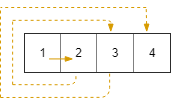
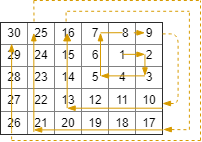
On a 2 dimensional grid with R rows and C columns, we start at (r0, c0) facing east.
Here, the north-west corner of the grid is at the first row and column, and the south-east corner of the grid is at the last row and column.
Now, we walk in a clockwise spiral shape to visit every position in this grid.
Whenever we would move outside the boundary of the grid, we continue our walk outside the grid (but may return to the grid boundary later.)
Eventually, we reach all R * C spaces of the grid.
Return a list of coordinates representing the positions of the grid in the order they were visited.
Input: R = 1, C = 4, r0 = 0, c0 = 0 Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]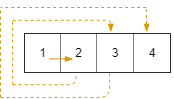
Input: R = 5, C = 6, r0 = 1, c0 = 4 Output: [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]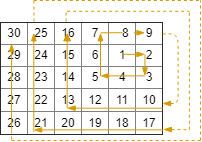
1 <= R <= 1001 <= C <= 1000 <= r0 < R0 <= c0 < C
impl Solution {
pub fn spiral_matrix_iii(r: i32, c: i32, r0: i32, c0: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut x = c0;
let mut y = r0;
let mut step = 2;
let direction = [(-1, 0), (0, -1), (1, 0), (0, 1)];
let mut ret = vec![vec![y, x]];
while (ret.len() as i32) < r * c {
for _ in 0..(step / 2) {
x += direction[step % 4].0;
y += direction[step % 4].1;
if x >= 0 && x < c && y >= 0 && y < r {
ret.push(vec![y, x]);
}
}
step += 1;
}
ret
}
}