-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 24
Cookbook
This vignette contains a series of examples showing how to initialize the safetyGraphics Shiny app in different scenarios. For a general overview of the app see this vignette. For more details about adding custom charts, see this vignette.
safetyGraphics requires R v4 or higher. These examples have been tested using RStudio v1.4, but should work on other platforms with proper configuration.
You can install {safetyGraphics} from CRAN like any other R package:
install.packages("safetyGraphics")
library("safetyGraphics")
Or to use the most recent development version from GitHub, call:
devtools::install_github("safetyGraphics/safetyCharts", ref="dev")
library(safetyCharts)
devtools::install_github("safetyGraphics/safetyGraphics", ref="dev")
library(safetyGraphics)
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp()
To run the app with no customizations using sample AdAM data from the {safetyData} package, install the package and run:
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp()
The next several examples focus on study-specific customizations for loading and mapping data.
The data passed in to the safetyGraphics app can be customized using the domainData parameter in safetyGraphicsApp(). For example, to run the app with SDTM data saved in {safetyData}, call:
sdtm <- list(
dm=safetyData::sdtm_dm,
aes=safetyData::sdtm_ae,
labs=safetyData::sdtm_lb
)
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp(domainData=sdtm)
Running the app for a single data domain, is similar:
justLabs <- list(labs=safetyData::adam_adlbc)
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp(domainData=justLabs)
Note that charts with missing data are automatically dropped and the filtering tab is not present since it requires demographics data by default.
Users can also import data from a wide-variety of data formats using standard R workflows and then initialize the app. The example below initializes the app using lab data saved as a sas transport file (.xpt)
xptLabs <- haven::read_xpt('https://github.com/phuse-org/phuse-scripts/blob/master/data/adam/cdiscpilot01/adlbc.xpt?raw=true')
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp(domainData=list(labs=xptLabs))
Next, let's initialize the the app with non-standard data. {safetyGraphics} automatically detects AdAM and SDTM data when possible, but for non-standard data, the user must provide a data mapping. This can be done in the app using the data/mapping tab, or can be done when the app is initialized by passing a mapping list to safetyGraphicsApp(). For example:
notAdAM <- list(labs=safetyData::adam_adlbc %>% rename(id = USUBJID))
idMapping<- list(labs=list(id_col="id"))
safetyGraphicsApp(domainData=notAdAM, mapping=idMapping)
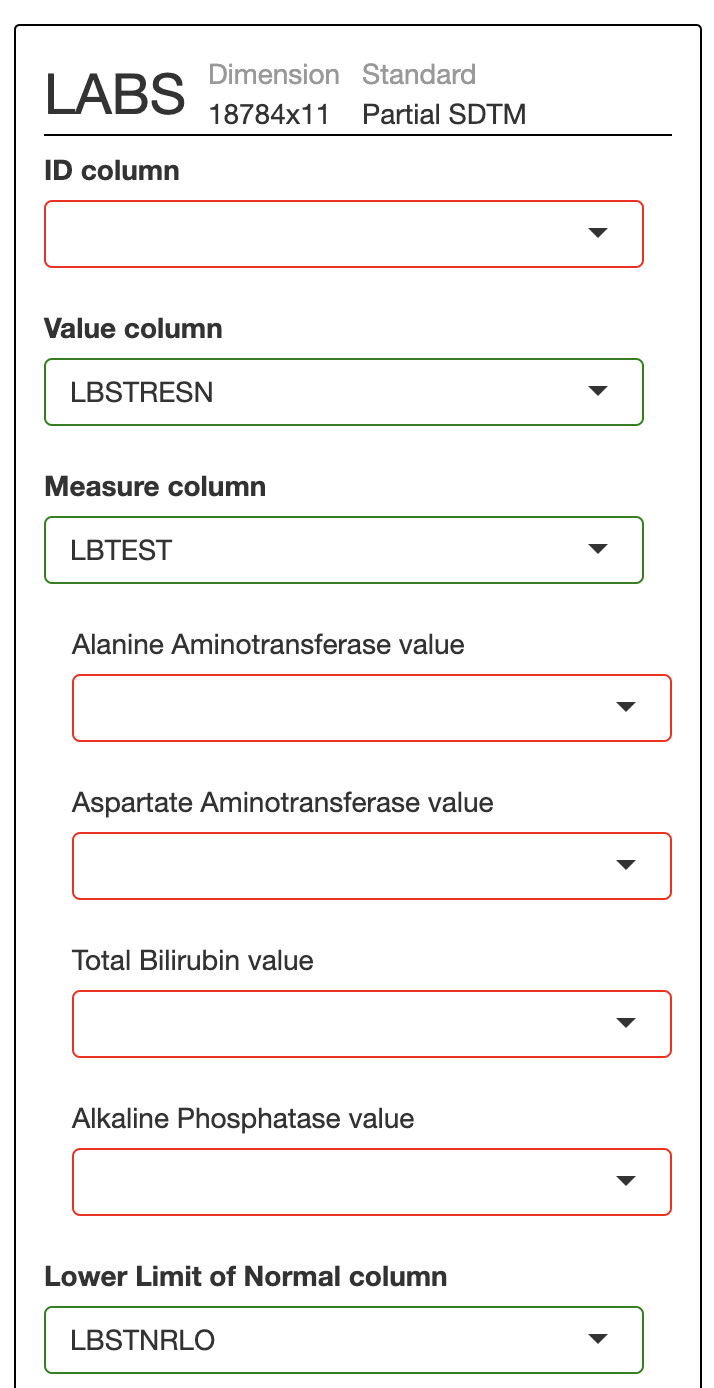
For a more realistic example, consider this labs data set (csv). The data can be loaded in to safetyGraphics with the code below, but several items in the mapping page need to be filled in:
labs <- read.csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SafetyGraphics/SafetyGraphics.github.io/master/pilot/SampleData_NoStandard.csv")
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp(domainData=list(labs=labs))
Fortunately there is no need to re-enter this mapping information in every time you re-start the app. After filling in these values once, you can export code to restart the app with the specified settings pre-populated. First, click on the setting icon in the header and then on "code" to see this page:

The YAML code provided here captures the updates you've made on the mapping page. To re-start the app with those settings, just save these YAML code in a new file called customSettings.yaml in your working directory, and then call:
labs <- read.csv("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SafetyGraphics/SafetyGraphics.github.io/master/pilot/SampleData_NoStandard.csv")
customMapping <- read_yaml("customSettings.yaml")
safetyGraphics::safetyGraphicsApp(
domainData=list(labs=labs),
mapping=customMapping
)
Note, that for more complex customizations, the setting page also provides a .zip file with a fully re-usable version of the app.
The remaining examples focus on creating charts that are reusable across many studies. For extensive details on adding and customizing different types of charts, see this vignette.
Users can also generate a list of charts and then drop charts that they don't want to include. For example, if you wanted to drop charts with type of "htmlwidgets" you could run this code.
library(purrr)
charts <- makeChartConfig() #gets charts from safetyCharts pacakge by default
notWidgets <- charts %>% purrr::keep(~.x$type != "htmlwidget")
safetyGraphicsApp(charts=notWidgets)
Users can also make modifications to the default charts by editing the list of charts directly.
charts <- makeChartConfig() #gets charts from safetyCharts pacakge by default
charts$aeTimelines$label <- "An AMAZING timeline"
safetyGraphicsApp(charts=charts)
This example creates a simple "hello world" chart that is not linked to the data or mapping loaded in the app.
helloWorld <- function(data, settings){
plot(-1:1, -1:1)
text(runif(20, -1,1),runif(20, -1,1),"Hello World")
}
# Chart Configuration
helloworld_chart<-list(
env="safetyGraphics",
name="HelloWorld",
label="Hello World!",
type="plot",
domain="aes",
workflow=list(
main="helloWorld"
)
)
safetyGraphicsApp(charts=list(helloworld_chart))
The code below adds a new simple chart showing participants' age distribution by sex.
ageDist <- function(data, settings){
p<-ggplot(data = data, aes_(x=as.name(settings$age_col))) +
geom_histogram() +
facet_wrap(as.name(settings$sex_col))
return(p)
}
ageDist_chart<-list(
env="safetyGraphics",
name="ageDist",
label="Age Distribution",
type="plot",
domain="dm",
workflow=list(
main="ageDist"
)
)
charts <- makeChartConfig()
charts$ageDist<-ageDist_chart
safetyGraphicsApp(charts=charts)
Here we extend example 9 to include the creating of a new data domain, which is passed to the meta option in safetyGraphicsApp().
# Example 5.2 - Add brand new Hello World data domain ... with an awesome custom chart!!
helloMeta <- tribble(
~text_key, ~domain, ~label, ~standard_hello, ~description,
"x_col", "hello", "x position", "x", "x position for points in hello world chart",
"y_col", "hello", "y position", "y", "y position for points in hello world chart"
) %>% mutate(
col_key = text_key,
type="column"
)
detectStandard(domain='hello', data = iris, meta=helloMeta)
helloData<-data.frame(x=runif(50, -1,1), y=runif(50, -1,1))
helloWorld <- function(data, settings){
plot(-1:1, -1:1)
text(data[[settings$x_col]], data[[settings$y_col]], "Custom Hello Domain!")
}
helloChart<-prepareChart(
list(
env="safetyGraphics",
name="HelloWorld",
label="Hello World!",
type="plot",
domain="hello",
workflow=list(
main="helloWorld"
)
)
)
safetyGraphicsApp(
meta=helloMeta,
domainData=list(hello=helloData),
charts=list(helloChart)
)
This example defines a new ECG data domain and adapts an existing chart for usage there. See this PR for a full implementation of the ECG domain in safetyCharts.
#
adeg <- readr::read_csv("https://physionet.org/files/ecgcipa/1.0.0/adeg.csv?download")
ecg_meta <-tibble::tribble(
~text_key, ~domain, ~label, ~description, ~standard_adam, ~standard_sdtm,
"id_col", "ecg", "ID column", "Unique subject identifier variable name.", "USUBJID", "USUBJID",
"value_col", "ecg", "Value column", "QT result variable name.", "AVAL", "EGSTRESN",
"measure_col", "ecg", "Measure column", "QT measure variable name", "PARAM", "EGTEST",
"studyday_col", "ecg", "Study Day column", "Visit day variable name", "ADY", "EGDY",
"visit_col", "ecg", "Visit column", "Visit variable name", "ATPT", "EGTPT",
"visitn_col", "ecg", "Visit number column", "Visit number variable name", "ATPTN", NA,
"period_col", "ecg", "Period column", "Period variable name", "APERIOD", NA,
"unit_col", "ecg", "Unit column", "Unit of measure variable name", "AVALU", "EGSTRESU"
) %>% mutate(
col_key = text_key,
type="column"
)
qtOutliers<-read_yaml('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SafetyGraphics/safetyCharts/dev/inst/config/safetyOutlierExplorer.yaml')
qtOutliers$label <- "QT Outlier explorer"
qtOutliers$domain <- "ecg"
safetyGraphicsApp(
meta=ecg_meta,
domainData=list(ecg=adeg),
charts=list(prepareChart(qtOutliers))
)