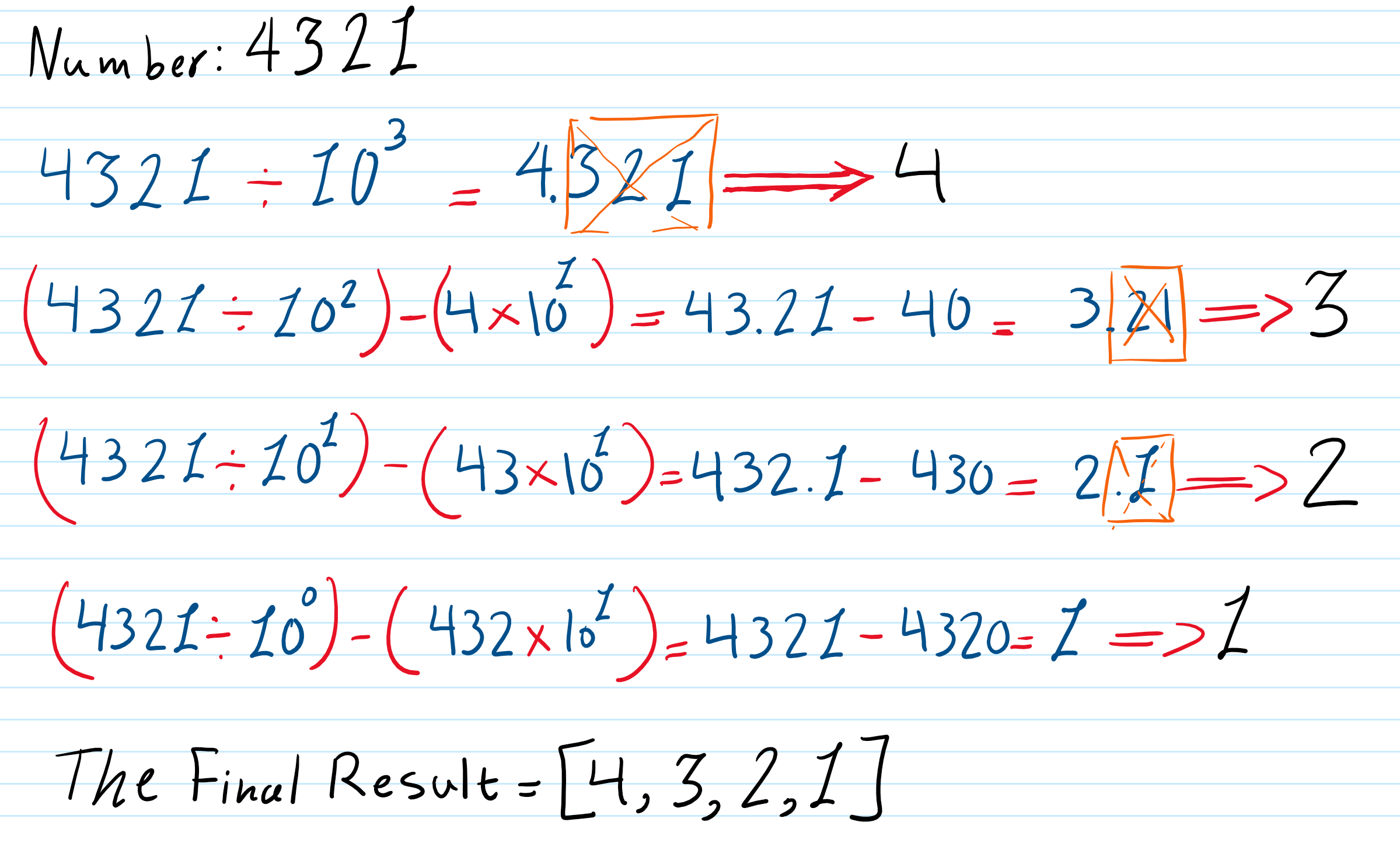The software computes and determines all possible numbers of desired digits. This software employs mathematics to solve the request by inference. The context of the program contains two major sections. The first part describes the logic behind this code, and the other part explains the program steps.
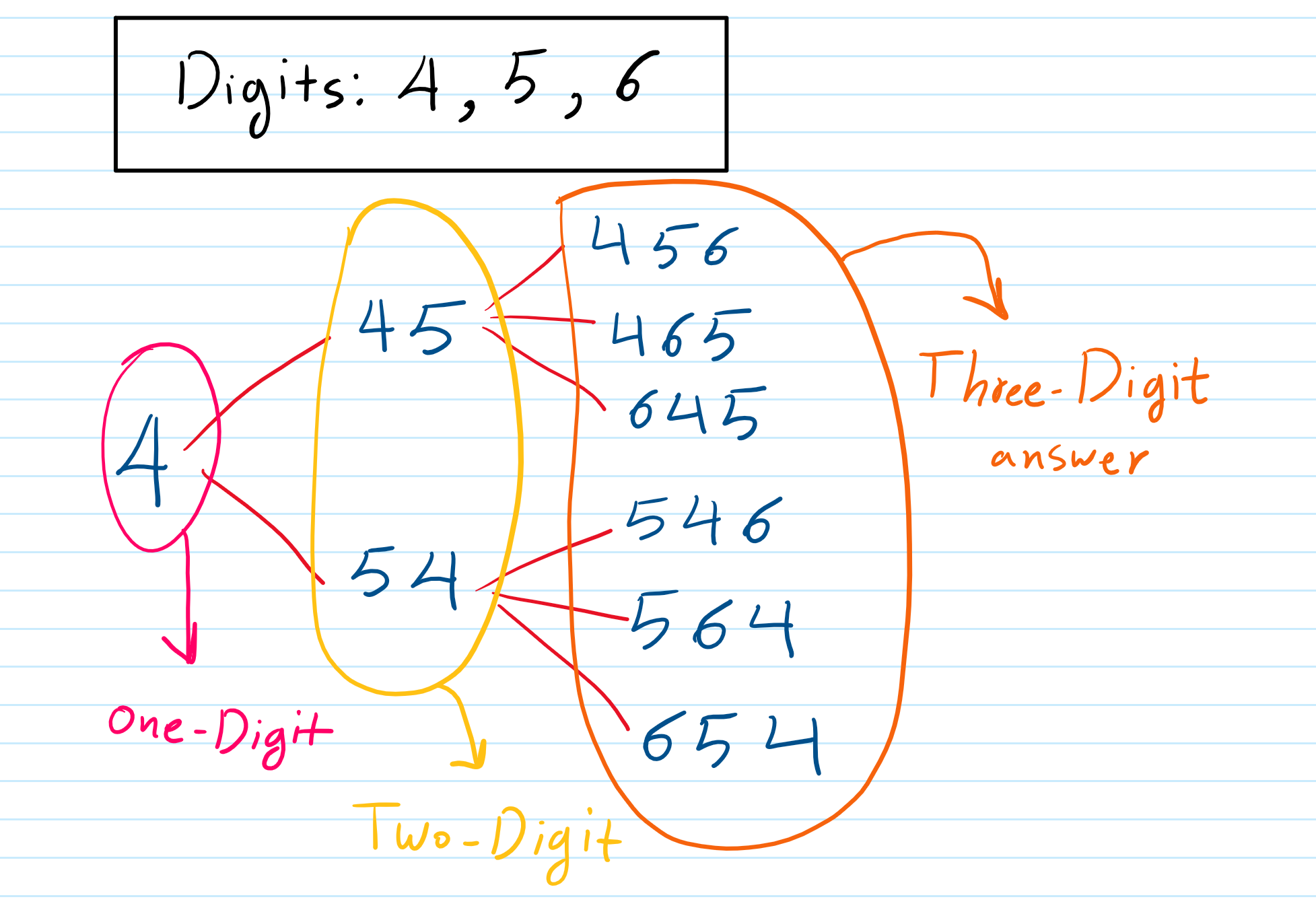
The First Section: Math utilizes factorial to find the number of possibilities. The tree structure helps us to find probable numbers through reasoning. Examples provide a better understanding. The digits 1, 2, 3 produce six possible three-digit answers. The solution is 3×2×1. Now, we can separate each part of the solution. The answer would be equal to 1 if we take only one digit and make a one-digit number. If we add another digit, the answer would be 2 (2×1). If we add the last digit, the answer would be 6 (3×2×1). The illustration below displays the process as a tree structure.
The Second Section: The program includes three functions. The first function, 'Number_Input,' receives digits from the user. The second function deletes duplicated numbers. The last 'function' carries the responsibility to determine the expected numbers. The software multiply numbers by ten, and then it adds the digit to the number. It finds all possible combinations before adding the new digit. The software sorts the input digits and starts from the last to the first, so zero would not make trouble. Also, the software would not allow placing zero as the first digit of numbers. The code separates digits of numbers to change combinations. It divides numbers by ten power order of digits. Then, it removes numbers after the radix point. The first number would come out, but the technique for other digits. The illustration below shows the process of the code.