Given two binary search trees root1 and root2.
Return a list containing all the integers from both trees sorted in ascending order.
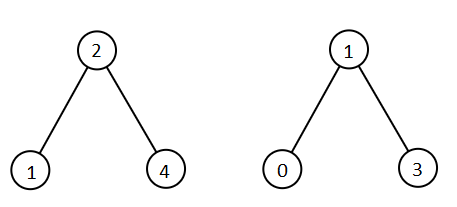
Input: root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3] Output: [0,1,1,2,3,4]
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2] Output: [-10,0,0,1,2,5,7,10]
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2] Output: [0,1,2,5,7]
Input: root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [] Output: [-10,0,10]
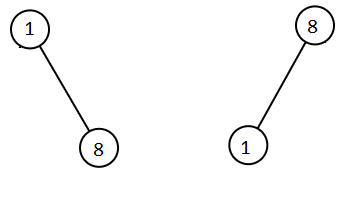
Input: root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1] Output: [1,1,8,8]
- Each tree has at most
5000nodes. - Each node's value is between
[-10^5, 10^5].
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def getAllElements(self, root1: TreeNode, root2: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
curr1, curr2 = root1, root2
nodes1, nodes2 = [], []
flag1, flag2 = True, True
ret = []
while nodes1 or curr1 or nodes2 or curr2:
if flag1:
while curr1:
nodes1.append(curr1)
curr1 = curr1.left
curr1 = nodes1.pop() if nodes1 else None
if flag2:
while curr2:
nodes2.append(curr2)
curr2 = curr2.left
curr2 = nodes2.pop() if nodes2 else None
if not curr2 or (curr1 and curr1.val <= curr2.val):
ret.append(curr1.val)
curr1 = curr1.right
flag1, flag2 = True, False
else:
ret.append(curr2.val)
curr2 = curr2.right
flag1, flag2 = False, True
return ret