-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Home
Integration guide for creating a wallet using Zion Key Management Service
ZKMS (Zion Key Management Service) is a service which provides a way for developers to manage seed security built into HTC EXODUS devices, which integrates Zion protection. All secure operations (input pin, display seed, sign transaction…) will be performed by the trusted OS and no secure data exposed to the rest of Android.
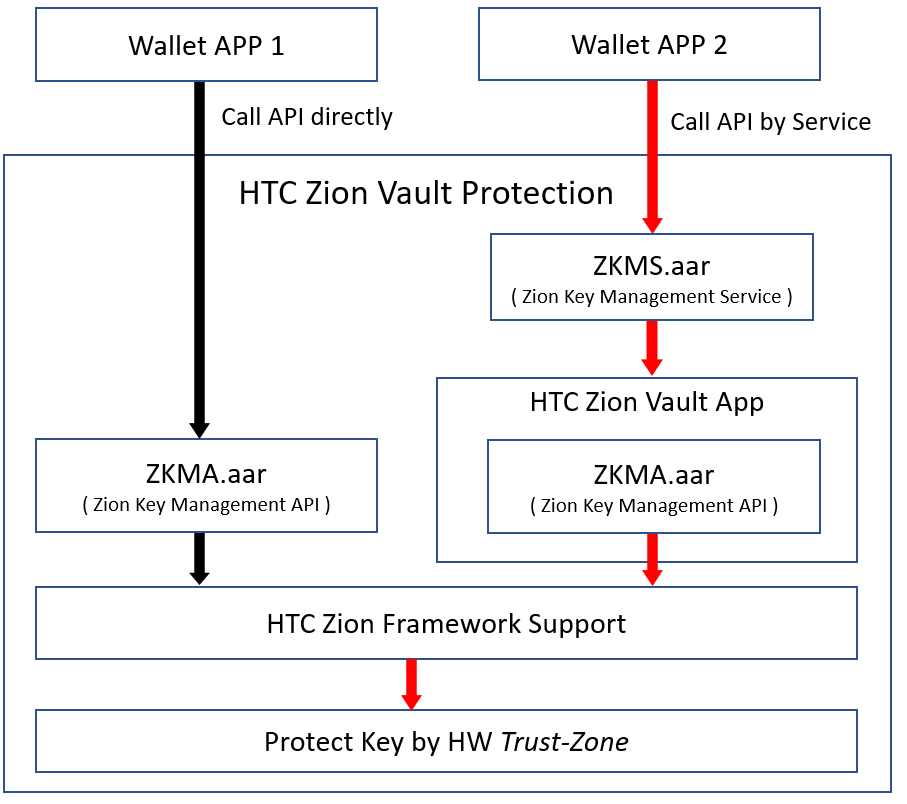
Figure 1. ZKMS API call flow
The caller can access ZKMA(*1) which exported by the HTC Zion Vault app by binding ZKMS.
*1) ZKMA(Zion Key Management API) is a secure API set
| ZKMA | ZKMS | |
|---|---|---|
| Library name | ZKMA.aar | ZKMS.aar |
| File Size | 7 MB~ | 20 KB~ |
| Architecture | Direct call API via ZKMA library | Call API via ZKMS service |
| HTC Zion Vault App | Unnecessary | Mandatory |
Table 1. A comparison between ZKMA and ZKMS library
Step 1. Add the JitPack repository to your .\build.gradle.
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}Step 2. Add the dependency to .\app\biuld.gradle , ex: is 3.3.0b
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.htczion:ZKMS:<version>'
}Most functions in ZKMS return a value. Definitions are listed in the RESULT class. If a function doesn't seem to work, please check the return value in the RESULT class. Return value definitions can be found at https://github.com/htczion/ZKMS/wiki/RESULT.java
ZKMS packaged as an AAR file that can be imported into any android app project.
Copy this .AAR file to your app project lib path:
<Project Name>\app\libs\ZKMS-release.aar
dependencies{
...
compile(name:'ZKMS-release', ext:'aar')
...
}Press the “Make project” button or run the command below to build your app:
./gradlew assembleReleaseThere are two ways for sdk users to access ZKMS APIs: (1) invoking app permissions and (2) APK signing.
The wallet app should declare the ACCESS_ZION permission in AndroiManifest.xml and implement the code for granting this permission. If the user grants Zion permission, your wallet app can then access ZKMS APIs.
<uses-permission android:name="com.htc.wallet.permission.ACCESS_ZION" />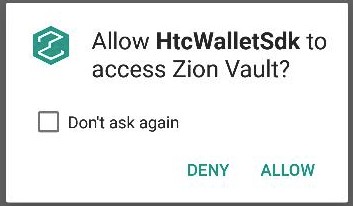
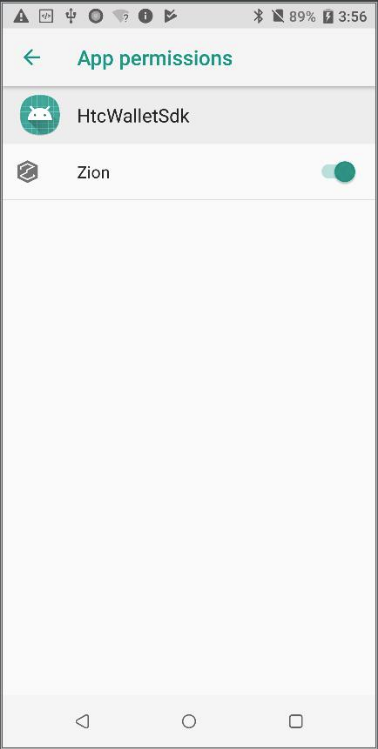
This permission can also be found under app permissions in Android Settings.
The other way for a wallet app to access ZKMS APIs is checking APK's signature, which does not require a permission prompt. HTC Zion Vault APK will check ZKMS users to see if the APK with ZKMS is trusted by checking the provider's signature in the form of a SHA-256 hash. For this to work, you should give us the SHA-256 hash of your provider signature. To get a SHA-256 hash, you can use the following terminal command:
_$ keytool -list -v -keystore <keystore path> -alias <key alias> -storepass <store password> -keypass <key password>_
For example:
$ keytool -list -v -keystore testkey.jks -alias testkey -storepass 123456 -keypass 123456
……
MD5: 43:35:0D:09:CB:9B:8B:DA:72:0B:E2:00:BE:0B:59:F2
SHA1: 28:A4:EC:BE:E6:DB:8B:F0:8B:21:96:6C:0A:29:45:83:94:C3:95:EA
SHA256: 67:29:26:4A:CD:35:1A:15:D4:2F:3D:00:9B:31:BB:40:0E:5E:82:41:76:BD:73:15:D0:DE:4E:4C:DA:BE:48:1C
Any ZKMS user should send their SHA-256 hash to the HTC RD contact window for verification.
ZKMS is an Android service which provided by the HTC Zion Vault app, which requires an HTC EXODUS device.

Figure 3. HTC Zion Vault App Icon
To bind ZKMS, a wallet APP must implement the code snippet as below.
ZKMSConnection mZKMSConnection = new ZKMSConnection();
private class ZKMSConnection implements ServiceConnection
{
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder)
{
try
{
mZKMS = IZKMS.Stub.asInterface(binder);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName)
{
}
}Once you have the mZKMS object, you can call ZKMS APIs.
boolean bBind = bindService(intent, mZKMSConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
if(bBind == true)
Log.d(TAG, "bind ZKMS success!");
else
Util.showUpdateDialog(sActivity, "ROM not support ZKMS.");Initialization prepares all resources and verifies that API function calls work correctly. For example, RESULT.E_SDK_SERVICE_TOO_OLD during initialization means the system service is too old to run, and to prompt the user to do a ROM update. Otherwise all APIs will return a failure or RuntimeException. The API requires two parameters to be provided by ZKMS: the API caller should provide the process ID (PID) and the ZKMS.aar version for validation by ZKMS.
int mPID = android.os.Process.myPid();
String mZKMS_version = com.htc.wallet.server.BuildConfig.VERSION_NAME;
int result = mZKMS.init(mPID, mZKMS_version);
switch (result) {
case RESULT.E_ZKMA_TOO_OLD:
// App should prompt the user to update APK or ROM
showUpdateDialog(mActivity, " PLEASE UPDATE Zion Vault APP or SYSTEM");
break;
case RESULT.E_SDK_ROM_SERVICE_TOO_OLD:
case RESULT.E_SDK_ROM_TZAPI_TOO_OLD:
// App should prompt the user to update ROM
showUpdateDialog(mActivity, "PLEASE UPDATE YOUR SYSTEM");
break;
case RESULT.E_TEEKM_TAMPERED:
// App should prompt the user it’s rooted device
showUpdateDialog(mActivity, "SDK can't support Rooted device");
break;
default:
Log.d(TAG, "init("+mPID+","+ mZKMS_version+") result=" + intValue);
}To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
Compatibility between ZKMA versions and ROM ApiVersion is described in README.md in the following format.:
1.1.0 (0.0003.01010001)
1.1.1
1.1.2
1.1.3
1.2.0 (0.0004.01010005)
1.2.1 (0.0004.01000006)
2.0.0 , ZKMS_ver= 2.0.0
For example, 1.1.0 (0.0003.01010001) can be broken down like this:
1.1.0 indicates ZKMA version based on the ZKMA.AAR version.
0.0003.01010001 indicates the combined API version based on the ROM version.
The combined API version number can be further divided into three numbers and read as follows:
0: The HW wallet.
0003: A hexadecimal number referring to the ROM currentServiceVer.
01010001: A hexadecimal number referring to the ROM currentTzapiVer.
ZKMS_ver= 2.0.0 indicates the supported ZKMS version.
If the combined API version field is empty, such as the listing for ZKMA 1.1.2, it means the ZKMA is compatible with the previous version, and no ROM update is necessary.
ZKMS is a service based on ZKMA. As such, the ZKMS version shouldn't be lower than the ZKMA version otherwise ZKMS will return the E_ZKMA_TOO_OLD error.
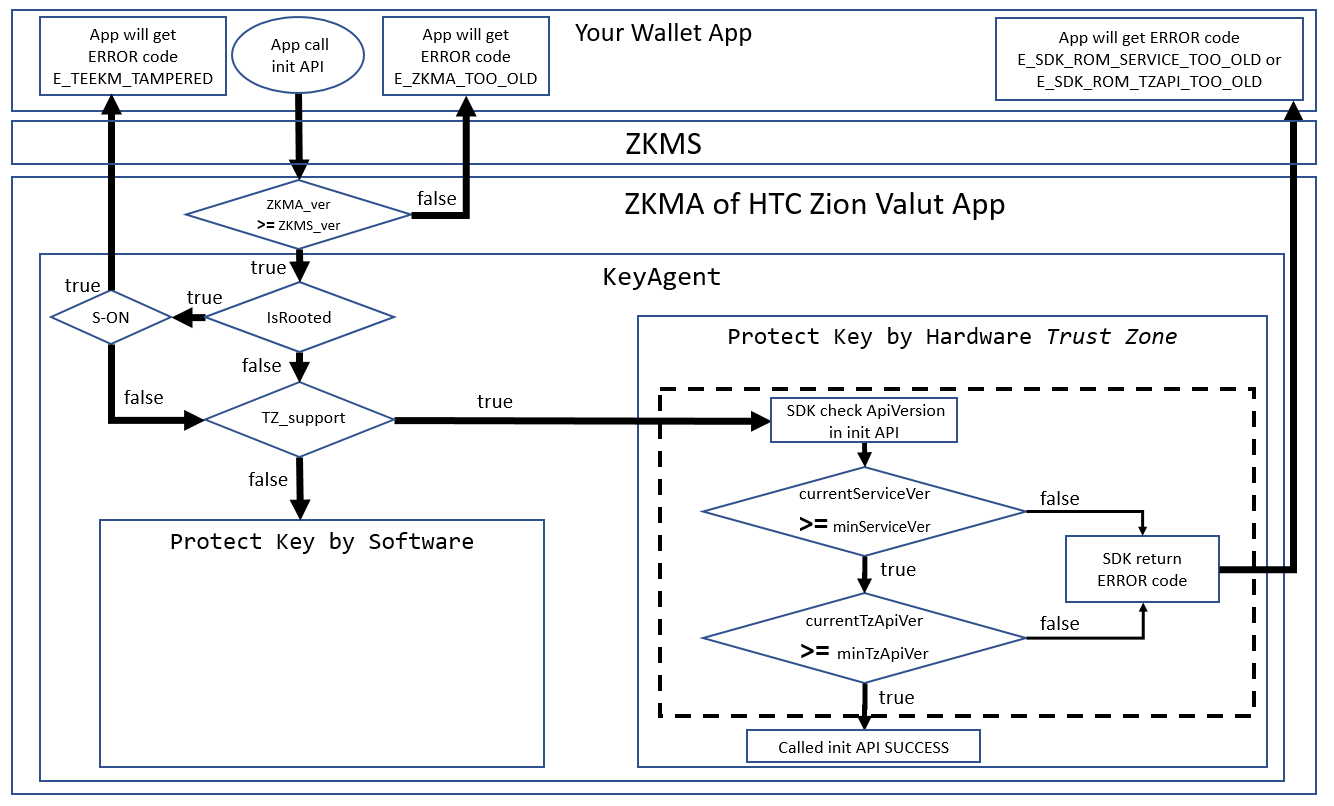
Figure 4. Init API check sequence
To check Trust Zone compatibility of the ROM, the init API sequence will check minServiceVer and minTzApiVer. If the ROM is too old, ZKMS will return either E_SDK_ROM_SERVICE_TOO_OLD or E_SDK_ROM_TZAPI_TOO_OLD to the caller.
The current ZKMA version of HTC Zion Vault app can be gotten with the getModuleVersion function.
String SdkVersion= mZKMS.getModuleVersion();API version information is distinct, and refers to the API level supported by your current EXODUS device hardware. If the API version is lower than the minimum defined by ZKMA, the app should show a dialog to prompt the user to update ROM.
String apiVersion= mZKMS.getApiVersion();For security, ZKMS does not support rooted S-ON devices. If ZKMS detects this situation, it will return the error RESULT.E_TEEKM_TAMPERED to the developers. The isRooted function allows the developer to check if the device rooted at any point.
int isRooted(); // 0: not root yet(RESULT.NOT_ROOTED), others: rooted or other errorsTo prevent the Trust Zone blocked UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
The ZKMS manager uses unique IDs to distinguish between callers of seed operations. This ID can be generated using the register function. This ID serves as a unique identifier for a wallet. Multiple registrations and multiple IDs are possible for a wallet needing to access multiple seeds.
long unique_id = mZKMS.register(wallet_name, sha256);If unique_id returns 0, registration has failed. Additionally, a wallet_name cannot be more than 32 characters.
To prevent the Trust Zone blocked UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
If no seed exists, you can set keyboard type as either qwertypad for a QWERTY layout or numberpad for a numeric layout.
// nType= 0:qwertypad(default), 1:numberpad
int result = mZKMS.setKeyboardType(unique_id, nType);To prevent the Trust Zone blocked UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
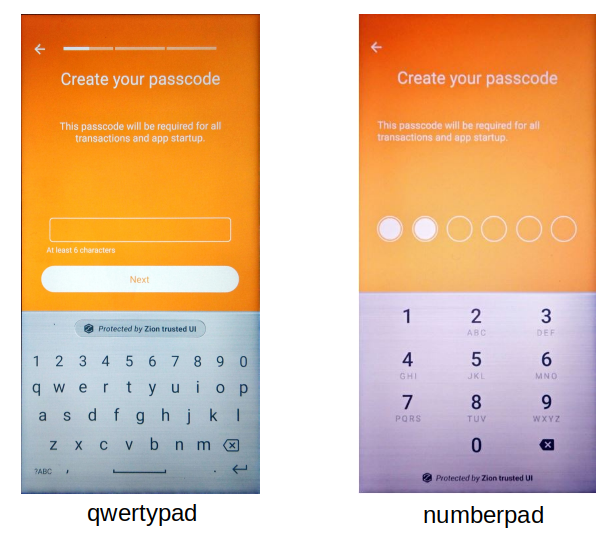
Figure 5-1. two keyboard type
If the user has not used cryptocurrency before, they will need to create a new wallet and generate new seeds. The createSeed function has been provided for this purpose. After invoking this function, the user will be prompted to set a passcode. Any seed-related function will prompt the user for this passcode.
Once the passcode setup is complete, the user will be asked to write down 12 words that represent their cryptographic seed (we call this the “12-word recovery phrase”). To ensure the user has accurately recorded the 12-word recovery phrase, they will be prompted to re-enter for confirmation before continuing.
int result = mZKMS.createSeed(unique_id);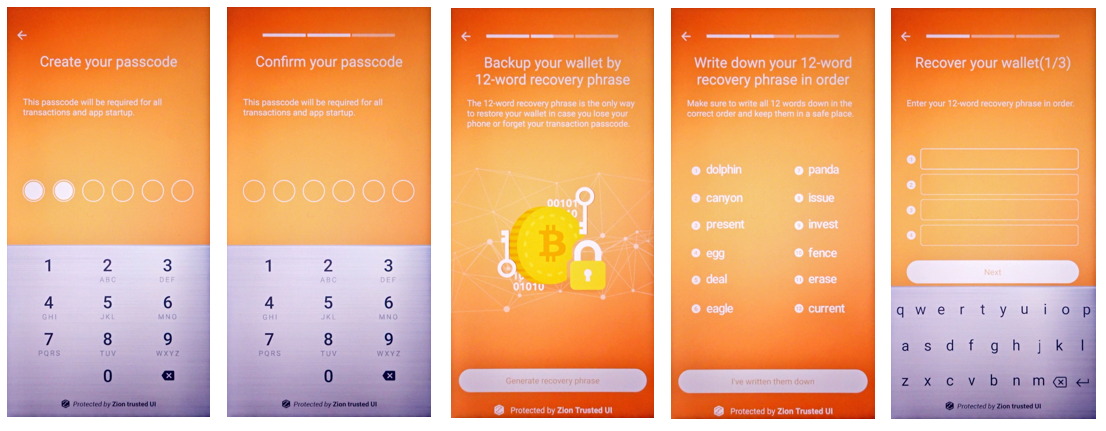
Figure 5-2. Seed creation process from the perspective of the user
To prevent the Trust Zone blocked UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
If there is a preexisting seed, the keyboard can still be specified as qwertypad or numberpad with the function changePIN_v2. The first screen will instruct the user to input the old PIN, and then the following screen will show the new keyboard specified by the nType parameter.
// nType= 0:qwertypad(default), 1:numberpad
int result = mZKMS.changePIN_v2(unique_id, nType);To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
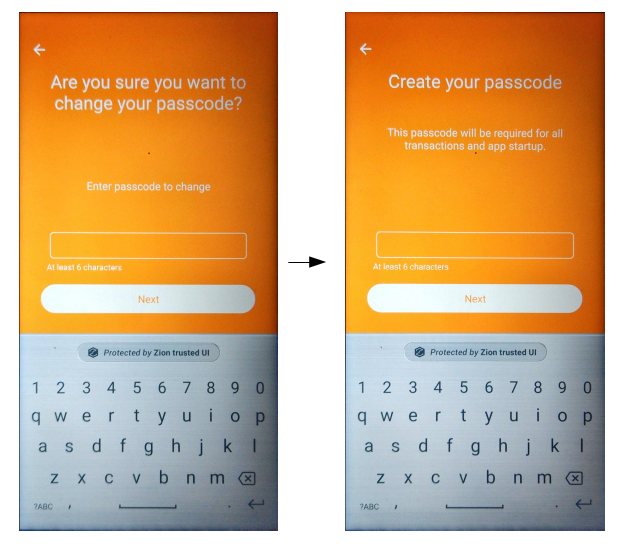
Figure 5-3. Change PIN V2
If the user has used cryptocurrency before, they may wish to restore an existing wallet instead of creating a new one. This capability is provided by the restoreSeed function. The user need only enter their 12-word recovery phrase to restore their wallet. Users will also be prompted to set a passcode.
int result = mZKMS.restoreSeed(unique_id);Prompt the user to enter their 12-word recovery phrase
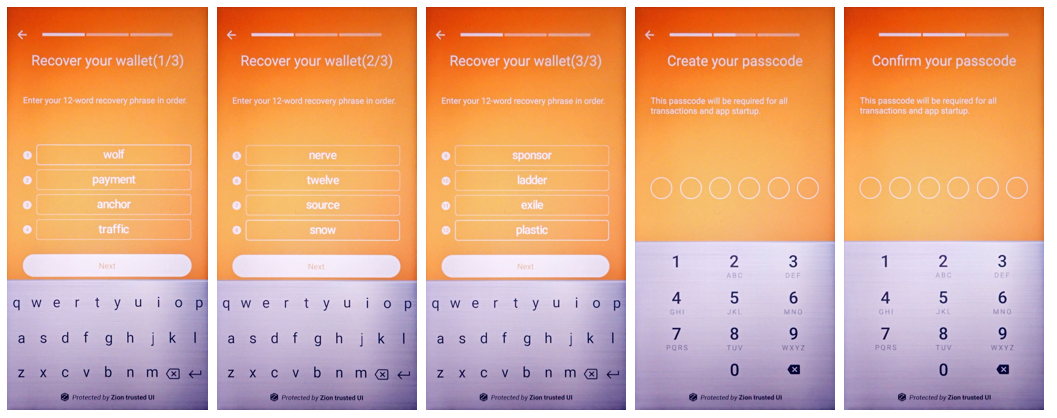
Figure 6. A guide to show the security UI for user to restore their seed
To prevent Trust Zone blocked UI thread, the developer must call this API in background thread.
An app needs to be able to distinguish between use cases where the user needs to create a new wallet, restore an existing wallet, or let the user check current wallet details. This function can be used to check if the device has an existing seed and wallet. If there is no preexisting seed, the user has not completed wallet setup. Users should be prompted to create a wallet or restore an existing one.
int result = mZKMS.isSeedExists(unique_id);To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
When creating a new wallet, the user will be prompted to write down their 12-word recovery phrase. If the user has lost their recovery phrase, the wallet app can use this function to display the recovery phrase again so that the user can record it in a safe place.
int result = mZKMS.showSeed(unique_id);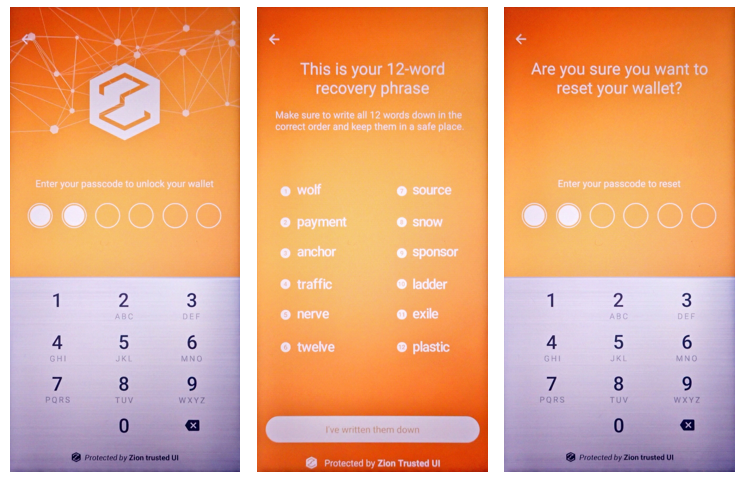
Figure 7. Trusted UI for the user to check their seed
To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
Because different types of crypto currency have different algorithms to generate the wallet address, ZKMS does not provide a way to retrieve an account address. Instead, it provides a way to retrieve the public key. Once the key is obtained, apps can generate their own account addresses.
// A holder for store your key
PublicKeyHolderParcel sendPublicKeyHolder, receivePublicKeyHolder;
// You can get a public key for send or receive purpose, index can be increased by SDK or parameter.
// coin_type: 0=BitCoin, 2=LiteCoin, 60=Ethereum
sendPublicKeyHolder = mZKMS.getSendPublicKey(unique_id, coin_type);
sendPublicKeyHolder = mZKMS.getSendPublicKeyWithIdx(unique_id, coin_type, keyIdx);
receivePublicKeyHolder = mZKMS.getReceivePublicKey(unique_id, coin_type);
receivePublicKeyHolder = mZKMS.getReceivePublicKeyWithIdx(unique_id, coin_type, keyIdx);To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
ZKMS can output xPub keys by BIP44 format.
PublicKeyHolder accountxPubKey = mZKMS.getAccountExtPublicKey(long unique_id, int purpose, int coinType, int account); // BIP44: m/purpose'/coin'/account'
PublicKeyHolder bipxPubKey = mZKMS.getBipExtPublicKey(long unique_id, int purpose, int coinType, int account, int change, int index); // BIP44: m/purpose'/coin'/account/change/index'To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
Wallet apps can use this function to transfer crytocurrency to other account addresses. Users are prompted for their passcode before executing the sign operation. Note: Signing operation will not upload the transaction on chains. Your app must upload it on its own.
With the seed and public key, you can sign transactions as appropriate for your coin type. To sign a transaction, you will need to pass data in the JSON format - including all raw transaction data for the signTransaction function. Signed raw transaction data bytes will be returned by the byteArrayHolderParcel parameter.
int result = mZKMS.signTransaction(unique_id, coin_type, rates, strJson, byteArrayHolderParcel);
// a byte array holder to receive the transaction data
public class ByteArrayHolder {
private static final int DEFAULT_ARRAY_SIZE = 2*1024; // 2KB
public byte[] byteArray;
public long receivedLength;
public ByteArrayHolder() {
byteArray = new byte[DEFAULT_ARRAY_SIZE];
receivedLength = 0;
}
}To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
JSON field definitions are set by each coin type. In case of Bitcoin, JSON format is as follows:
{
"tx_version": "01", // Bitcoin=1
"tx_inputs_count": "01",
"tx_inputs": [
{
"path": "m/44'/0'/0'/0/0", // key path
"tx_id": "9c6700b994e811bc6c4ca6c83a3776fafa4f720f06a2240d3efb451791aa7b8b", // Last transaction Hash
"tx_index": "00",
"scriptSig": "4104e0bf225f8998c7e3dc99899ce2f08d87969ee1bdc0f0759941134f375fd1e8eecba4db44e3f76dce7fd16262c2ca9e93628eafde3d5a6ffa99ae13e74bbc54f6ac",
"sequence": "FEFFFFFF",
"amount": "80841e" // ex:Little-Endian(0.02*100000000)=80841e
}
],
"tx_outputs_count": "01",
"tx_outputs": [
{
"amount": "40420f", // ex:Little-Endian(0.01*100000000)=40420f
"address": "3P14159f73E4gFr7JterCCQh9QjiTjiZrG"
}
],
"tx_changes_count": "01",
"tx_changes": [
{
"path": "m/44'/0'/0'/0/0",
"amount": "d63d0f" // ex:Little-Endian(0.00099887*100000000)=d63d0f
}
],
"lock_time": "0"
}The Transaction Fee will be calculated automatically by the formula as follows:
Fee = tx_inputs.amount - tx_outputs.amount - tx_changes.amount
A. BitCoin:
// A bitcoin JSON sample
{
"tx_version": "01",
"tx_inputs_count": "01",
"tx_inputs": [
{
"path": "m/44'/0'/0'/0/0",
"tx_id": "9c6700b994e811bc6c4ca6c83a3776fafa4f720f06a2240d3efb451791aa7b8b",
"tx_index": "00",
"scriptSig": "4104e0bf225f8998c7e3dc99899ce2f08d87969ee1bdc0f0759941134f375fd1e8eecba4db44e3f76dce7fd16262c2ca9e93628eafde3d5a6ffa99ae13e74bbc54f6ac",
"sequence": "ffffffff",
"amount": "e86f7932"
}
],
"tx_outputs_count": "01",
"tx_outputs": [
{
"amount": "48bc4631",
"address": "3P14159f73E4gFr7JterCCQh9QjiTjiZrG"
}
],
"tx_changes_count": "01",
"tx_changes": [
{
"path": "m/44'/0'/0'/0/0",
"amount": "002d3101"
}
],
"lock_time": "1234"
}B. Litecoin:
// A litecoin JSON sample
{
"tx_version": "01",
"tx_inputs_count": "01",
"tx_inputs": [
{
"path": "m/44'/02'/0'/0/0",
"tx_id": "9c6700b994e811bc6c4ca6c83a3776fafa4f720f06a2240d3efb451791aa7b8b",
"tx_index": "00",
"scriptSig": "76a914feb5f43851477b22f68db0523351c4debbc67a7588ac",
"sequence": "ffffffff",
"amount": "e86f7932"
}
],
"tx_outputs_count": "01",
"tx_outputs": [
{
"amount": "48bc4631",
"address": "n4jjuARyw1nnHhta1fR5khPFS5i1BDakX6"
}
],
"tx_changes_count": "01",
"tx_changes": [
{
"path": "m/44'/02'/0'/0/0",
"amount": "002d3101"
}
],
"lock_time": "00"
}
C. Ethereum:
// A ethereum JSON sample
{
"path": "m/44'/60'/0'/0/0",
"tx": {
"nonce": "01",
"gas_price": "09184e72a000",
"gas_limit": "493e0",
"to": "d8A7297522A2e30bE59f66e8CB2B06c89a50490c",
"value": "38d7ea4c68000",
"erc_flag": "0",
"data": "",
"chain_id": "04"
}
}
// A Ethereum ERC20 JSON sample
{
"path": "m/44'/60'/0'/0/0",
"tx": {
"nonce": "04",
"gas_price": "0165a0bc00",
"gas_limit": "928a",
"to": "B8c77482e45F1F44dE1745F52C74426C631bDD52",
"value": "",
"erc_flag": "20",
"data": "a9059cbb00000000000000000000000058a61a7144c8c7545794447a9a3e9a3d56066c200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001bc16d674ec80000",
"chain_id": "04"
}
}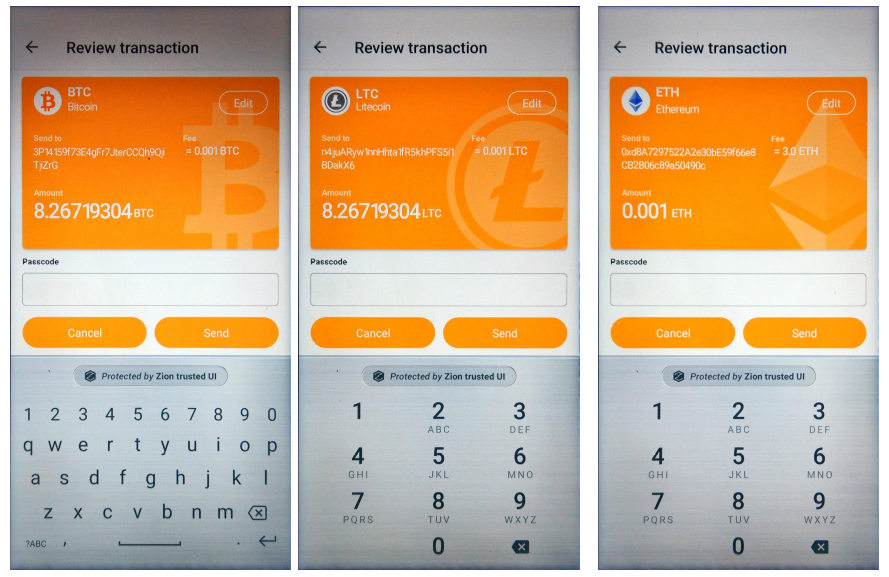
Figure 8. Trusted UI for signing BTC/LTC/ETH transaction
To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
Signing transaction for Ethereum ERC20:
For Ethereum ERC20 Trusted UI, the parameters of extra tag can be used for customizing the icons, background color, token name, full display name of token, and decimal amount for the Trusted UI. For example, if I assign my parameters in the extra tag as following JSON data format, and then the secure UI will show UI as these parameters.
{
"path":"m\/44'\/60'\/0'\/0\/0",
"tx":{
"nonce":"5",
"gas_price":"12a05f200",
"gas_limit":"5d82",
"to":"0d8775f648430679a709e98d2b0cb6250d2887ef",
"value":"",
"erc_flag":"20",
"data":"a9059cbb000000000000000000000000c24c375a77baf82750c46f1c76c809d5ad4c6769000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000003db72f26a08530000",
"chain_id":"1"
},
"currency":"USD",
"extra": {
"erc20_icon": "**<144*144 png image file raw data converted as HEX string>**",
"erc20_symbol": "HAK",
"erc20_displayname": "HAWK_TOKEN",
"erc20_decimal": "18"
}
}The parameters of extra tag are defined as follows:
erc20_icon: ERC20 Token icon binary data, the icon is png file format and don’t exceed 144 X 144 pixels, please convert to HEX String before put on json field.
erc20_symbol: ERC20 token name
erc20_displayname: full display name of ERC20 token
erc20_decimal: A decimal length for display (each token specifies a decimal length, the correct decimal length of the target token is required)
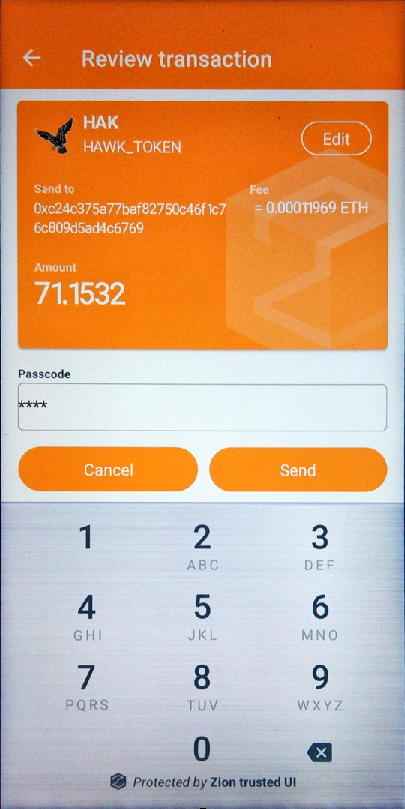
Figure 9. Signing a transaction in the Trusted UI with an ERC20 extra tag
For Ethereum ERC20 smart contract methods, ZKMS supports the ERC20 transfer function with data parsing. For other functions, the trusted UI will show an unknown function with raw HEX data for user confirmation.
contract ERC20Interface {
function totalSupply() public view returns (uint);
function balanceOf(address tokenOwner) public view returns (uint balance);
function allowance(address tokenOwner, address spender) public view returns (uint remaining);
function transfer(address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success); **// ZKMS support it now.**
function approve(address spender, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
function transferFrom(address from, address to, uint tokens) public returns (bool success);
event Transfer(address indexed from, address indexed to, uint tokens);
event Approval(address indexed tokenOwner, address indexed spender, uint tokens);
}Signing transaction for Ethereum ERC721:
For Ethereum ERC721, the parameters of extra tag can be used to customize the icon and the full name of ERC721 token for secure UI. Unlike ERC20, the erc_flag and erc20_symbol for the ERC721 tag can’t be used for customizing the Trusted UI. For the Trusted UI display, erc_flag must be “721” and erc20_symbol must be "ERC-721". Assigning the parameters in the extra tag like following example JSON data format will cause the Trusted UI to be shown with the specified parameters.
{
"path": "m/44'/60'/0'/0/0",
"tx" : {
"nonce": "04",
"gas_price": "0165a0bc00",
"gas_limit": "493e0",
"to": "B8c77482e45F1F44dE1745F52C74426C631bDD52",
"value": "",
"erc_flag": "721",
"data": "a9059cbb00000000000000000000000058a61a7144c8c7545794447a9a3e9a3d56066c200000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001bc16d674ec80000",
"chain_id": "03"
}
}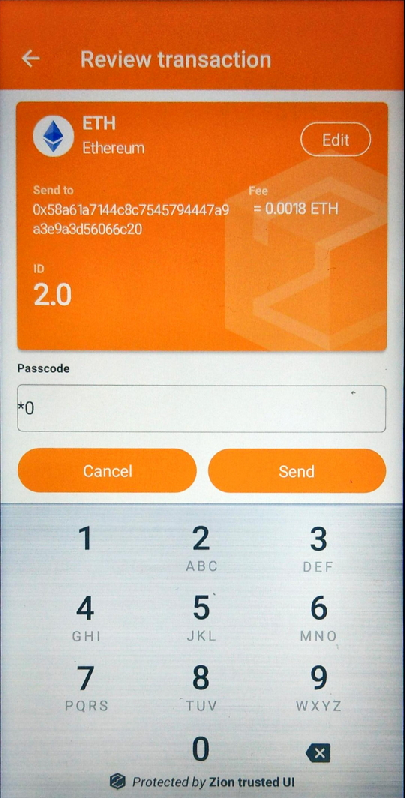
Figure 10. Trusted UI for signing a ERC721 transaction
For Ethereum ERC721 smart contract methods, ZKMS only supports the ERC20 transfer method now. For data formats not supported by ZKMS, the Trusted UI signature screen shows an unknown method with raw HEX data for the user to confirm.
If the user wants to create a new wallet, a wallet app needs to clear current wallet first. Clearing the current wallet completely is necessary for its continued security. To that end, the clearSeed function will clear all secure data related to the current wallet.
int result = mZKMS.clearSeed(unique_id);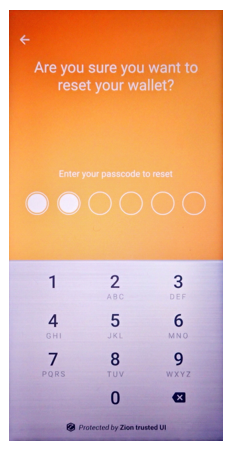
Figure 11. Show the security UI for clear an existing seed
To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
When you create a new wallet or restore an existing wallet, you will be asked to create the passcode to protect seed access. If it is decided that a passcode is inadequate or otherwise needs to be changed, the following function can be used:
int result = mZKMS.changePIN(unique_id);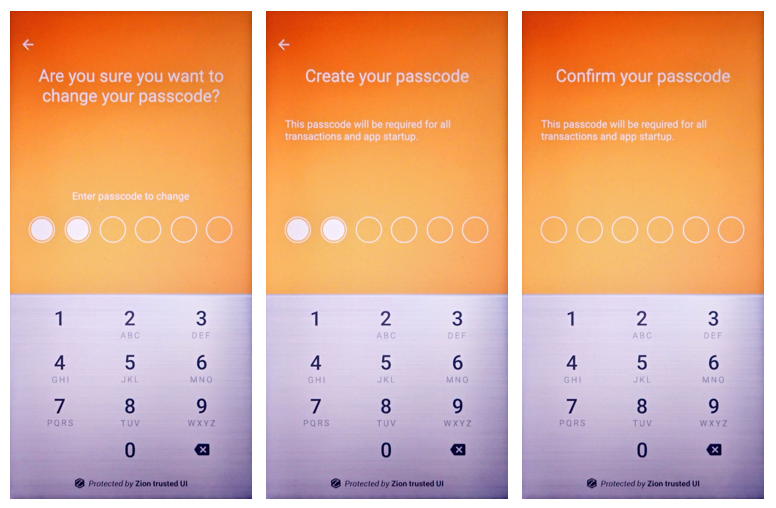
Figure 12. Trusted UI prompting the user to change their passcode
To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
Any passcode confirmation action will also show the Trusted UI prompting for a passcode.
int result = mZKMS.confirmPIN(unique_id, resId = 3);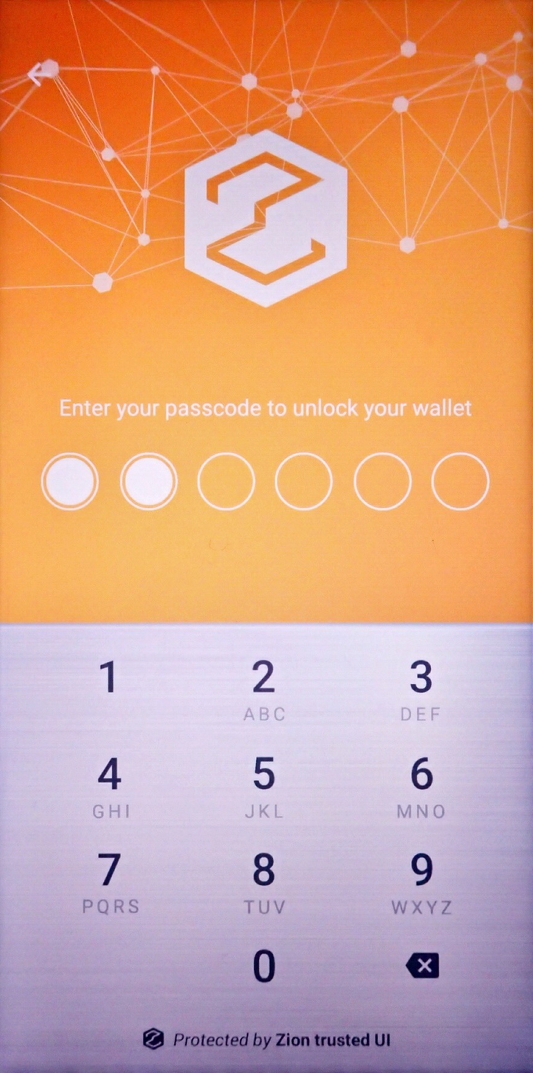
Figure 13. Trusted UI prompting the user for passcode confirmation
To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
The unregister function releases the unique id, and it will also release seed data stored by ZKMS. If this function is called, the seed data will also be cleared.
int result = mZKMS.unregister(wallet_name, sha256, unique_id);To prevent the blocked Trust Zone UI thread, the developer must call this API in a background thread.
This function releases all resources which allocated by ZKMS, and no future ZKMS functions will be executed.
nt result = mZKMS.deinit(mPID);Error codes are delivered by return values, and are handled by ZKMS in three different types. Type1 refers to a normal behavior, like E_TEEKM_UI_BACK, E_TEEKM_UI_CANCEL and so on, and can be safely ignored. Type2 is a silent error, and will not show any UI prompt by ZKMS, and apps are required to handle this without a ZKMS error prompt, such as E_TEEKM_SEED_NOT_FOUND, E_TEEKM_TIME_TIMEOUT, E_SDK_ROM_SERVICE_TOO_OLD, E_SDK_ROM_TZAPI_TOO_OLD and so on. If the error code is neither type1 nor type2, ZKMS will handle it by through the default error dialog on the screen.
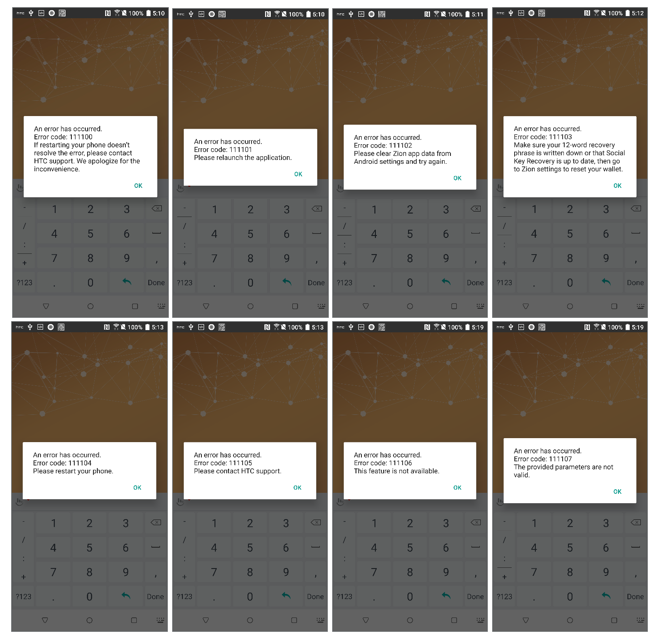
Figure 14. Default error dialogs if an error detected by ZKMS
All error codes are defined in RESULT.java and are named accordingly.
ZKMS supports message signing. If message contains a non-ASCII character, the Trusted UI will show hex data instead of a readable string.
int result = mZKMS.signMessage(unique_id, coin_type, strJson, ByteArrayHolderParcel);Below is a sample Ethereum JSON message format for signing. The data fields in JSON only support ASCII strings. In the sample JSON data field, “48656c6c6f” is HEX string data of “Hello”. In other words, you must convert your ASCII string to HEX string data first, then put it into the data field for composing the input strJson parameter. The version field is implemented by EIP191 and must be set to 0x45.
{
"path": "m/44'/60'/0'/0/0",
"message" : {
"version": "45",
"data": "48656c6c6f"
}
}Message data in JSON should contain version and data tags.
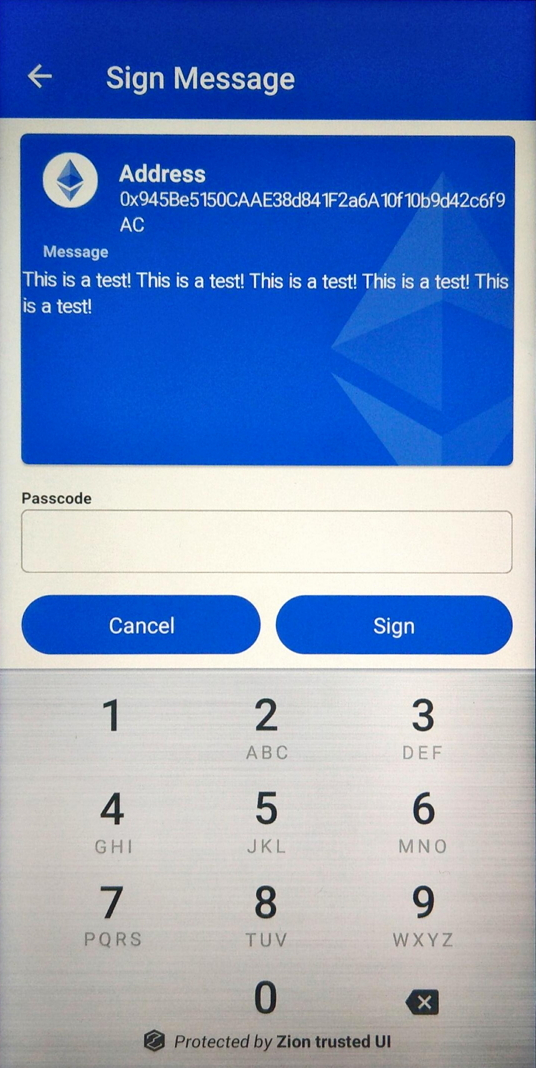
Figure 15. Trusted UI message signing confirmation
This is a simple demo for API usage.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private static Activity sActivity;
private IZKMS mZKMS;
public int mPID;
int intValue = RESULT.UNKNOWN;
String mZKMS_version;
String mApi_Version;
long uid;
String wallet_name = "MyWallet";
String sha256 = "123456789";
Handler mHandler;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
sActivity = this;
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void getPermissions(View v){ // 1. get ACCESS_ZION permission
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(sActivity, TargetActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
startActivity(intent);
}
ZKMSConnection mZKMSConnection = new ZKMSConnection();
private class ZKMSConnection implements ServiceConnection
{
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder binder)
{
Log.i(TAG,"onServiceConnected");
try
{
mZKMS = IZKMS.Stub.asInterface(binder);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName componentName)
{
Log.i(TAG,"onServiceDisconnected");
}
}
public void bindService(View v){ // 2. bind ZKMS Service
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.htc.wallet.server.ZKMS");
intent.setPackage("com.htc.wallet");
boolean bBind = MainActivity.this.bindService(intent, mZKMSConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
if(bBind == true)
Log.d(TAG, "bind ZKMS success!");
else
Log.d(TAG, "ROM not support ZKMS.");
}
public void demoAPIs(View v){ // 3. call ZKMS APIs in background thread
mHandler = new Handler();
mHandler.post(apiRunnable);
}
final Runnable apiRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if ((ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(sActivity, "com.htc.wallet.permission.ACCESS_ZION") != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) ||
(mZKMS == null)) {
Toast.makeText(sActivity,"No ACCESS_ZION permission or bind ZKMS", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return;
}
// 3-1. init
mPID = android.os.Process.myPid();
mZKMS_version = com.htc.wallet.server.BuildConfig.VERSION_NAME;
intValue = mZKMS.init(mPID, com.htc.wallet.server.BuildConfig.VERSION_NAME);
// 3-2. getApiVersion
mApi_Version = mZKMS.getApiVersion();
// 3-3. register
uid = mZKMS.register(wallet_name, sha256);
// 3-4. call ZKMS APIs, ex: create Seed
intValue = mZKMS.createSeed(uid);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}