| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Easy |
|
Given the root of a binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:
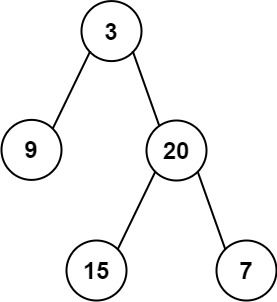
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000] Explanation: The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,9,20,15,7] Output: [3.00000,14.50000,11.00000]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
We can use the Breadth-First Search (BFS) method to traverse the nodes of each level and calculate the average value of each level.
Specifically, we define a queue
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def averageOfLevels(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[float]:
q = deque([root])
ans = []
while q:
s, n = 0, len(q)
for _ in range(n):
root = q.popleft()
s += root.val
if root.left:
q.append(root.left)
if root.right:
q.append(root.right)
ans.append(s / n)
return ans/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
List<Double> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int n = q.size();
long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
root = q.pollFirst();
s += root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(root.right);
}
}
ans.add(s * 1.0 / n);
}
return ans;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
vector<double> ans;
while (!q.empty()) {
int n = q.size();
long long s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
s += root->val;
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
ans.push_back(s * 1.0 / n);
}
return ans;
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
ans := []float64{}
for len(q) > 0 {
n := len(q)
s := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
s += root.Val
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, root.Right)
}
}
ans = append(ans, float64(s)/float64(n))
}
return ans
}// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::VecDeque;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {
pub fn average_of_levels(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<f64> {
let mut ans = vec![];
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
if let Some(root_node) = root {
q.push_back(root_node);
}
while !q.is_empty() {
let n = q.len();
let mut s: i64 = 0;
for _ in 0..n {
if let Some(node) = q.pop_front() {
let node_borrow = node.borrow();
s += node_borrow.val as i64;
if let Some(left) = node_borrow.left.clone() {
q.push_back(left);
}
if let Some(right) = node_borrow.right.clone() {
q.push_back(right);
}
}
}
ans.push((s as f64) / (n as f64));
}
ans
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var averageOfLevels = function (root) {
const q = [root];
const ans = [];
while (q.length) {
const n = q.length;
const nq = [];
let s = 0;
for (const { val, left, right } of q) {
s += val;
left && nq.push(left);
right && nq.push(right);
}
ans.push(s / n);
q.splice(0, q.length, ...nq);
}
return ans;
};We can also use the Depth-First Search (DFS) method to calculate the average value of each level.
Specifically, we define an array
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def averageOfLevels(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> List[float]:
def dfs(root, i):
if root is None:
return
if len(s) == i:
s.append([root.val, 1])
else:
s[i][0] += root.val
s[i][1] += 1
dfs(root.left, i + 1)
dfs(root.right, i + 1)
s = []
dfs(root, 0)
return [a / b for a, b in s]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Long> s = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> cnt = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
List<Double> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
ans.add(s.get(i) * 1.0 / cnt.get(i));
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int i) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (s.size() == i) {
s.add((long) root.val);
cnt.add(1);
} else {
s.set(i, s.get(i) + root.val);
cnt.set(i, cnt.get(i) + 1);
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
using ll = long long;
class Solution {
public:
vector<ll> s;
vector<int> cnt;
vector<double> averageOfLevels(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, 0);
vector<double> ans(s.size());
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
ans[i] = (s[i] * 1.0 / cnt[i]);
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int i) {
if (!root) return;
if (s.size() == i) {
s.push_back(root->val);
cnt.push_back(1);
} else {
s[i] += root->val;
cnt[i]++;
}
dfs(root->left, i + 1);
dfs(root->right, i + 1);
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
s := []int{}
cnt := []int{}
var dfs func(root *TreeNode, i int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, i int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if len(s) == i {
s = append(s, root.Val)
cnt = append(cnt, 1)
} else {
s[i] += root.Val
cnt[i]++
}
dfs(root.Left, i+1)
dfs(root.Right, i+1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
ans := []float64{}
for i, t := range s {
ans = append(ans, float64(t)/float64(cnt[i]))
}
return ans
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var averageOfLevels = function (root) {
const s = [];
const cnt = [];
function dfs(root, i) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (s.length == i) {
s.push(root.val);
cnt.push(1);
} else {
s[i] += root.val;
cnt[i]++;
}
dfs(root.left, i + 1);
dfs(root.right, i + 1);
}
dfs(root, 0);
return s.map((v, i) => v / cnt[i]);
};