There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex ui and vertex vi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex source to vertex destination.
Given edges and the integers n, source, and destination, return true if there is a valid path from source to destination, or false otherwise.
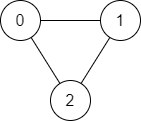
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2 Output: true Explanation: There are two paths from vertex 0 to vertex 2: - 0 → 1 → 2 - 0 → 2
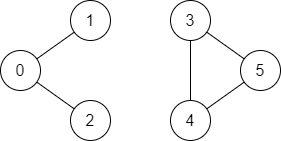
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5 Output: false Explanation: There is no path from vertex 0 to vertex 5.
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1- There are no duplicate edges.
- There are no self edges.
class Solution:
def validPath(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], source: int, destination: int) -> bool:
paths = {}
nodes = [source]
seen = {source}
for u, v in edges:
if u not in paths:
paths[u] = []
if v not in paths:
paths[v] = []
paths[u].append(v)
paths[v].append(u)
while nodes:
node0 = nodes.pop()
for node1 in paths.get(node0, [node0]):
if node1 == destination:
return True
if node1 not in seen:
nodes.append(node1)
seen.add(node1)
return False