The LinuxServer.io team brings you another container release featuring easy user mapping and community support. Find us for support at:
- forum.linuxserver.io
- IRC on freenode at
#linuxserver.io - Podcast covers everything to do with getting the most from your Linux Server plus a focus on all things Docker and containerisation!
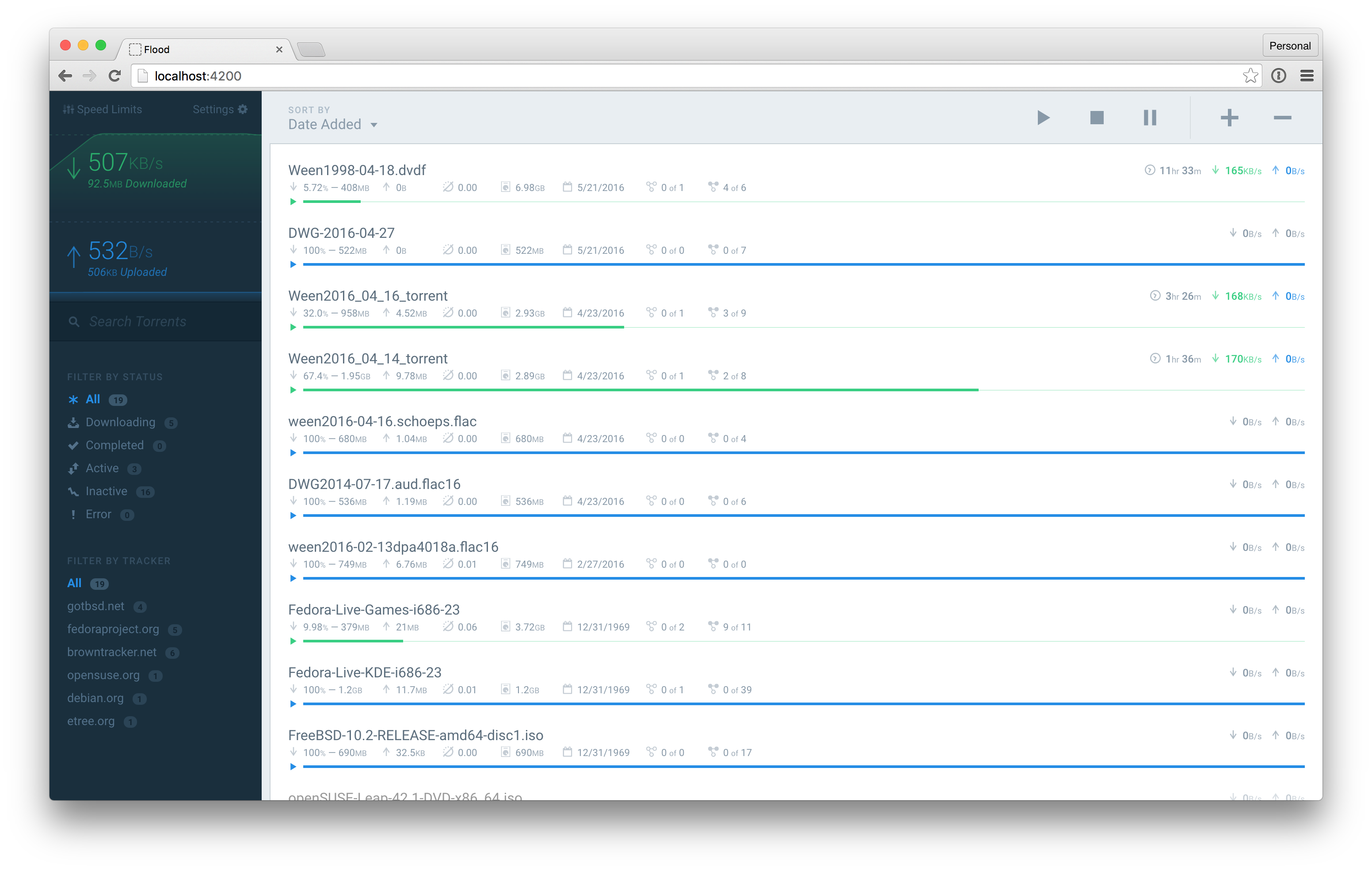
Flood, a modern web UI for rTorrent with a Node.js backend and React frontend.
docker create \
--name=flood \
-v <path to data>:/config \
-v <path to downloads>:/downloads \
-e PGID=<gid> -e PUID=<uid> \
-p 3000:3000 \
linuxserver/flood
The parameters are split into two halves, separated by a colon, the left hand side representing the host and the right the container side. For example with a port -p external:internal - what this shows is the port mapping from internal to external of the container. So -p 8080:80 would expose port 80 from inside the container to be accessible from the host's IP on port 8080 http://192.168.x.x:8080 would show you what's running INSIDE the container on port 80.
-p 3000- the port(s)-v /config- where flood should store it's config files-v /downloads- path to your downloads folder-e PGIDfor GroupID - see below for explanation-e PUIDfor UserID - see below for explanation
It is based on alpine linux with s6 overlay, for shell access whilst the container is running do docker exec -it flood /bin/bash.
Sometimes when using data volumes (-v flags) permissions issues can arise between the host OS and the container. We avoid this issue by allowing you to specify the user PUID and group PGID. Ensure the data volume directory on the host is owned by the same user you specify and it will "just work" ™.
In this instance PUID=1001 and PGID=1001. To find yours use id user as below:
$ id <dockeruser>
uid=1001(dockeruser) gid=1001(dockergroup) groups=1001(dockergroup)
-
Shell access whilst the container is running:
docker exec -it flood /bin/bash -
To monitor the logs of the container in realtime:
docker logs -f flood -
container version number
docker inspect -f '{{ index .Config.Labels "build_version" }}' flood
- image version number
docker inspect -f '{{ index .Config.Labels "build_version" }}' linuxserver/flood
- dd.MM.yy: Initial Release.