An e-book manager based off of Material Design
http://cooperhammond.github.io/miskatonic-book-manager
This project was created using Javascript's node.js. The project includes both a database management program using MongoDB and a client side webpage using React that interfaces with the database management program.
The client is created as its own, self-contained node project that can be run on any JavaScript compatible web server. Currently, it is running on Github Pages, here. Please note that once you access this page, the heroku server will take maybe 10 seconds to boot up, and as such, it will display that there is no data available until it has fully booted up and downloaded the data.
The client side GUI was created using React for specific components of the webpage, such as reusable buttons, data boxes, and tables. React was developed by Facebook to make creation of GUIs easier and more interactive.
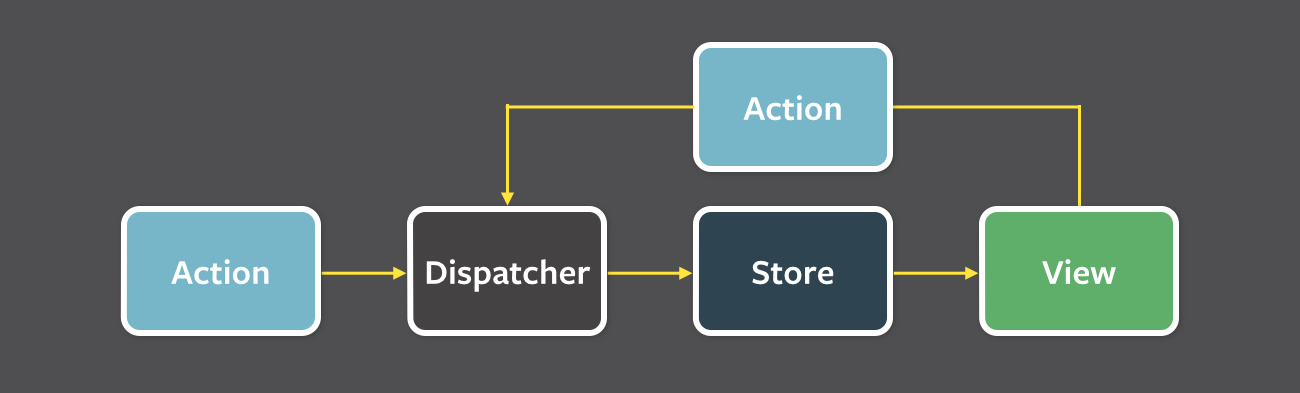
The client side data flow and management is done using flux architecture. Flux architecture was also made by Facebook to complement React's composa.ble view components by utilizing a unidirectional data flow:
The Miskatonic Book Manager client has two stores:
- A Data Store: keeps track of all data and interfaces with the server database. All data is associated by item type of
student,book, andcodes. - A Focus Store: keeps track of what view to show, such as the specific items or a general overview.
The Data Store has actions based on the CRUD database principle:
C: createItem(itemType, data)
R: readItems(itemType)
U: updateItem(itemType, id, data)
D: deleteItem(itemType, id)
The Focus Store has actions to change the view of the GUI:
changeView(args)
closePopup()
openPopup()
In total, there are 10 different components that make up the GUI: AppRender, DataDisplayTable, DeleteButton, MainFocusBox, MainSidebar, Popup, ReportButton, SideFocusButton, and StatisticBoxes.
The control types of the GUI include drop-down lists, text fields, email fields, number selection fields, clickable table rows, clickable emails, scannable QR codes, delete buttons, close buttons, create buttons, sidebar buttons, and a download button.
All data inputs are sanitized, most notably the email input and number selection input.
Created with Google's Material Design in mind, the GUI aims to react with button presses, have clean shadows, and generally look nice.
The server is also created as its own standalone node project for easy uploading to a Heroku server. The server does not actually host the MongoDB database, but rather provides an API for the client to interact with. When the client interacts with the API, the database is updated accordingly. The API is currently hosted on Heroku at https://miskatonic-book-manager-server.herokuapp.com/.
The production MongoDB database is currently running on an mLab server right now, but the Mongo database can be run locally as well.
The server was created using node, and as such, uses the standard library for hosting a server: express. To interact with the Mongo database, it uses the mongoose library.
Each of the items has a unique schema.
The Student Schema has standard attributes like name and email, but also has an array of ObjectIds that reference to codes:
| Key | Attributes |
|---|---|
firstName |
type: String, required: true |
lastName |
type: String, required: true |
email |
type: String, required: true |
grade |
type: Number, required: true |
codes |
type: Array of ObjectIds, default: [] |
The Book Schema has standard attributes like title and author, but also has an array of ObjectIds that reference to codes:
| Key | Attributes |
|---|---|
title |
type: String, required: true |
author |
type: String, required: true |
codes |
type: Array of ObjectIds, default: [] |
readers |
type: Number, default: 0 |
The Code Schema ties the books and students together:
| Key | Attributes |
|---|---|
code |
type: String, default: randomCodeGen |
book |
type: ObjectId, reference: Book, required: true |
student |
type: ObjectId, reference: Student |
All of the models have hooks built in to delete references of themselves when they're deleted, so as to retain database integrity.
With the three item types being students, books, and codes, there are 5 root routes for each item type:
| Route | Request Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
/:itemtype/create |
POST |
Creates the item |
/:itemtype/ |
GET |
Returns all items of :itemtype |
/:itemtype/:id |
GET |
Return specific item by :id |
/:itemtype/:id/update |
PUT |
Update specific item by :id |
/:itemtype/:id/delete |
DELETE |
Delete specific item by :id |
There is also an additional route for the Excel report to be downloaded:
| Route | Request Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
/report/download |
GET |
Downloads the .xlsx report |
To truly run this app locally, you'll want to run your own instance of MongoDB, and create a .env file in the /server folder with the DB_ROUTE variable assigned.
Make sure you have yarn installed.
Then, you'll want to navigate to the /server, /client and root directory and run yarn install in each.
After you've done that, you can run yarn dev from the root, and it'll start up the server locally, and run the client locally.
But why do all of that when you can just go to the live deployment?