This project implements a framework for an adaptive feedforward controller for mobile platforms. The controller works on top of existing motor models and builds a compensation model during runtime, to reduce the error between target velocity and actual measured velocity. Different online learning methods were implemented, including Locally Weighted Projection Regression (LWPR), Sparse Online Gaussian Process (SOGP) and Recursive Least Squares (RLS).
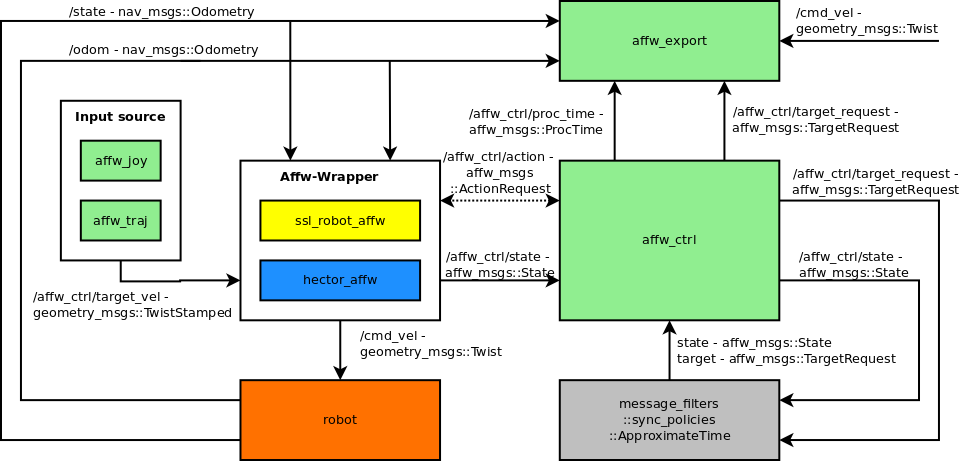
The following diagram shows the package structure and message flow:
The green boxes are part of this repository. The affw-wrapper contains the robot specific part. The diagram contains two examples, hector tracker and SSL robot.
This is a standard ROS package with multiple sub-projects and can be compiled using catkin. The affw_ctrl project includes the affw library (affw_ctrl/lib/affw), which is seperated from the ROS-specific code and has its own CMake project. In the CMakeFile there are some flags for enabling or disabling different learning methods. The CMake project downloads required libraries automatically.
An example project for the hector tracker can be found at https://github.com/tu-darmstadt-ros-pkg/hector_tracker_affw and can can be used as reference for other robot platforms.
The controller provides a service for querying the action compensation on topic "/affw_ctrl/action":
ActionRequest.srv:
affw_msgs/State state
---
float32[] outVel
The State message is defined as:
affw_msgs/State:
std_msgs/Header header
float32[] vel
float32[] custom
The size of outVel and vel must correspond to the action dimension, the custom array can have an arbitrary size, but must not change size and can contain additional information like pose.
The robot state has to be supplied asynchronous on topic "/affw_ctrl/state". The type is affw_msgs/State again, but the custom field is not used. The vel field must be filled with the reference velocity that can be compared to the target velocity used in the action request.
Here is an example launch file to bring up the affw_ctrl node:
<launch>
<!-- learning method, e.g. lwpr, sogp, rls -->
<param name="learner" value="lwpr" />
<!-- overwrite parameters from config file: key=value:key=value -->
<param name="custom_params" value="" />
<!-- location for config files. It should contain affw.cfg. It is also used to save the compensation models. -->
<param name="configFolder" value="$(find your_robot_affw)/config" />
<!-- start affw controller node -->
<node name="affw_ctrl" pkg="affw_ctrl" type="affw_ctrl" output="screen" />
</launch>The config file should be placed into the config folder configured in the launch file and must be renamed to affw.cfg.
# update method: comp = comp + k * (v_target - v_reference)
# the size must correspond to the action dimension
kterm_st2ac.k=1 1
# number of latest target velocities to use in input vector
nTargetVel=1
# calculate target acceleration from the latest two target velocities and use it in input vector
useAcc=true
# number of velocity measurements to use in input vector
nFrames=0
# interpolate velocity measurements to current request timestamp, if they are used
interpState=true
# time difference between velocity measurements if multiple measurements are used
frameDt=0.1
# read the compensation model of the configured learner from config folder
reload_model=false
# the time offset can be used, if the timestamp of the reference velocity does not match the request timestamp
timeOffset=0.0
# if update model is false, the current compensation model will not be updated, but predictions are still possible
updateModel=true
# if true, the action compensation will be forced to be zero if the target velocity is zero
forceZeroIfStateZero=true
# minimum data that has to be seen, before prediction is allowed
min_nData=800
# upper bounds are used for normalization. The size of upperInputBounds must correspond to the input size
# The size depends on the config above. The input order is: targetVelocity measuredVelocity targetAcceleration
# Example: if the action dimension is 2 and the above parameters are used:
# maxVel_1=3, maxVel_2=5, maxAcc_1=4, maxAcc_2=10
upperInputBounds=3 5 4 10
# The size of upperOutputBounds must correspond to the action dimension. This is the maximum absolute compensation value
upperOutputBounds=1.5 1.5
# lwpr specific parameters. See LWPR doc for reference
lwpr.cutoff=0.001
lwpr.initAlpha=250
lwpr.initD=50
lwpr.updateD=true
lwpr.metaRate=250
lwpr.penalty=1e-06
lwpr.useMeta=true
lwpr.wGen=0.1
lwpr.initLambda=0.999
lwpr.finalLambda=0.9999
lwpr.tauLambda=0.9999
lwpr.max_wMax=0.0
# SOGP specific parameters
sogp.l=0.5
sogp.alpha=1
sogp.noise=0.1
The currently learned model can be saved by sending a path to "/affw_ctrl/save_model". It is automatically saved, if the node is shut down, but not reloaded automatically unless configured in the config file (see above).
The update mechanism of the compensation model can be switched off by sending false to "/affw_ctrl/update_model". In this case, the current state of the model is used for prediction, but no new data is fed to the model.
There are some packages for testing the affw controller: The affw_joy package can be used to control the robot with a gamepad. The affw_traj package can read and execute a trajectory from a csv file for evaluation purposes. The affw_export package can be used to record data from the affw controller to csv-files for debugging purposes.
Please refer to the example project mentioned above for corresponding launch files.