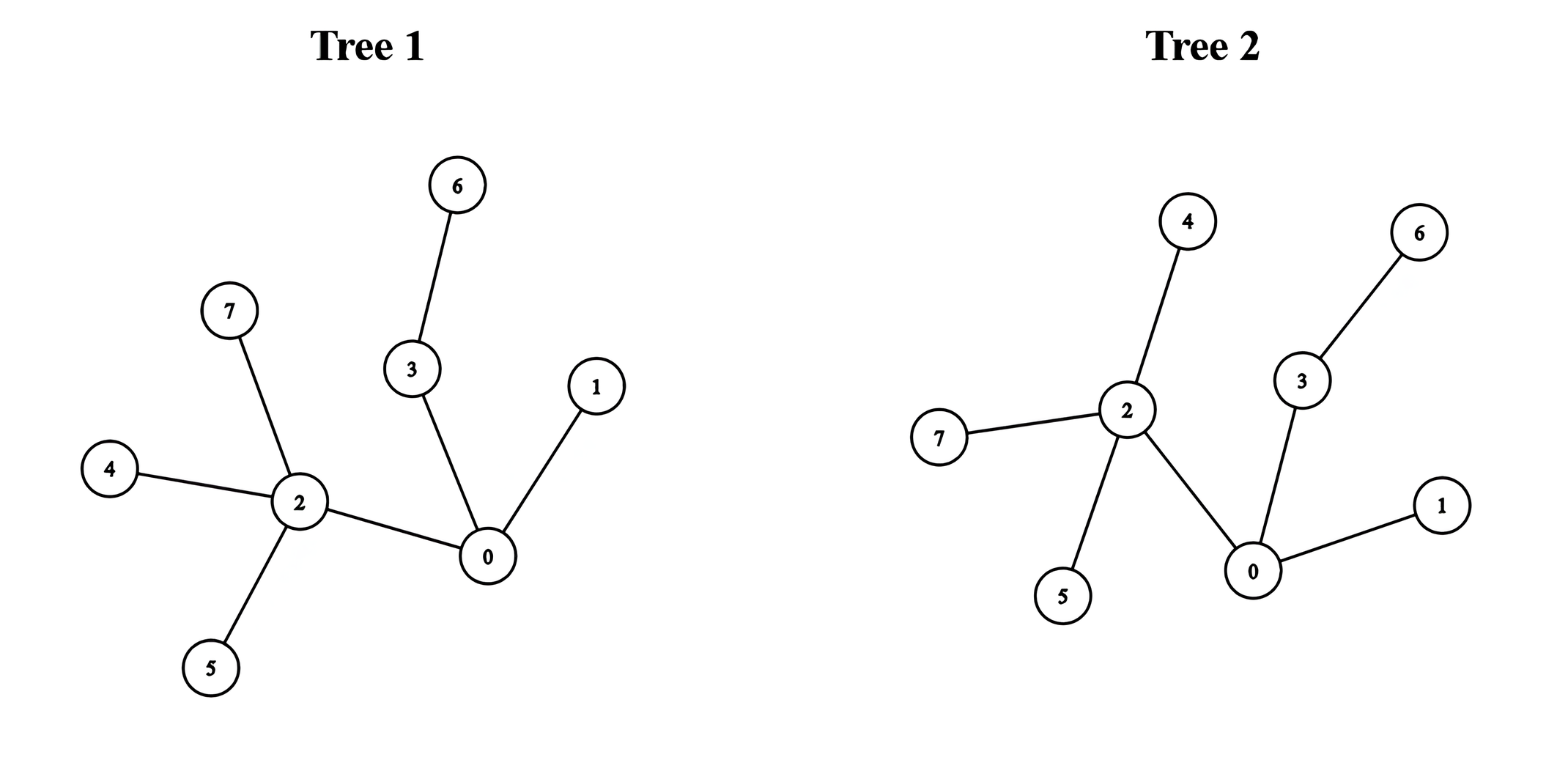
Example 2:
Input:
edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]], edges2 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]]Output: 5
Explanation:
We can obtain a tree of diameter 5 by connecting node 0 from the first tree with node 0 from the second tree.
Constraints:
1 <= n, m <= 10^5edges1.length == n - 1edges2.length == m - 1edges1[i].length == edges2[i].length == 2edges1[i] = [ai, bi]0 <= ai, bi < nedges2[i] = [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < m- The input is generated such that
edges1andedges2represent valid trees.
给你两棵 无向 树,分别有 n 和 m 个节点,节点编号分别为 0 到 n - 1 和 0 到 m - 1
。给你两个二维整数数组 edges1 和 edges2 ,长度分别为 n - 1 和 m - 1 ,其中 edges1[i] = [ai, bi] 表示在第一棵树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条边,edges2[i] = [ui, vi] 表示在第二棵树中节点 ui 和
vi 之间有一条边。
你必须在第一棵树和第二棵树中分别选一个节点,并用一条边连接它们。
请你返回添加边后得到的树中,最小直径 为多少。
一棵树的 直径 指的是树中任意两个节点之间的最长路径长度。
示例 1:
输入:
edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], edges2 = [[0,1]]输出: 3
解释:
将第一棵树中的节点 0 与第二棵树中的任意节点连接,得到一棵直径为 3 的树。
示例 2:
输入:
edges1 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]], edges2 = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[2,7]]输出: 5
解释:
将第一棵树中的节点 0 和第二棵树中的节点 0 连接,可以得到一棵直径为 5 的树。
提示:
1 <= n, m <= 10^5edges1.length == n - 1edges2.length == m - 1edges1[i].length == edges2[i].length == 2edges1[i] = [ai, bi]0 <= ai, bi < nedges2[i] = [ui, vi]0 <= ui, vi < m- 输入保证
edges1和edges2分别表示一棵合法的树。
-
树的直径计算
树的直径是指树中两点之间的最长路径的长度。计算方法如下:
- 使用深度优先搜索(DFS)遍历树的节点。
- 对每个节点,记录其到达的 最大深度 和 次大深度。
- 当前节点的直径可以通过最大深度和次大深度的和来计算,即
maxDepth + secondMaxDepth。 - 在整个 DFS 过程中,动态维护全局的最大直径。
通过
getDiameter函数,可以分别计算两棵树的直径diameter1和diameter2。 -
半径和剩余部分计算
-
半径计算:
树的半径是直径的一半,向上取整。公式为:radius = Math.ceil(diameter / 2)半径表示直径中间的某个节点到直径两端的最远距离。
-
剩余部分计算:
剩余部分是直径减去半径,公式为:rest = diameter - radius
对于两棵树,分别计算其
radius1、radius2和对应的剩余部分rest1、rest2。 -
-
合并树的直径处理逻辑
当将两棵树通过某些边连接时,连接两棵树的直径中点(即通过半径节点连接)时,合并树的直径是最小的:
- 如果树 1 的直径小于树 2,则将树 1 的中点添加到树 2 的中点作为其子节点,此时需要调整树 1 的半径:
radius1++; - 反之,调整树 2 的半径:
radius2++。
合并后树的直径等于四个子树中最大的两个部分之和,即:
max(radius1, rest1, radius2, rest2) + 次大部分具体步骤:
- 将
radius1, rest1, radius2, rest2按降序排列。 - 取前两部分之和作为合并后的最小直径。
- 如果树 1 的直径小于树 2,则将树 1 的中点添加到树 2 的中点作为其子节点,此时需要调整树 1 的半径:
-
合并后的最小直径计算示例
假设:
- 树 1 的直径为
6,则radius1 = 3, rest1 = 3; - 树 2 的直径为
2,则radius2 = 1, rest2 = 1。
在合并时,将树 2 的中点添加到树 1 的中点作为其子节点:
- 树 2 的半径调整为
2:radius1 = 2; - 排序后为
[3, 3, 2, 1],取前两项相加,得到合并后的最小直径:3 + 3 = 6。
- 树 1 的直径为
- 时间复杂度:
O(n1 + n2),其中n1和n2是两棵树的节点数,使用 DFS 分别遍历两棵树一次计算直径。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n1 + n2),用于存储图的邻接表结构和递归调用栈。
/**
* @param {number[][]} edges1
* @param {number[][]} edges2
* @return {number}
*/
var minimumDiameterAfterMerge = function (edges1, edges2) {
const diameter1 = getDiameter(edges1);
const diameter2 = getDiameter(edges2);
// 计算两棵树的半径
let radius1 = Math.ceil(diameter1 / 2);
let radius2 = Math.ceil(diameter2 / 2);
// 计算剩余部分
const rest1 = diameter1 - radius1;
const rest2 = diameter2 - radius2;
// 调整较小半径的树
if (diameter1 < diameter2) {
radius1++;
} else {
radius2++;
}
// 取最大的两部分
const sorted = [radius1, rest1, radius2, rest2].sort((a, b) => b - a);
return sorted[0] + sorted[1];
};
/**
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
var getDiameter = function (edges) {
const n = edges.length;
const graph = Array.from({ length: n + 1 }, () => []);
// 构建图
for (let [a, b] of edges) {
graph[a].push(b);
graph[b].push(a);
}
let diameter = 0;
// 深度优先搜索计算直径
const dfs = (node, parent) => {
let maxDepth = 0,
secondMaxDepth = 0;
for (let neighbor of graph[node]) {
if (neighbor !== parent) {
const depth = dfs(neighbor, node) + 1;
// 更新最大和次大深度
if (depth > maxDepth) {
secondMaxDepth = maxDepth;
maxDepth = depth;
} else if (depth > secondMaxDepth) {
secondMaxDepth = depth;
}
}
}
diameter = Math.max(diameter, maxDepth + secondMaxDepth);
return maxDepth;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return diameter;
};| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 310 | 最小高度树 | 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 图 1+ |
🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 1245 | 树的直径 🔒 | 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 2+ |
🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |