GeneticPromptLab uses genetic algorithms for automated prompt engineering (for LLMs), enhancing quality and diversity through iterative selection, crossover, and mutation, while efficiently exploring minimal yet diverse samples from the training set.
GeneticPromptLab is a Python library designed to harness the power of genetic algorithms for automated prompt engineering for large language models (LLMs). By iteratively applying selection, crossover, and mutation processes, GeneticPromptLab enhances the quality and diversity of prompts, leading to improved performance in automated question-answering and classification tasks.
pip install genetic-prompt-lab
This library specifically leverages Sentence Transformers for embedding generation and k-means clustering to sample minimal yet diverse data from training sets. This strategic sampling ensures efficient exploration and optimization of prompts over multiple generations.
graph TD;
A[Initialize OpenAI Client] --> B[Load Dataset Configuration]
B --> C[Setup QuestionsAnswersOptimizer]
C --> D[Run Genetic Algorithm]
subgraph Genetic Algorithm Process
D --> GA[Start Genetic Algorithm]
GA --> Init[Generate Initial Prompts]
Init --> FE1
subgraph Fitness Evaluation
FE1[Current Population]
FE1 --> FE2[Evaluate Individual Fitness]
FE2 --> FE3[Calculate Average Fitness]
end
FE1 --> STP[Select Top Prompts]
STP --> Cross[Crossover]
subgraph Crossover Mechanism
Cross --> Cross1[Select Parent Prompts]
Cross1 --> Cross2[Apply Crossover Logic]
Cross2 --> Cross3[Generate Offspring Prompts]
end
Cross3 --> Mut[Mutation]
subgraph Mutation Mechanism
Mut --> Mut1[Select Prompts for Mutation]
Mut1 --> Mut2[Apply Mutation Logic]
Mut2 --> Mut3[Generate Mutated Prompts]
end
Mut3 --> Check[Check Convergence]
Check -- No --> FE1
Check -- Yes --> Finish[End Genetic Algorithm]
end
Finish --> Out[Output]
style D fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:4px
style Genetic Algorithm Process fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style Fitness Evaluation fill:#fdd,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style Crossover Mechanism fill:#dfd,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style Mutation Mechanism fill:#ddf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
- Genetic Algorithm Implementation: Complete genetic algorithm cycle including initialization, fitness evaluation, selection, crossover, and mutation for prompt engineering.
- Integration with Sentence Transformers: Utilizes Sentence Transformers for generating embeddings, enabling effective clustering and sampling.
- Diverse Sampling: Uses k-means clustering to select a representative subset of data, ensuring diverse genetic material for algorithm initialization and evolution.
- Dynamic Mutation and Crossover: Incorporates custom mutation and crossover operations tailored to prompt characteristics and task requirements.
- Multi-Dataset Support: Pre-configured to run experiments on the TREC and AG News datasets, demonstrating its adaptability to different types of text classification tasks.
To install GeneticPromptLab, clone this repository and install the required packages:
git clone https://github.com/username/GeneticPromptLab.git
cd GeneticPromptLab
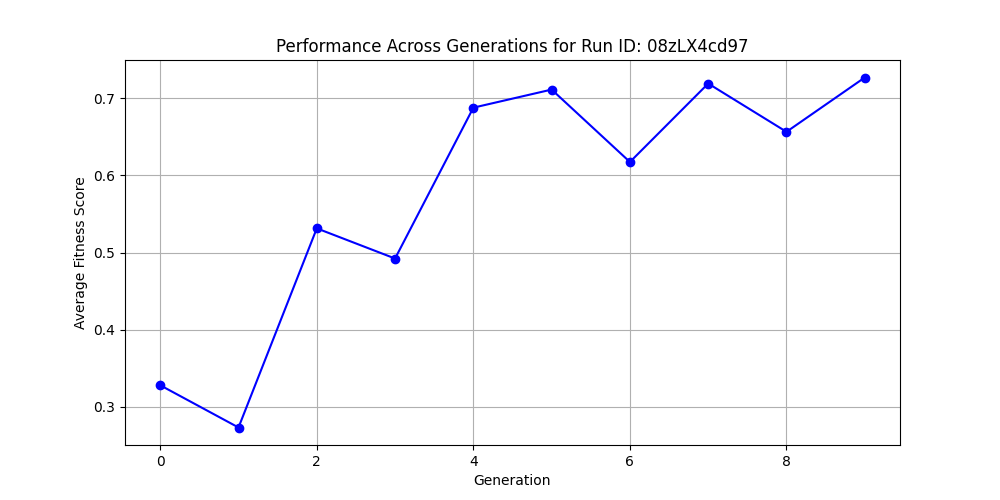
pip install -r requirements.txtThe TREC dataset comprises 4,500 English questions categorized into various labels. Below is the performance improvement graph showing the evolution of prompt effectiveness over 10 generations.
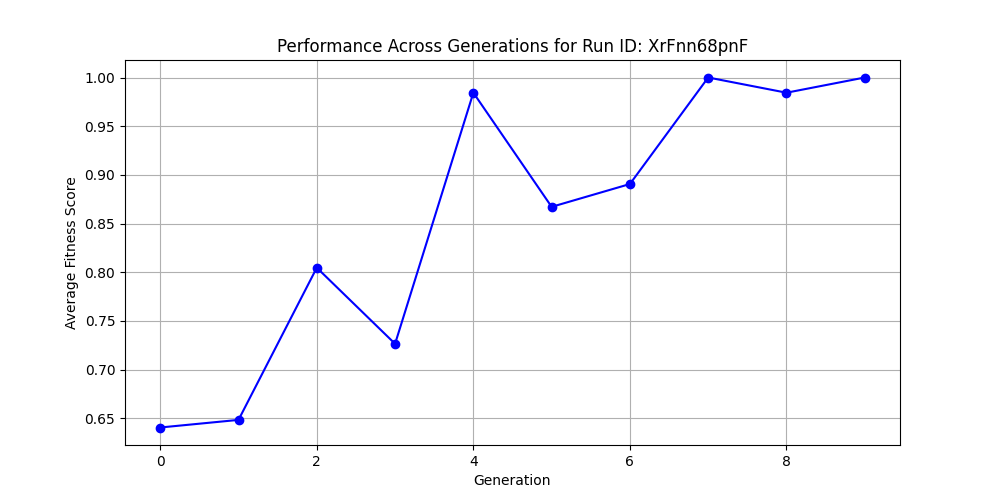
The AG News dataset contains over 1 million news articles classified into categories like World, Sports, Business, and Sci/Tech. Below is the performance graph for the AG News dataset.
To run GeneticPromptLab on the AG News dataset:
from GeneticPromptLab import QuestionsAnswersOptimizer, agnews
from openai import OpenAI
# Load API key
with open("openai_api.key", "r") as f:
key = f.read().strip()
# Initialize client
client = OpenAI(api_key=key)
# Get AG News dataset & Initialize the optimizer
lab = QuestionsAnswersOptimizer(
client=client,
problem_description=problem_description,
train_questions_list=train_questions_list,
train_answers_label=train_answers_label,
test_questions_list=test_questions_list,
test_answers_label=test_answers_label,
label_dict=label_dict,
model_name=model_name,
sample_p=sample_p,
init_and_fitness_sample=population_size,
window_size_init=2,
num_retries=num_retries)
# Run the genetic algorithm
optimized_prompts = lab.genetic_algorithm()
print(optimized_prompts)- Description: This is the instance of the OpenAI client that the optimizer uses to send queries. It's essential for communicating with the GPT model.
- Example Usage:
client = OpenAI(api_key=key)
- Description: A string that describes the problem context or dataset. This helps to set the stage for the prompts, providing the GPT model with a background for better understanding and response generation.
- Example Usage: Derived from the
agnews()function which returns a detailed description of the AG News dataset.
- Description: A list of questions from the training dataset. These are used by the genetic algorithm to generate initial prompts and evaluate their effectiveness.
- Example Usage: List of questions derived from the
train_data['question'].tolist()method in theagnews()function.
- Description: A list of corresponding labels for the training questions. These are crucial for training as they provide the correct answers for the questions.
- Example Usage: List of labels derived from the
train_data['label'].tolist()method in theagnews()function.
- Description: A list of questions from the testing dataset. While primarily not used directly in training, they can be useful for additional validation if incorporated.
- Example Usage: Similar to
train_questions_list, but derived from the test data.
- Description: Corresponding labels for the test questions. These are used to validate the effectiveness of the prompts on unseen data.
- Example Usage: Similar to
train_answers_label, but for test data.
- Description: A dictionary mapping numerical labels to their descriptive counterparts. It helps in understanding and converting between numerical labels and their meaning.
- Example Usage: Loaded from a JSON file in the
agnews()function.
- Description: The name of the SentenceTransformer model used for encoding the questions into embeddings. The choice of model can significantly affect the clustering and thus the genetic algorithm's ability to sample distinct data points.
- Example Usage:
'multi-qa-MiniLM-L6-cos-v1'as specified in theagnews()function.
- Description: The proportion of the training dataset to sample for running the genetic algorithm. A smaller sample can be used to speed up computations during development or in cases of limited computational resources.
- Example Usage:
0.01means that 1% of the training data is used.
- Description: The initial number of prompts to generate and also the number of prompts evaluated for fitness each generation. This setting controls the breadth of exploration in the genetic space.
- Example Usage:
8initializes and evaluates eight prompts per generation.
- Description: This parameter controls the number of questions considered for creating a single prompt. It can affect the complexity and specificity of the generated prompts.
- Example Usage:
2means that two questions are combined to create each prompt.
- Description: Specifies how many times the fitness of each prompt should be re-evaluated to ensure accuracy. This is important because the stochastic nature of GPT responses can lead to variability in performance.
- Example Usage:
2retries for each prompt to average out the variability.
- create_prompts(data): Generates prompts based on input data.
- generate_init_prompts(n): Produces initial prompts for the genetic algorithm.
- sample_distinct(n): Samples a distinct subset of data or embeddings.
- genetic_algorithm(mutation_rate): Executes the genetic algorithm process.
- evaluate_fitness(prompts): Evaluates the fitness of each prompt.
- select_top_prompts(fitness_scores, population, top_fraction): Selects the top-performing prompts based on fitness scores.
- crossover_using_gpt(prompts): Performs crossover between prompts.
- mutate_prompts(prompts, mutation_rate): Applies mutations to the given prompts.
[1] H. Tanaka, N. Mori, and M. Okada, "Genetic Algorithm for Prompt Engineering with Novel Genetic Operators," IEEE, 2023.
[2] Q. Guo et al., "Connecting Large Language Models with Evolutionary Algorithms Yields Powerful Prompt Optimizers," arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.15611, 2023.
[3] C. Feng, Y. Sun, K. Li, P. Zhou, J. Lv, and A. Lu, "Genetic Auto-prompt Learning for Pre-trained Code Intelligence Language Models," arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.00185, 2023.
[4] R. Pryzant et al., "Automatic Prompt Optimization with "Gradient Descent" and Beam Search," Microsoft Azure AI, 2023.
[5] V.-T. Do et al., "Automatic Prompt Selection for Large Language Models," arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.05802, 2023.
[6] G. Sabbatella et al., "Bayesian Optimization for Prompt Tuning of Black-box Large Language Models," Mathematics, vol. 12, no. 6, p. 929, 2024.
[7] H. Sun et al., "Towards an Automatic Prompt Optimization Framework for AI Image Generation," Conference paper, 2023.
[8] A. Priyanshu and S. Vijay, "Adaptkeybert: An attention-based approach towards few-shot & zero-shot domain adaptation of keybert," arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.07499, 2022.
[9] R. Ma et al., "RLPrompt: Optimizing Discrete Text Prompts with Reinforcement Learning," arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.12548, 2022.
[10] X. Wang et al., "PromptAgent: Strategic Planning with Language Models Enables Expert-level Prompt Optimization," arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.10880, 2023.
[11] T. Kojima et al., "Large Language Models are Zero-Shot Reasoners," Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 35, 2022.
[12] A. Bhattacharjee et al., "Zero-shot LLM-guided Counterfactual Generation for Text," arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.06704, 2023.
[13] S. Vijay and A. Priyanshu, "NERDA-Con: Extending NER models for Continual Learning--Integrating Distinct Tasks and Updating Distribution Shifts," arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14607, 2022.
[14] X. Lin et al., "Prompt Optimization with Human Feedback," arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.18290, 2023.
@inproceedings{genetic-prompt-lab,
title = {GeneticPromptLab: A Framework for Automated Prompt Optimization using Genetic Algorithms and Diverse Sampling Strategies},
author = {Aman Priyanshu, Supriti Vijay},
year = {2024},
publisher = {{GitHub}},
url = {https://github.com/AmanPriyanshu/GeneticPromptLab}
}
Contributions, suggestions, and feedback are welcome! If you have any ideas to enhance the app or encounter any issues, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request on the GitHub repository. Thank you for your interest in our research work.
- If you use or share this work, please provide attribution with the following information:
_"GeneticPromptLab" by Aman Priyanshu and Supriti Vijay, licensed under the MIT License
- When sharing adaptations of this work, please include a statement indicating that changes were made, such as:
This work is adapted from "GeneticPromptLab" by Aman Priyanshu and Supriti Vijay, licensed under the MIT License. Original work available at: https://github.com/AmanPriyanshu/GeneticPromptLab