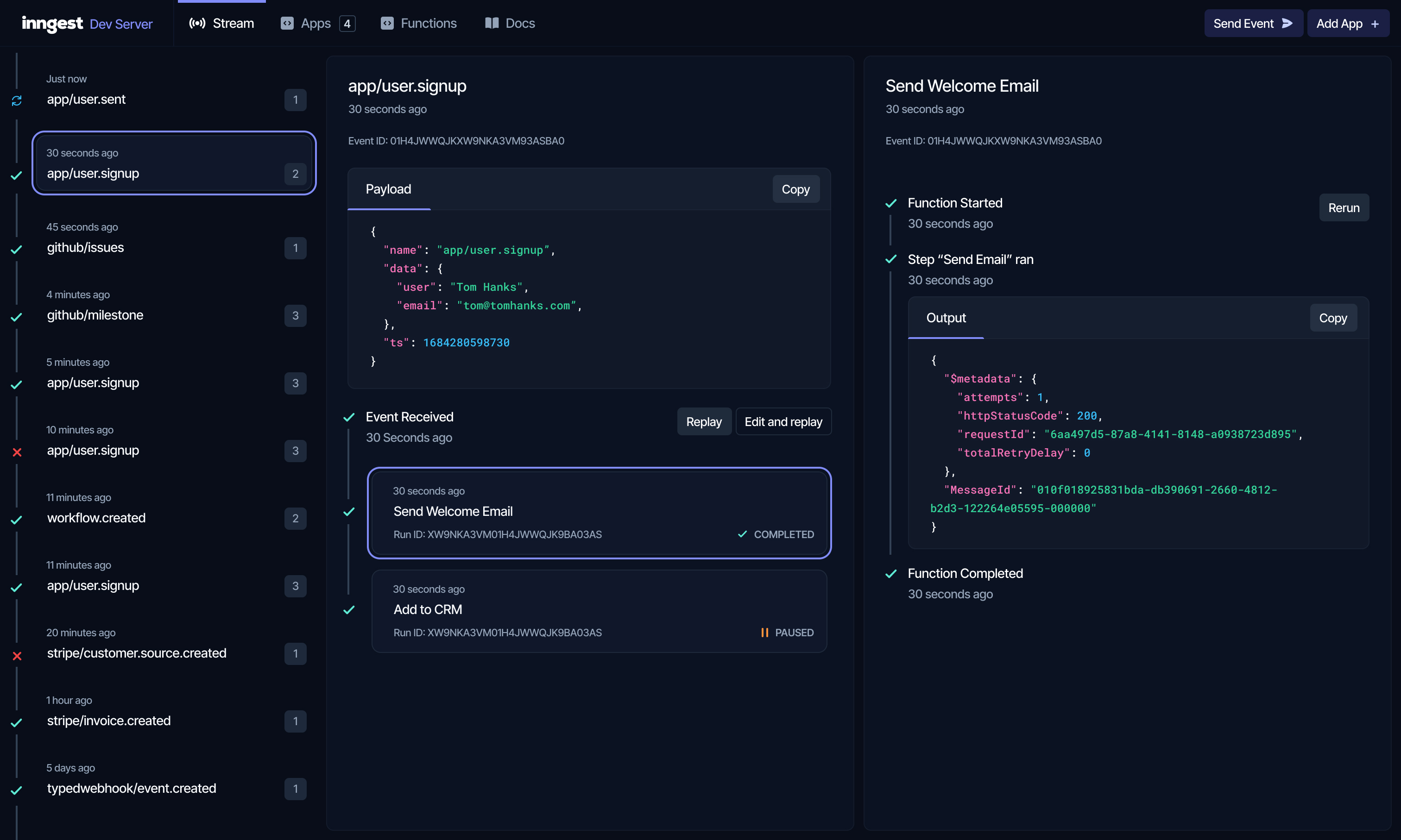
Inngest is the developer platform for easily building reliable workflows with zero infrastructure.
- Write background jobs and workflows in your existing codebase using the Inngest SDK
- Run the open source Inngest Dev Server on your machine for a complete local development experience, with production parity.
- The Inngest Platform invokes your code wherever you host it, via HTTPS. Deploy to your existing setup, and deliver products faster without managing infrastructure.
npx inngest-cli@latest dev
Inngest makes it easy to develop serverless workflows in your existing codebase, without any new infrastructure. Inngest Functions are triggered via events — decoupling your code within your application.
- You define your Inngest functions using the Inngest SDK and serve them through a simple API endpoint.
- Inngest automatically invokes your functions via HTTPS whenever you send events from your application.
Inngest abstracts the complex parts of building a robust, reliable, and scalable architecture away from you, so you can focus on writing amazing code and building applications for your users.
- Run your code anywhere - We call you via HTTPS so you can deploy your code to serverless, servers or the edge.
- Zero-infrastructure required - No queues or workers to configure or manage — just write code and Inngest does the rest.
- Build complex workflows with simple primitives - Our SDK provides easy to learn
steptools likerun,sleep,sleepUntil, andwaitForEventthat you can combine using code and patterns that you're used to create complex and robust workflows.
Read more about our vision and why this Inngest exists
👉 Read the full quick start guide here
- NPM install our SDK for your typescript project:
npm install inngest - Run the Inngest dev server:
npx inngest-cli@latest dev(This repo's CLI) - Integrate Inngest with your framework in one line via the
serve()handler - Write and run functions in your existing framework or project
Here's an example:
import { Inngest } from "inngest";
const inngest = new Inngest({ name: "My App" });
// This function will be invoked by Inngest via HTTP any time the "app/user.signup"
// event is sent to to Inngest
export default inngest.createFunction(
{ name: "User onboarding communication" },
{ event: "app/user.signup" },
async ({ event, step }) => {
await step.run("Send welcome email", async () => {
await sendEmail({
email: event.data.email,
template: "welcome",
});
});
}
);
// Elsewhere in your code (e.g. in your sign up handler):
inngest.send({
name: "app/user.signup",
data: {
email: "test@example.com",
},
});That's it - your function is set up!
Fundamentally, there are two core pieces to Inngest: events and functions. Functions have several subcomponents for managing complex functionality (eg. steps, edges, triggers), but high level an event triggers a function, much like you schedule a job via an RPC call to a queue. Except, in Inngest, functions are declarative. They specify which events they react to, their schedules and delays, and the steps in their sequence.
Inngest’s architecture is made up of 6 core components:
- Event API receives events from clients through a simple POST request, pushing them to the message queue.
- Event Stream acts as a buffer between the API and the Runner, buffering incoming messages to ensure QoS before passing messages to be executed.
- A Runner coordinates the execution of functions and a specific run’s State. When a new function execution is required, this schedules running the function’s steps from the trigger via the executor. Upon each step’s completion, this schedules execution of subsequent steps via iterating through the function’s Edges.
- Executor manages executing the individual steps of a function, via drivers for each step’s runtime. It loads the specific code to execute via the DataStore. It also interfaces over the State store to save action data as each finishes or fails.
- Drivers run the specific action code for a step, e.g. within Docker or WASM. This allows us to support a variety of runtimes.
- State stores data about events and given function runs, including the outputs and errors of individual actions, and what’s enqueued for the future.
- DataStore stores persisted system data including Functions and Actions version metadata.
- Core API is the main interface for writing to the DataStore. The CLI uses this to deploy new functions and manage other key resources.
And, in this CLI:
- The DevServer combines all the components and basic drivers for each into a single system which reads all functions from your application running on your machine, handles incoming events via the API and executes functions, all returning a readable output to the developer.
For specific information on how the DevServer works and how it compares to production read this doc.
- Join our online community for support, to give us feedback, or chat with us.
- Post a question or idea to our GitHub discussion board
- Read the documentation
- Explore our public roadmap
- Follow us on Twitter
- Join our mailing list for release notes and project updates
We’re excited to embrace the community! We’re happy for any and all contributions, whether they’re feature requests, ideas, bug reports, or PRs. While we’re open source, we don’t have expectations that people do our work for us — so any contributions are indeed very much appreciated. Feel free to hack on anything and submit a PR.
Check out our contributing guide to get started.