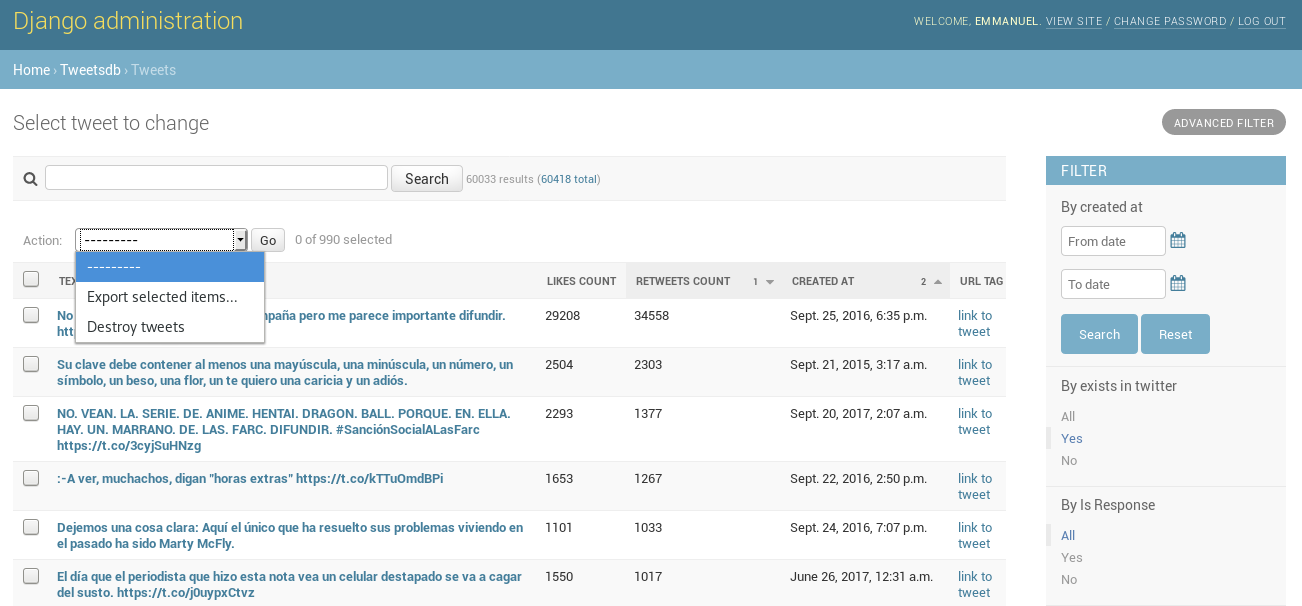
Django-based Dashboard for analyzing, filtering and erasing tweets stored from api or from csv file.
It stores the data in a mysqlite database, and you can manipulate them through an admin interface powered by Django.
Currently it have some nice features as:
- A configurable filter system
- You can delete twets
- A tagging system
- A weighted-scores system.
- Even you can select some tweets and export them in a csv!
First, clone the repo into your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/divisiondeariza/tweets-dashboard.gitthen install dependences. In order to avoid collitions with your local packages, It's recomended to use a virtual enviroment for this
pip install -r requirements.txtThen create and update the database, and create a superuser
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuserthen update your API keys in the libs/twitter_utils/secrets.py file. To get API keys go to https://apps.twitter.com/
then start the server:
python manage.py runserverThen you can use it in http://localhost:8000/admin/tweetsDB/tweet/ with the password and username you just created.
There are two ways of populate the database with your tweets, by the twitter API directly or by using the csv archive file.
This is de easiest way of populate the database, just run:
python manage.py populate --from-apiAnd it will be update yout database automatically. This way have two inconvinients:
- It may take a long time.
- It probably will not retrieve yout oldest tweets, specially if you've been a long time in twitter
You can populate the database by parsing the csv file in your twitter archive (you can request it from here).
python manage.py populate --from-file path/to/your/archive.csvThe csv from archive contains some information about all your tweets (and retweets) omits some quite interesting information like how many retweets and favourites has each tweet. You can feed the database already loaded with archive running this command:
python manage.py feed_from_apiBy default, this only updates tweets that have not been updated before. For update favourites and retweets count for all tweets in database run:
python manage.py feed_from_api --update-allI recommend use the csv file method the first time you use the system, or there are tweets unreacheables by unsing the API method. Use the API method otherwise.
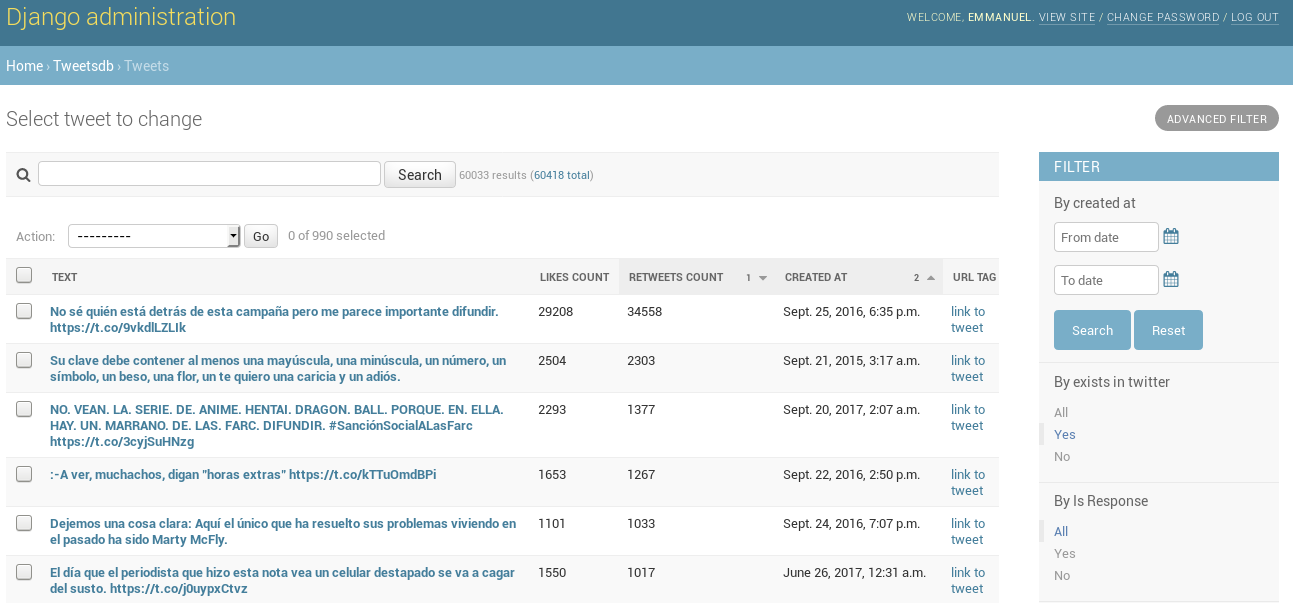
There are some basic ways of filtering tweets:
- By creation date.
- By existence (i.e. was loaded but doesn't exist in twitter anymore).
- By if it's a tweet in response to someone or not.
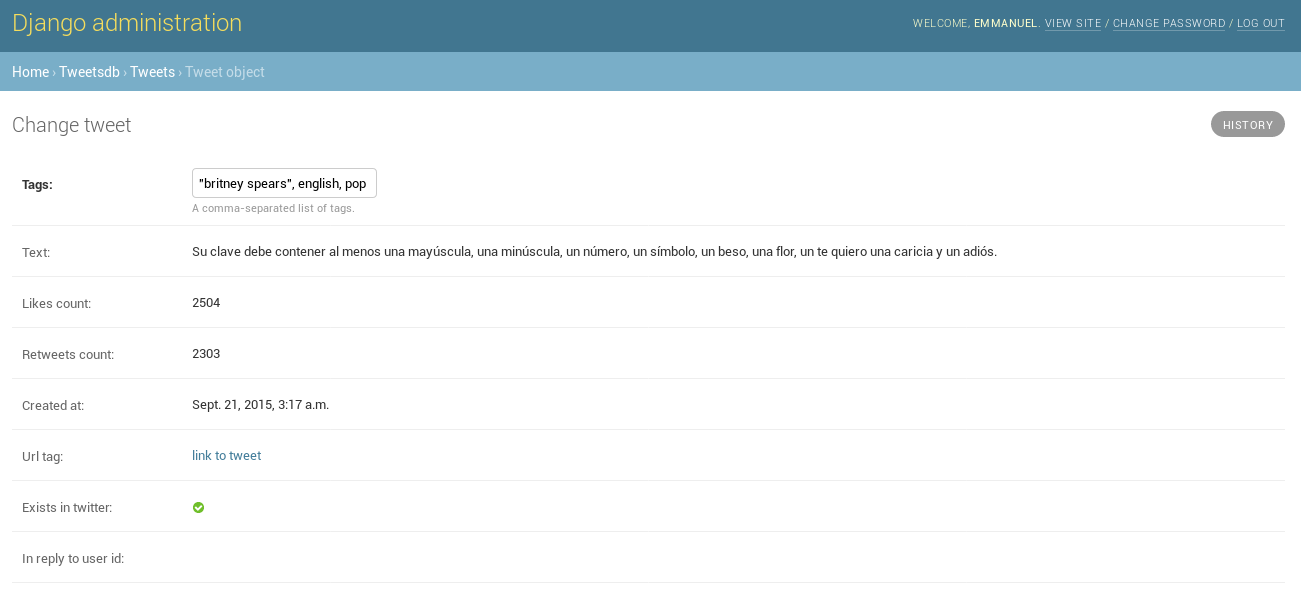
- By tags (using the tagging system)
- By key words in tweets itselves
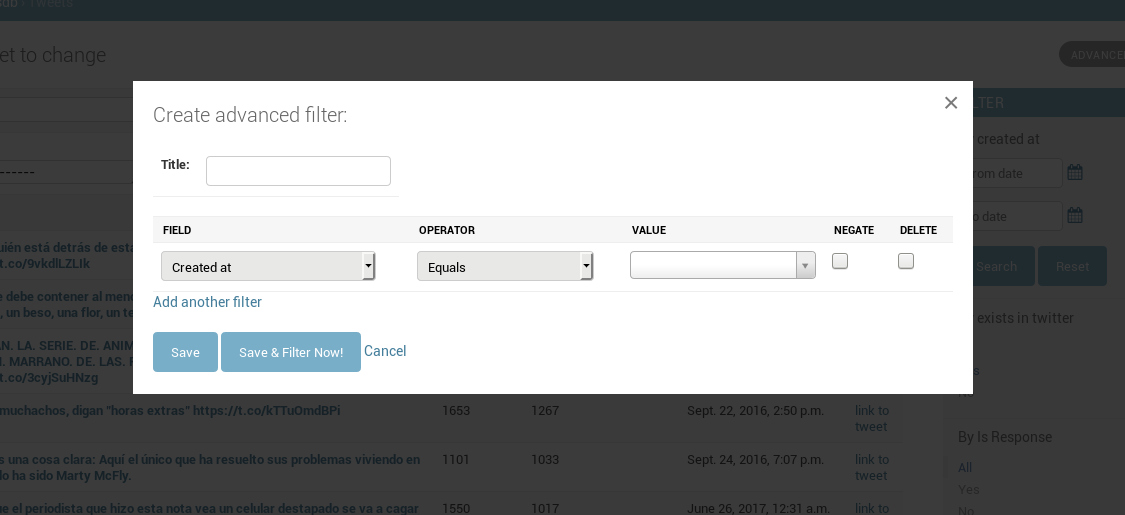
It also has a system for filtering tweets in a query-styled way, which can also be combined with the other filters.
It may be useful to tag some tweets (say, in those you talk about politics set tag 'politics'), and use them as filters latter.
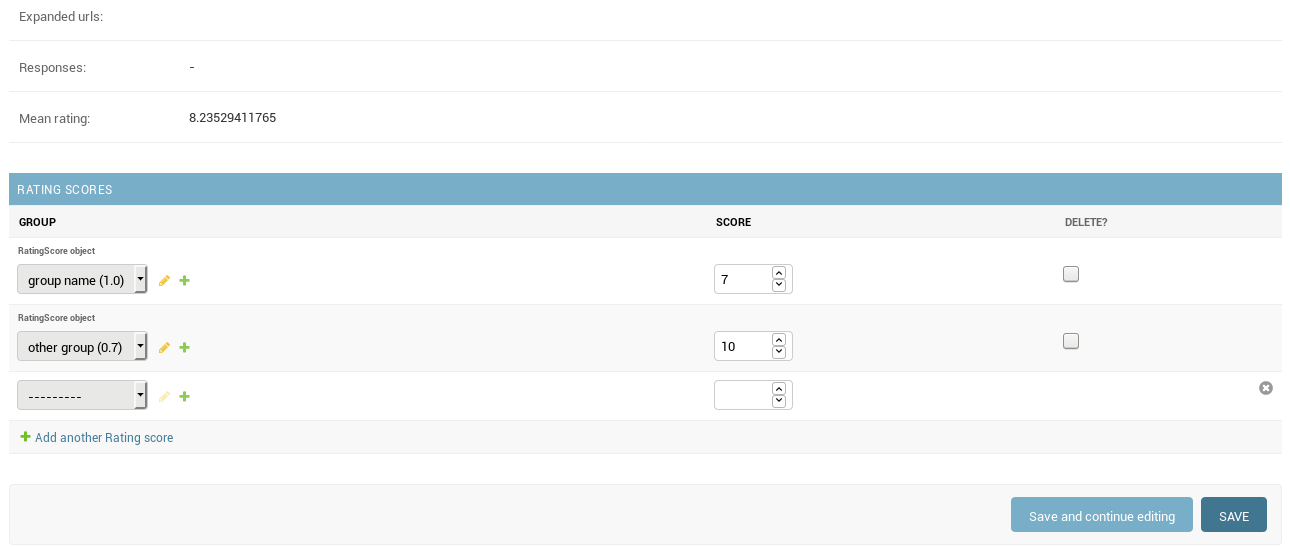
You can add custom scores (ratings) for different metrics to every tweet and assing a weight to each rating, and then sort them in the dashboard by the weigthed-mean of them.
There are some actions you can do over severat tweets at the same time.
You can bulk delete selected tweets directly from dashboard, they will be erased from twitter but remain in databased and are marked as non existent.
You can select some tweets and export them in a csv file.