🔬 Proof of Concept of Dijkstra's algorithm in .NET
Based on Elemar Jr's post Finding the best path between two points using Dijkstra (in portuguese)
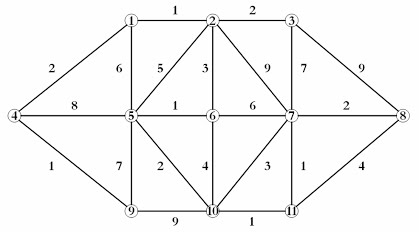
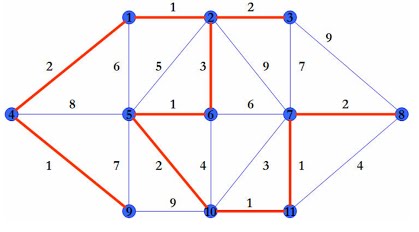
This PoC validates the usage of Dijkstra's algorithm to find the fastest way between two points.
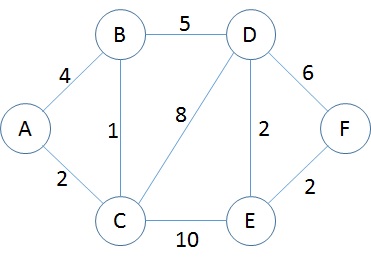
In this sample, the direction of the edge is bi-directional. It means that connecting A to B node is the same as B to A.
var a = new SimpleNode("A");
var b = new SimpleNode("B");
var c = new SimpleNode("C");
var d = new SimpleNode("D");
var e = new SimpleNode("E");
var f = new SimpleNode("F");
a.ConnectTo(b, 4);
a.ConnectTo(c, 2);
b.ConnectTo(c, 1);
b.ConnectTo(d, 5);
c.ConnectTo(d, 8);
c.ConnectTo(e, 10);
d.ConnectTo(f, 6);
d.ConnectTo(e, 2);
e.ConnectTo(f, 2);
var dijkstra = new Dijkstra.Dijkstra();
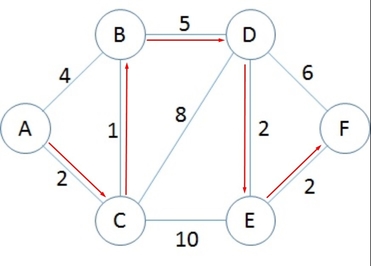
var result = dijkstra.FindShortestPath(a, f);In this sample, the connection works only in one way. If connected A to B, only A to B flow is allowed, B from A not. We can use different values for the connection for each direction. A to B 5 then B to A 10
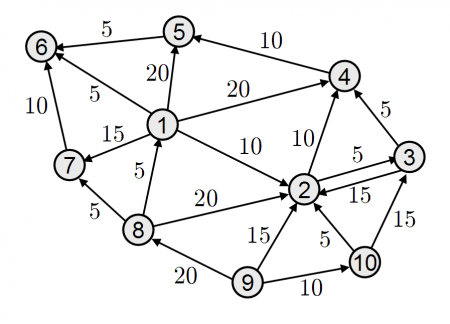
- Both directions made in 2<->3 nodes
var one = new DirectionalNode("1");
var two = new DirectionalNode("2");
var three = new DirectionalNode("3");
var four = new DirectionalNode("4");
var five = new DirectionalNode("5");
var six = new DirectionalNode("6");
var seven = new DirectionalNode("7");
var height = new DirectionalNode("8");
var nine = new DirectionalNode("9");
var ten = new DirectionalNode("10");
one.ConnectTo(two, 10);
one.ConnectTo(four, 20);
one.ConnectTo(five, 20);
one.ConnectTo(six, 5);
one.ConnectTo(seven, 15);
two.ConnectTo(four, 10);
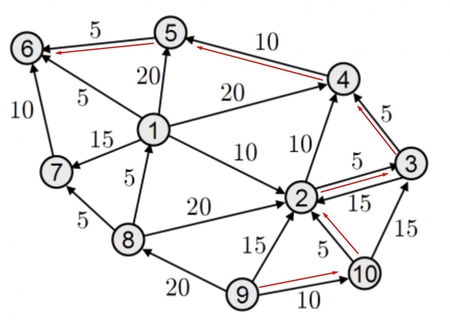
two.ConnectTo(three, 5); //connects two and three with a value of 5
three.ConnectTo(four, 5);
three.ConnectTo(two, 15); //connects three and two with a value of 15
four.ConnectTo(five, 10);
five.ConnectTo(six, 5);
//six doesn't have outbound connections, only inbound
seven.ConnectTo(six, 10);
height.ConnectTo(one, 5);
height.ConnectTo(two, 20);
height.ConnectTo(seven, 5);
nine.ConnectTo(two, 15);
nine.ConnectTo(height, 20);
nine.ConnectTo(ten, 10);
ten.ConnectTo(two, 5);
ten.ConnectTo(three, 15);
var dijkstra = new Dijkstra.Dijkstra();
var result = dijkstra.FindShortestPath(nine, six);//TODO