| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
中等 |
1374 |
第 335 场周赛 Q2 |
|
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root 和一个正整数 k 。
树中的 层和 是指 同一层 上节点值的总和。
返回树中第 k 大的层和(不一定不同)。如果树少于 k 层,则返回 -1 。
注意,如果两个节点与根节点的距离相同,则认为它们在同一层。
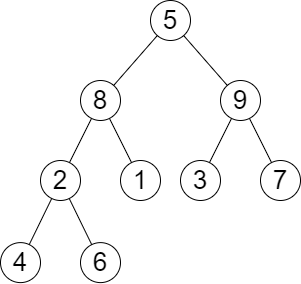
示例 1:
输入:root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], k = 2 输出:13 解释:树中每一层的层和分别是: - Level 1: 5 - Level 2: 8 + 9 = 17 - Level 3: 2 + 1 + 3 + 7 = 13 - Level 4: 4 + 6 = 10 第 2 大的层和等于 13 。
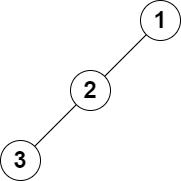
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,null,3], k = 1 输出:3 解释:最大的层和是 3 。
提示:
- 树中的节点数为
n 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= 1061 <= k <= n
我们可以使用 BFS 遍历二叉树,同时记录每一层的节点和,然后对节点和数组进行排序,最后返回第
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthLargestLevelSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
arr = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
t = 0
for _ in range(len(q)):
root = q.popleft()
t += root.val
if root.left:
q.append(root.left)
if root.right:
q.append(root.right)
arr.append(t)
return -1 if len(arr) < k else nlargest(k, arr)[-1]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Long> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
long t = 0;
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
root = q.pollFirst();
t += root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(root.right);
}
}
arr.add(t);
}
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
Collections.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
return arr.get(k - 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
long long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<long long> arr;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
long long t = 0;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
t += root->val;
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
arr.push_back(t);
}
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
sort(arr.rbegin(), arr.rend());
return arr[k - 1];
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthLargestLevelSum(root *TreeNode, k int) int64 {
arr := []int{}
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
t := 0
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
t += root.Val
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, root.Right)
}
}
arr = append(arr, t)
}
if n := len(arr); n >= k {
sort.Ints(arr)
return int64(arr[n-k])
}
return -1
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function kthLargestLevelSum(root: TreeNode | null, k: number): number {
const arr: number[] = [];
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
let t = 0;
for (let n = q.length; n > 0; --n) {
root = q.shift();
t += root.val;
if (root.left) {
q.push(root.left);
}
if (root.right) {
q.push(root.right);
}
}
arr.push(t);
}
if (arr.length < k) {
return -1;
}
arr.sort((a, b) => b - a);
return arr[k - 1];
}我们也可以使用 DFS 遍历二叉树,同时记录每一层的节点和,然后对节点和数组进行排序,最后返回第
时间复杂度
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthLargestLevelSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
def dfs(root, d):
if root is None:
return
if len(arr) <= d:
arr.append(0)
arr[d] += root.val
dfs(root.left, d + 1)
dfs(root.right, d + 1)
arr = []
dfs(root, 0)
return -1 if len(arr) < k else nlargest(k, arr)[-1]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Long> arr = new ArrayList<>();
public long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode root, int k) {
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
Collections.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
return arr.get(k - 1);
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int d) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (arr.size() <= d) {
arr.add(0L);
}
arr.set(d, arr.get(d) + root.val);
dfs(root.left, d + 1);
dfs(root.right, d + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
long long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<long long> arr;
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int d) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (arr.size() <= d) {
arr.push_back(0);
}
arr[d] += root->val;
dfs(root->left, d + 1);
dfs(root->right, d + 1);
};
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
sort(arr.rbegin(), arr.rend());
return arr[k - 1];
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthLargestLevelSum(root *TreeNode, k int) int64 {
arr := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, d int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if len(arr) <= d {
arr = append(arr, 0)
}
arr[d] += root.Val
dfs(root.Left, d+1)
dfs(root.Right, d+1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
if n := len(arr); n >= k {
sort.Ints(arr)
return int64(arr[n-k])
}
return -1
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function kthLargestLevelSum(root: TreeNode | null, k: number): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode, d: number) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (arr.length <= d) {
arr.push(0);
}
arr[d] += root.val;
dfs(root.left, d + 1);
dfs(root.right, d + 1);
};
const arr: number[] = [];
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.length < k) {
return -1;
}
arr.sort((a, b) => b - a);
return arr[k - 1];
}