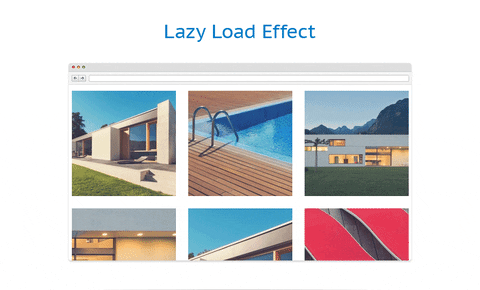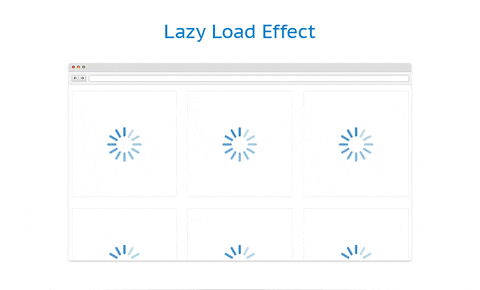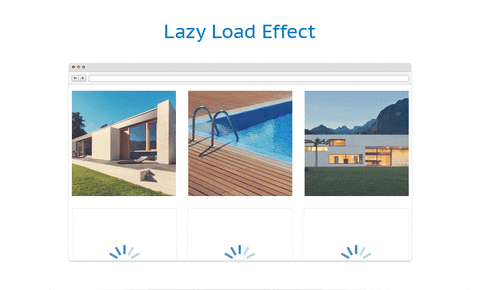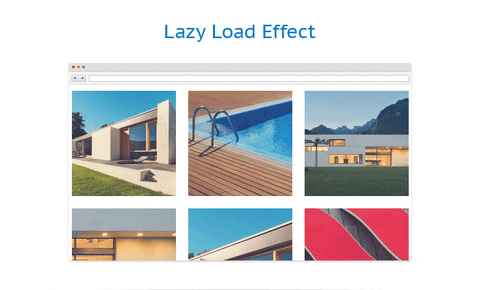
Server-side rendering is the most common method for displaying information onto the screen. It works by converting HTML files in the server into usable information for the browser.
Whenever you visit a website, your browser makes a request to the server that contains the contents of the website and the speed that content is served depends on:
- Your internet speed
- the location of the server
- how many users are trying to access the site
We can use templates on the server side (such as Handlebars). This partly automates the creation of our HTML documents by using programming functionality like loops or regular expressions. This allows us to create dynamic websites which are written on our server and then sent to the front-end.
In this example, our page would be rendered with a heading, paragraph and link, i.e. everything on the HTML page. When the link given after the paragraph is clicked, an entire new HTML page will be rendered, not just the new content.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Example Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Website</h1>
<p>This is an example of my new website</p>
<a href="http://example.testsite.com/other.html.">Link</a>
</body>
</html>
In this example, instead of getting all of the content from the HTML document itself, we have a bare-bones HTML document with a JavaScript file that will render the rest of the site using the browser.
Everything else is handled by a client-side JavaScript library, in this case, Vue.js, and custom JavaScript code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Example Website</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">
<app></app>
</div>
<script src="https://vuejs.org"type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="location/of/app.js"type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
</html>
Templating allows us to modularise out our front-end semantic code. If we are making a shopping cart for example, with a HTML page for each product, we are setting ourselves up for a lot of repetitive, boring code. We are also violating the DRY (Don't repeat yourself) principle.
Instead of hard coding this we can write a template which contains the code that stays the same across all product pages, with variables in place for things like the product name and image link.
Templating allows you to do great things such as:
To generate multiple versions of a HTML element templates can loop through sections of code, adding in key words and values. This can reduce the amount of html code you have to write, and make editting it easier.
<ul class="people_list">
{{#each people}}
<li>{{this}}</li>
{{/each}}
</ul>
You can use coditional logic to populate parts of your html document depenent on whether data exists or not
<div class="entry">
{{#if author}}
<h1>{{firstName}} {{lastName}}</h1>
{{/if}}
</div>
The benefits of server-side rendering over client-side rendering | Medium