| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
|
给定一个二叉树,我们称从根节点到任意叶节点的任意路径中的节点值所构成的序列为该二叉树的一个 “有效序列” 。检查一个给定的序列是否是给定二叉树的一个 “有效序列” 。
我们以整数数组 arr 的形式给出这个序列。从根节点到任意叶节点的任意路径中的节点值所构成的序列都是这个二叉树的 “有效序列” 。
示例 1:
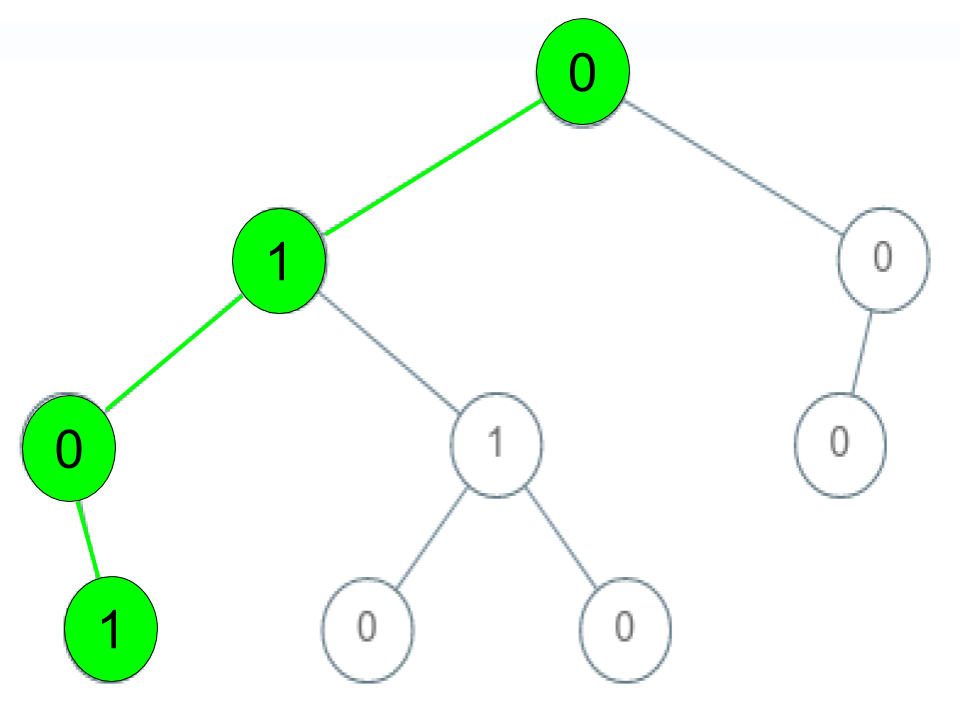
输入:root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,0,1] 输出:true 解释: 路径 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 是一个“有效序列”(图中的绿色节点)。 其他的“有效序列”是: 0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0 0 -> 0 -> 0
示例 2:
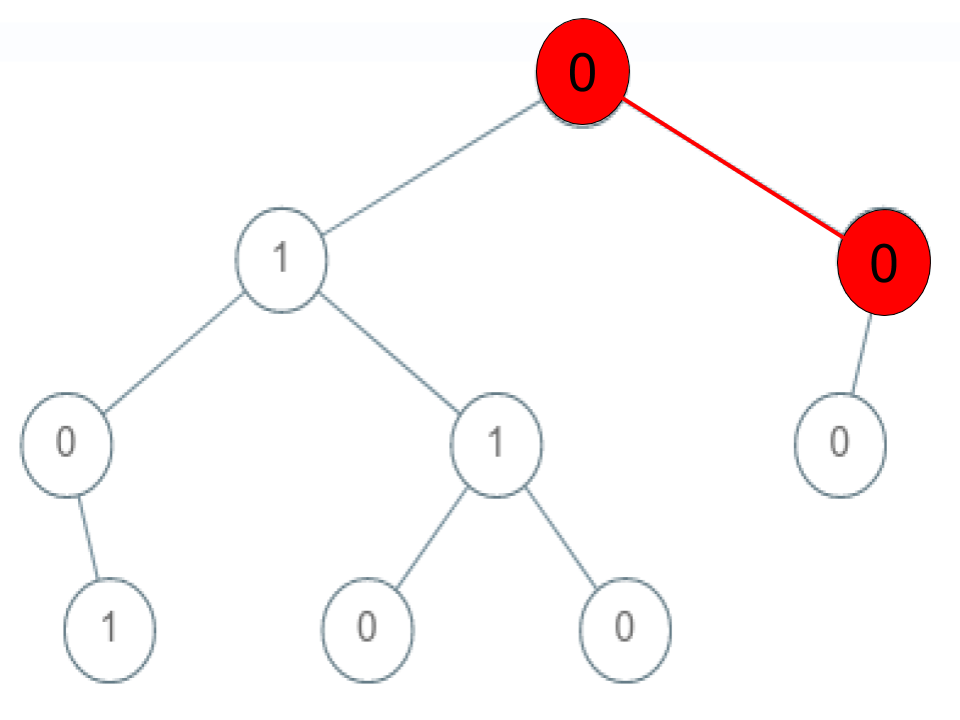
输入:root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,0,1] 输出:false 解释:路径 0 -> 0 -> 1 不存在,所以这不是一个“序列”。
示例 3:
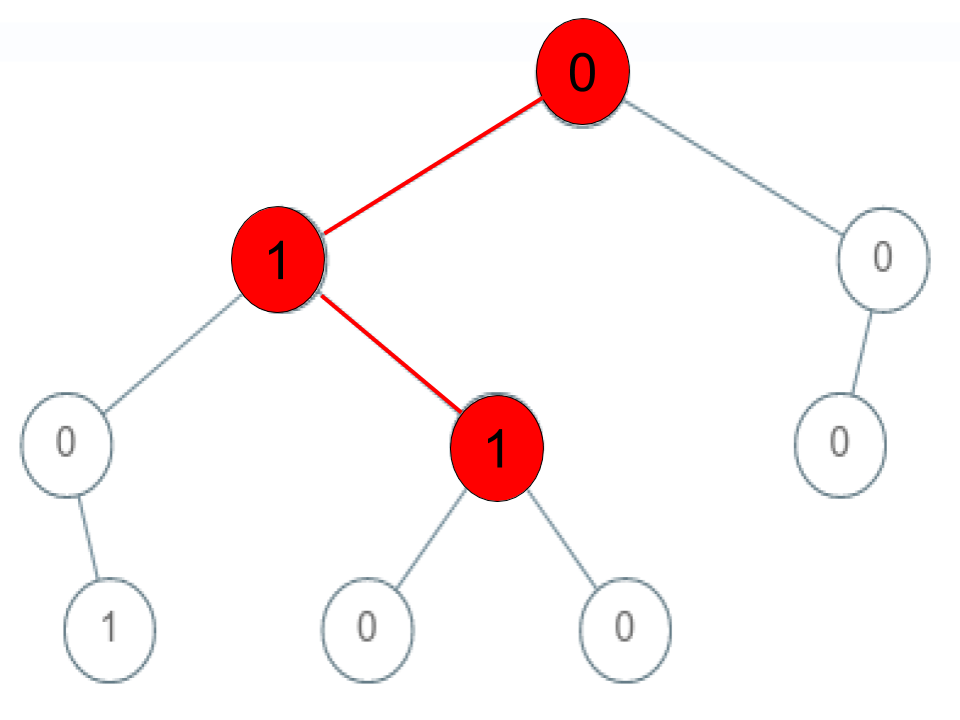
输入:root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,1] 输出:false 解释:路径 0 -> 1 -> 1 是一个序列,但不是一个“有效序列”(译者注:因为序列的终点不是叶节点)。
提示:
1 <= arr.length <= 50000 <= arr[i] <= 9- 每个节点的值的取值范围是
[0 - 9]
根据题目,我们设计一个递归函数
在递归函数中,如果当前节点为空,或者当前节点的值与数组中的值不相等,那么直接返回
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidSequence(self, root: TreeNode, arr: List[int]) -> bool:
def dfs(root, u):
if root is None or root.val != arr[u]:
return False
if u == len(arr) - 1:
return root.left is None and root.right is None
return dfs(root.left, u + 1) or dfs(root.right, u + 1)
return dfs(root, 0)/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int[] arr;
public boolean isValidSequence(TreeNode root, int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
return dfs(root, 0);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode root, int u) {
if (root == null || root.val != arr[u]) {
return false;
}
if (u == arr.length - 1) {
return root.left == null && root.right == null;
}
return dfs(root.left, u + 1) || dfs(root.right, u + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSequence(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& arr) {
function<bool(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int u) -> bool {
if (!root || root->val != arr[u]) return false;
if (u == arr.size() - 1) return !root->left && !root->right;
return dfs(root->left, u + 1) || dfs(root->right, u + 1);
};
return dfs(root, 0);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func isValidSequence(root *TreeNode, arr []int) bool {
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, u int) bool
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, u int) bool {
if root == nil || root.Val != arr[u] {
return false
}
if u == len(arr)-1 {
return root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil
}
return dfs(root.Left, u+1) || dfs(root.Right, u+1)
}
return dfs(root, 0)
}