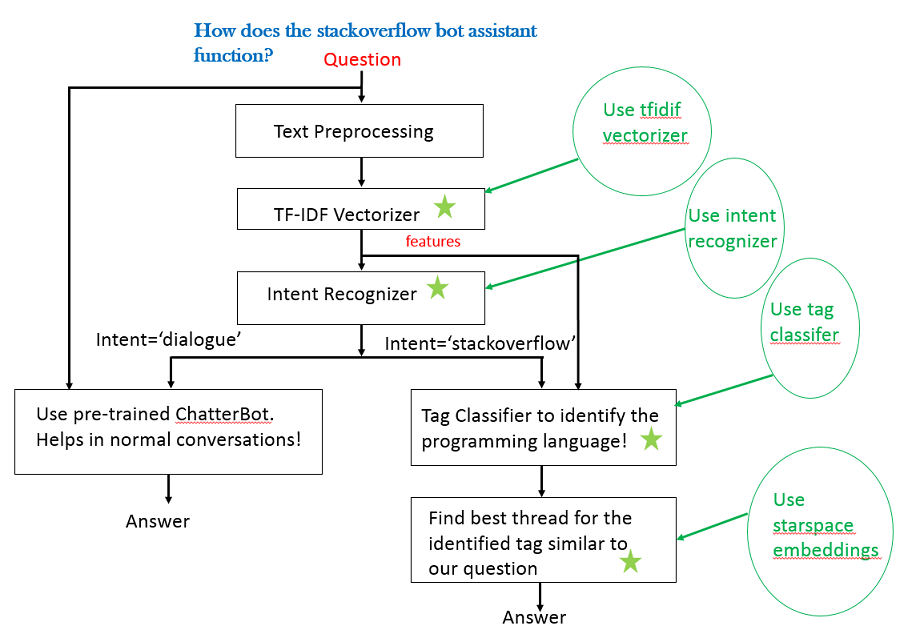
To understand the above flow of chatbot working we need to understand various building blocks and how they are prepared to work!
First things first, this chat-bot project is set-up on Telegram and AWS
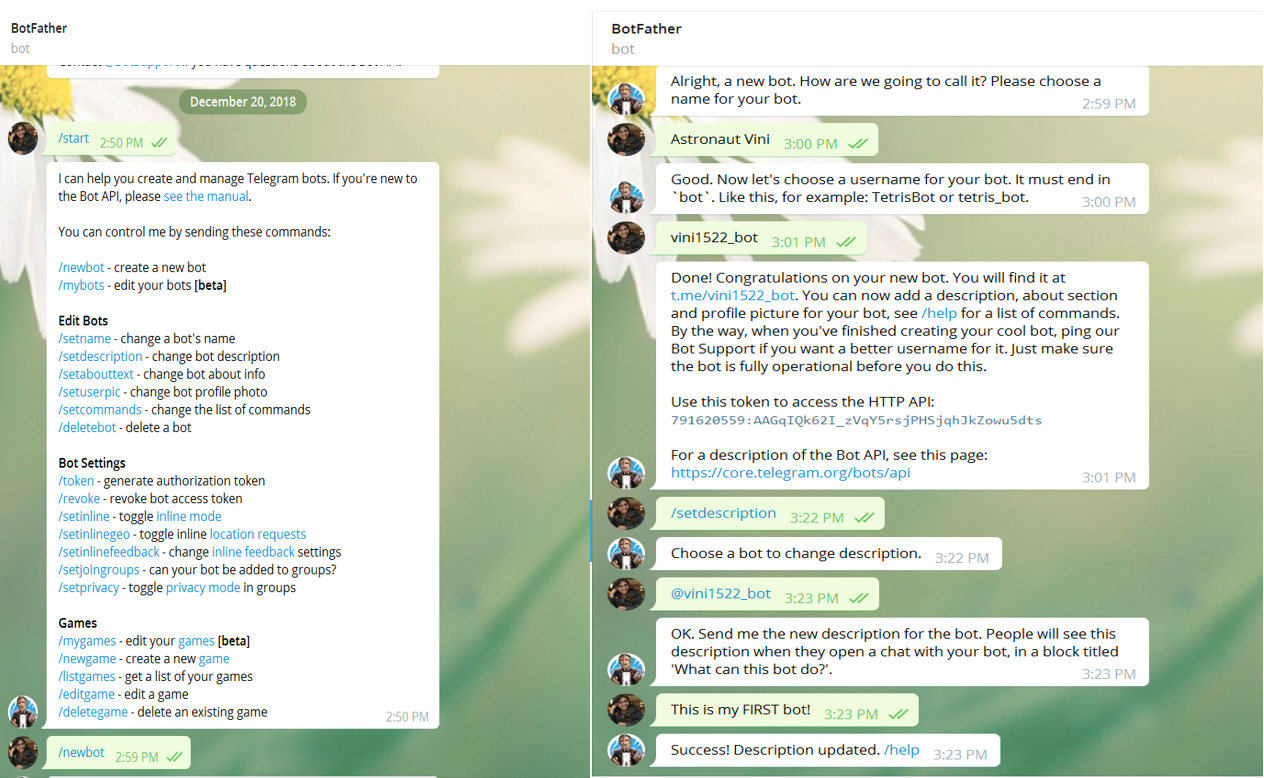
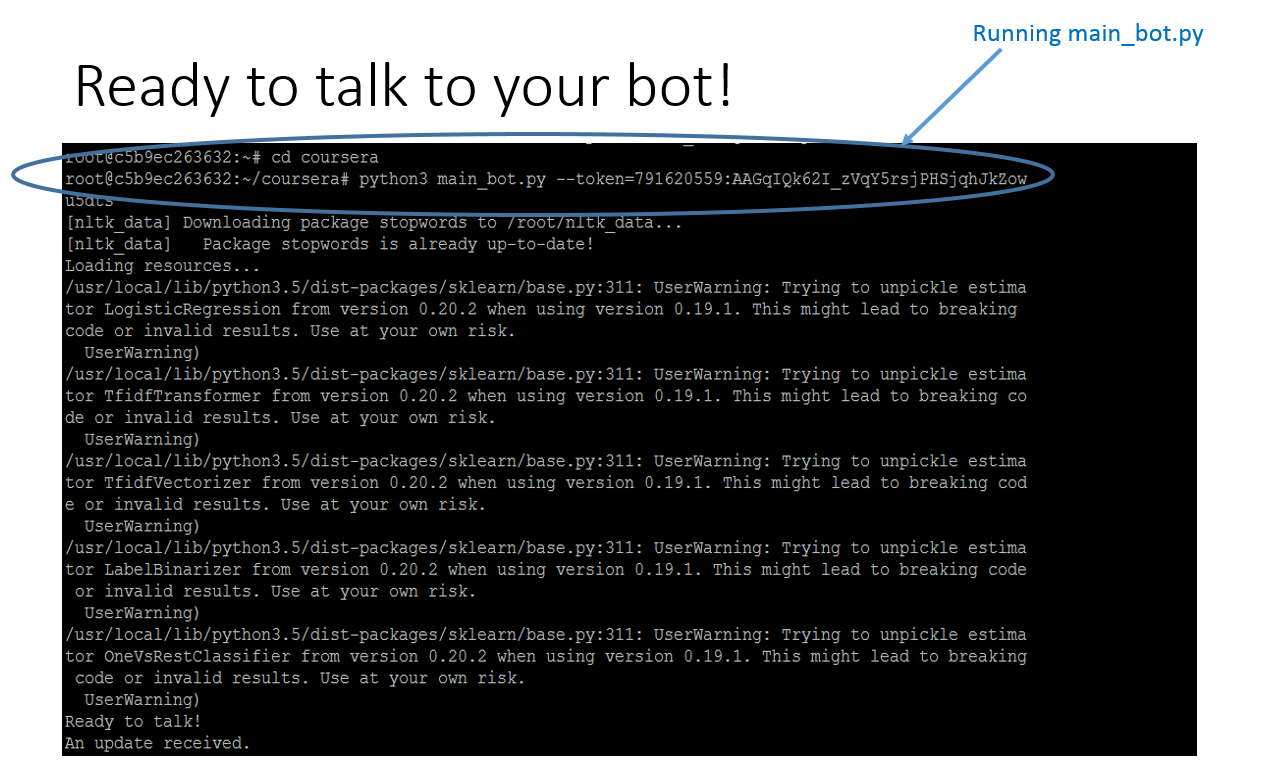
Telegram: Integrating the bot to telegram requires us to generate a token. First we need to create a personal account on Telegram and then talk to @BotFather The command "/newbot" will create a bot for you. You will be prompted to enter a name and a username for your bot. After that, you will be given a token. When you will have main_bot.py script ready you can start interacting your bot by running the below command:
Now the question is where we will run this command?
It is on AWS machine because we are setting up our bot on AWS and all the necessary dependencies will be available on AWS machine.
Firstly, let's create a telegram bot by interacting with BotFather and get the token:
AWS:
- We will be hosting our bot on AWS. We need to sign up at AWS console and launch a free tier instance (Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS) using the instructions given here: AWS-tutorial
- Here we are working on windows 8.1 and to interact with AWS Linux instance for transferring files we need a PuTTY (a free SSH client for Windows) using the instructions given here: PuTTY for windows
- In the below figure we see example of transferring a file from our local Machine to AWS linux machine
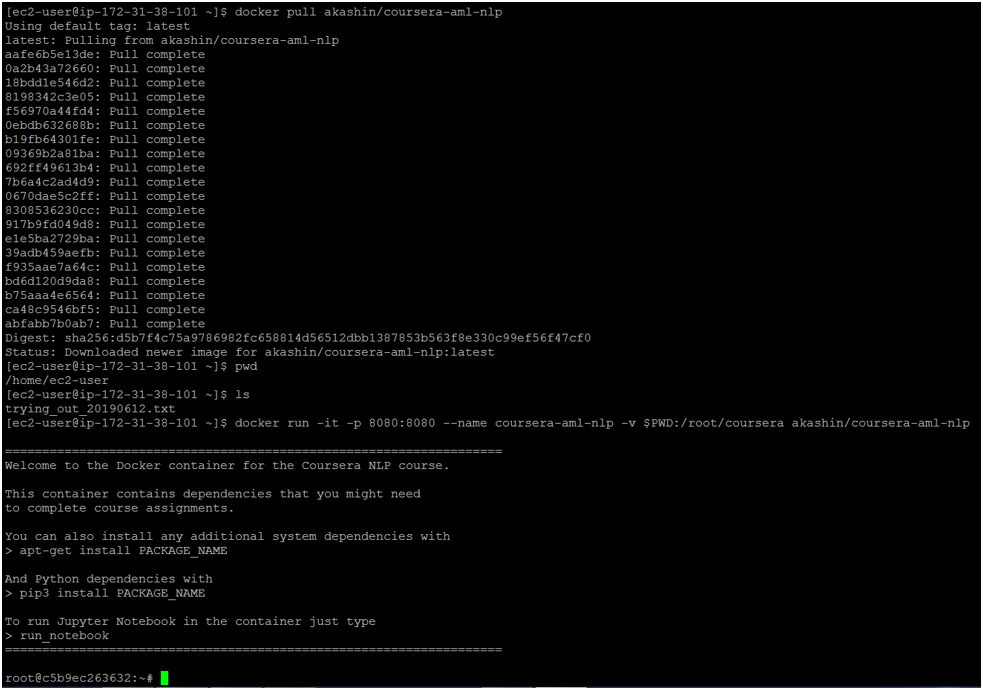
- On AWS linux machine we can install docker and pull the docker image
akashin/coursera-aml-nlpto set up with all the dependencies for this project.
-
Once telegram bot and AWS linux is ready we can focus on the main goal i.e. to prepare models to run the bot. Dataset provided:
dialogues.tsv: Dialogue phrases from movie subtitles (negative samples).Tagged_posts.tsv: StackOverflow posts, tagged with one programming language (positive samples). -
Checkout chatbot_project.ipynb. It performs specifically two tasks:
-
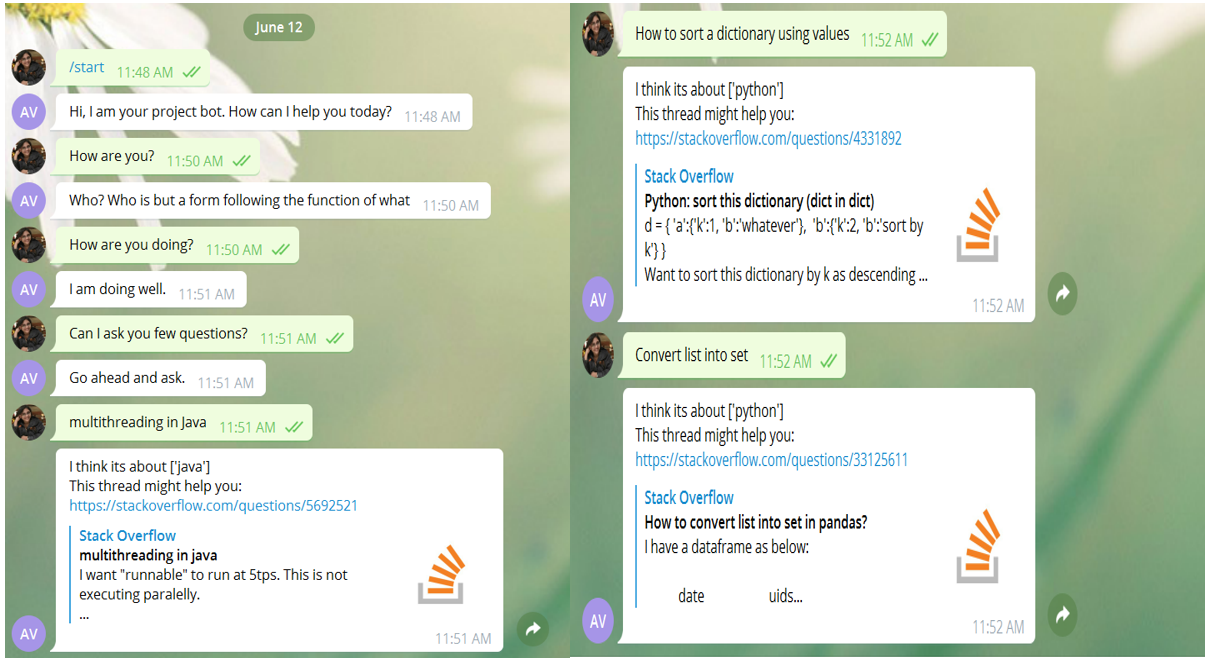
Intent and Language Recognition
- First we need to distinguish programming related questions from general ones.
- Later the programming related questions need to be tagged with the corresponding programming language (here only one!)
-
Ranking questions with embeddings
- To find a relevant answer (a thread from StackOverflow) on a question you will use vector representations to calculate similarity between the question and existing threads.
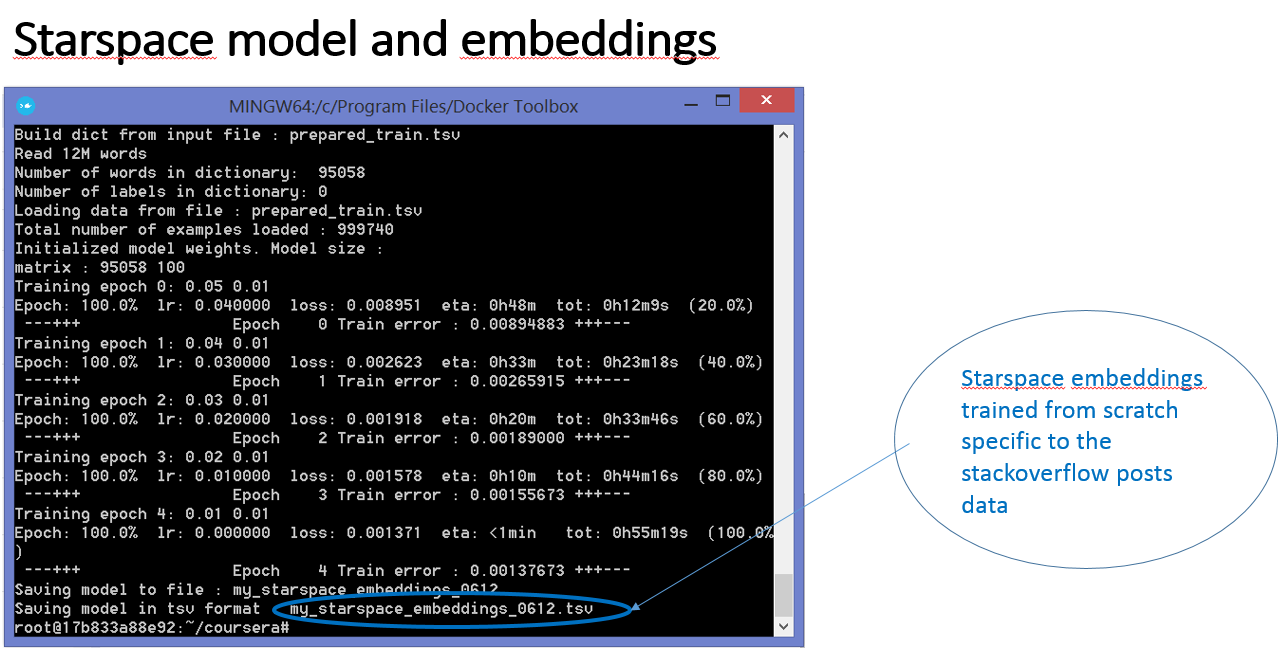
- To find similarity between texts means to find cosine similarity between their representative vectors. These vectors are Starspace embeddings trained specifically on Stack Overflow posts.
-
On running of Chatbot_project.ipynb we will obtain
- Tfidf Vectorizer
- Intent recognizer
- Tag classifer
- Folder containing embeddings of stackoverflow posts/threads segregated “tag” wise. This saves lot of time at runtime in generating the embeddings needed to compare various stackoverflow threads and rank them as per the closest similarity to our question.
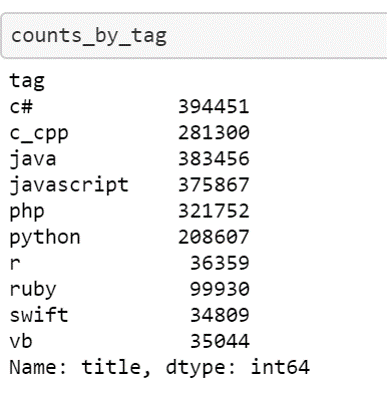
Following is the count of threads under each tag:
Next question is how are the embeddings for question or stackoverflow threads generated? It is by using Starspace model.
Starspace Embeddings:
- Details of starspace embeddings, how they are generated and how they work is mentioned in the following notebook: Starspace_embeddings_Stackoverflow.ipynb
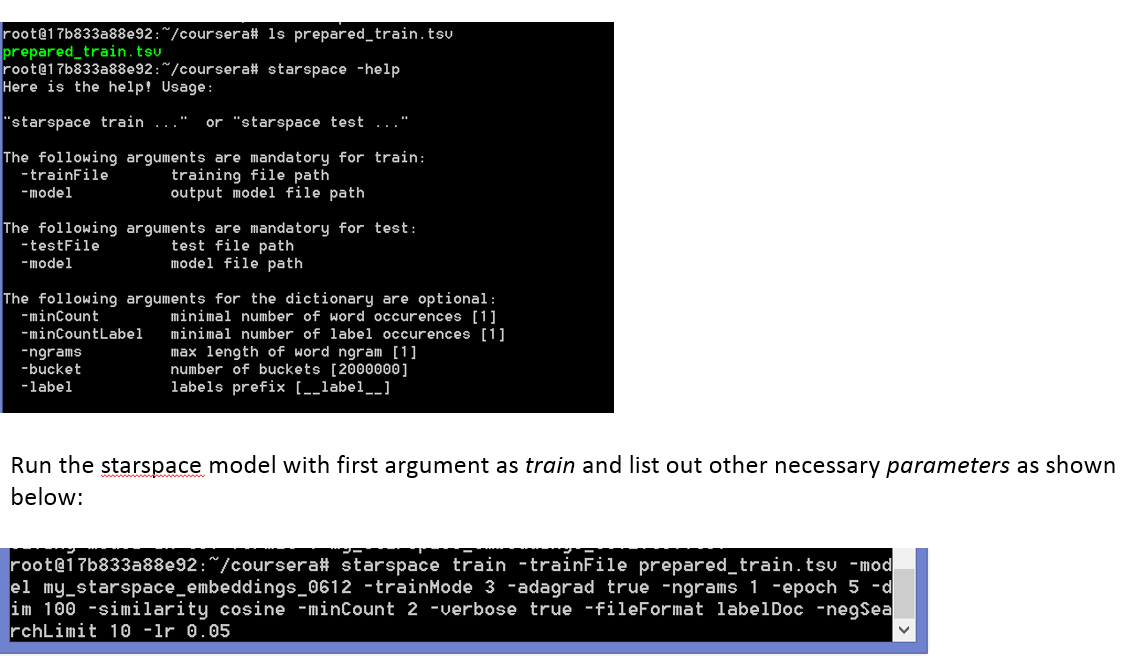
- Basically we need StarSpace neural model StarSpace to train embeddings on the given dataset (stackoverflow posts)
- Since Starspace cannot run on windows, we will use the docker image
akashin/courser-aml-nlpwhich contains Starspace and can help us generate embeddings file.