| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
简单 |
|
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
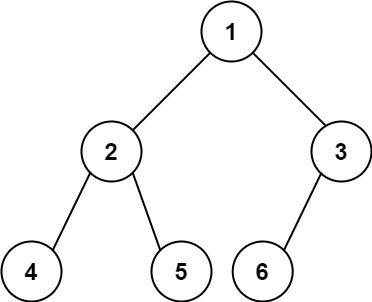
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = [] 输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1] 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
进阶:遍历树来统计节点是一种时间复杂度为 O(n) 的简单解决方案。你可以设计一个更快的算法吗?
递归遍历整棵树,统计结点个数。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
return 1 + self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + countNodes(root->left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return 1 + countNodes(root.Left) + countNodes(root.Right)
}use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn count_nodes(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if let Some(node) = root {
let node = node.borrow();
let left = Self::depth(&node.left);
let right = Self::depth(&node.right);
if left == right {
Self::count_nodes(node.right.clone()) + (1 << left)
} else {
Self::count_nodes(node.left.clone()) + (1 << right)
}
} else {
0
}
}
fn depth(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> i32 {
if let Some(node) = root {
Self::depth(&node.borrow().left) + 1
} else {
0
}
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var countNodes = function (root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right);
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int CountNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + CountNodes(root.left) + CountNodes(root.right);
}
}对于此题,我们还可以利用完全二叉树的特点,设计一个更快的算法。
完全二叉树的特点:叶子结点只能出现在最下层和次下层,且最下层的叶子结点集中在树的左部。需要注意的是,满二叉树肯定是完全二叉树,而完全二叉树不一定是满二叉树。
若满二叉树的层数为
我们可以先对
- 若
$left = right$ ,说明左子树是一颗满二叉树,那么左子树的结点总数为$2^{left} - 1$ ,加上$root$ 结点,就是$2^{left}$ ,然后递归统计右子树即可。 - 若
$left \gt right$ ,说明右子树是一个满二叉树,那么右子树的结点总数为$2^{right} - 1$ ,加上$root$ 结点,就是$2^{right}$ ,然后递归统计左子树即可。
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def depth(root):
d = 0
while root:
d += 1
root = root.left
return d
if root is None:
return 0
left, right = depth(root.left), depth(root.right)
if left == right:
return (1 << left) + self.countNodes(root.right)
return (1 << right) + self.countNodes(root.left)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = depth(root.left);
int right = depth(root.right);
if (left == right) {
return (1 << left) + countNodes(root.right);
}
return (1 << right) + countNodes(root.left);
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
int d = 0;
for (; root != null; root = root.left) {
++d;
}
return d;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int left = depth(root->left);
int right = depth(root->right);
if (left == right) {
return (1 << left) + countNodes(root->right);
}
return (1 << right) + countNodes(root->left);
}
int depth(TreeNode* root) {
int d = 0;
for (; root; root = root->left) {
++d;
}
return d;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
left, right := depth(root.Left), depth(root.Right)
if left == right {
return (1 << left) + countNodes(root.Right)
}
return (1 << right) + countNodes(root.Left)
}
func depth(root *TreeNode) (d int) {
for ; root != nil; root = root.Left {
d++
}
return
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var countNodes = function (root) {
const depth = root => {
let d = 0;
for (; root; root = root.left) {
++d;
}
return d;
};
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const left = depth(root.left);
const right = depth(root.right);
if (left == right) {
return (1 << left) + countNodes(root.right);
}
return (1 << right) + countNodes(root.left);
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int CountNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = depth(root.left);
int right = depth(root.right);
if (left == right) {
return (1 << left) + CountNodes(root.right);
}
return (1 << right) + CountNodes(root.left);
}
private int depth(TreeNode root) {
int d = 0;
for (; root != null; root = root.left) {
++d;
}
return d;
}
}