| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
1374 |
Weekly Contest 335 Q2 |
|
You are given the root of a binary tree and a positive integer k.
The level sum in the tree is the sum of the values of the nodes that are on the same level.
Return the kth largest level sum in the tree (not necessarily distinct). If there are fewer than k levels in the tree, return -1.
Note that two nodes are on the same level if they have the same distance from the root.
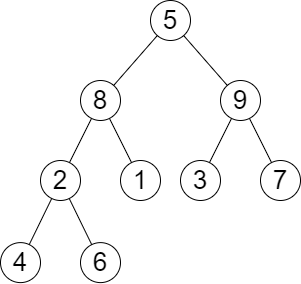
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,8,9,2,1,3,7,4,6], k = 2 Output: 13 Explanation: The level sums are the following: - Level 1: 5. - Level 2: 8 + 9 = 17. - Level 3: 2 + 1 + 3 + 7 = 13. - Level 4: 4 + 6 = 10. The 2nd largest level sum is 13.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,2,null,3], k = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The largest level sum is 3.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 2 <= n <= 1051 <= Node.val <= 1061 <= k <= n
We can use BFS to traverse the binary tree, while recording the sum of nodes at each level, then sort the array of node sums, and finally return the $k$th largest node sum. Note that if the number of levels in the binary tree is less than
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthLargestLevelSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
arr = []
q = deque([root])
while q:
t = 0
for _ in range(len(q)):
root = q.popleft()
t += root.val
if root.left:
q.append(root.left)
if root.right:
q.append(root.right)
arr.append(t)
return -1 if len(arr) < k else nlargest(k, arr)[-1]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode root, int k) {
List<Long> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
long t = 0;
for (int n = q.size(); n > 0; --n) {
root = q.pollFirst();
t += root.val;
if (root.left != null) {
q.offer(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
q.offer(root.right);
}
}
arr.add(t);
}
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
Collections.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
return arr.get(k - 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
long long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<long long> arr;
queue<TreeNode*> q{{root}};
while (!q.empty()) {
long long t = 0;
for (int n = q.size(); n; --n) {
root = q.front();
q.pop();
t += root->val;
if (root->left) {
q.push(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
q.push(root->right);
}
}
arr.push_back(t);
}
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
sort(arr.rbegin(), arr.rend());
return arr[k - 1];
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthLargestLevelSum(root *TreeNode, k int) int64 {
arr := []int{}
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
t := 0
for n := len(q); n > 0; n-- {
root = q[0]
q = q[1:]
t += root.Val
if root.Left != nil {
q = append(q, root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
q = append(q, root.Right)
}
}
arr = append(arr, t)
}
if n := len(arr); n >= k {
sort.Ints(arr)
return int64(arr[n-k])
}
return -1
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function kthLargestLevelSum(root: TreeNode | null, k: number): number {
const arr: number[] = [];
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
let t = 0;
for (let n = q.length; n > 0; --n) {
root = q.shift();
t += root.val;
if (root.left) {
q.push(root.left);
}
if (root.right) {
q.push(root.right);
}
}
arr.push(t);
}
if (arr.length < k) {
return -1;
}
arr.sort((a, b) => b - a);
return arr[k - 1];
}We can also use DFS to traverse the binary tree, while recording the sum of nodes at each level, then sort the array of node sums, and finally return the $k$th largest node sum. Note that if the number of levels in the binary tree is less than
The time complexity is
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def kthLargestLevelSum(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], k: int) -> int:
def dfs(root, d):
if root is None:
return
if len(arr) <= d:
arr.append(0)
arr[d] += root.val
dfs(root.left, d + 1)
dfs(root.right, d + 1)
arr = []
dfs(root, 0)
return -1 if len(arr) < k else nlargest(k, arr)[-1]/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private List<Long> arr = new ArrayList<>();
public long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode root, int k) {
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
Collections.sort(arr, Collections.reverseOrder());
return arr.get(k - 1);
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int d) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (arr.size() <= d) {
arr.add(0L);
}
arr.set(d, arr.get(d) + root.val);
dfs(root.left, d + 1);
dfs(root.right, d + 1);
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
long long kthLargestLevelSum(TreeNode* root, int k) {
vector<long long> arr;
function<void(TreeNode*, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int d) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (arr.size() <= d) {
arr.push_back(0);
}
arr[d] += root->val;
dfs(root->left, d + 1);
dfs(root->right, d + 1);
};
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.size() < k) {
return -1;
}
sort(arr.rbegin(), arr.rend());
return arr[k - 1];
}
};/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func kthLargestLevelSum(root *TreeNode, k int) int64 {
arr := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(root *TreeNode, d int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
if len(arr) <= d {
arr = append(arr, 0)
}
arr[d] += root.Val
dfs(root.Left, d+1)
dfs(root.Right, d+1)
}
dfs(root, 0)
if n := len(arr); n >= k {
sort.Ints(arr)
return int64(arr[n-k])
}
return -1
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function kthLargestLevelSum(root: TreeNode | null, k: number): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode, d: number) => {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (arr.length <= d) {
arr.push(0);
}
arr[d] += root.val;
dfs(root.left, d + 1);
dfs(root.right, d + 1);
};
const arr: number[] = [];
dfs(root, 0);
if (arr.length < k) {
return -1;
}
arr.sort((a, b) => b - a);
return arr[k - 1];
}