Hackathon team: Xinlian Liu (lead), Yanling Liu (lead), Samar Samarjeet (platform), Chun-Hung Lin (deployment)
High quality delineation of important features is a critical component in biomedical image interpretation for accurate diagnosis and/or assessment of a disease. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) based Deep Learning (DL) techniques have been proven highly successful in image classification and segmentation tasks by utilizing large number of training images, potentially promising higher throughput and more consistent results in biomedical image interpretation. Computerized tools enhanced by DL are rapidly proving to be a state-of-the-art solution toward improved accuracy in biomedical image interpretation. Furthermore, researchers have reported successful training of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) models to generate synthetic training images as potential solutions to solve the scarcity of training sets.
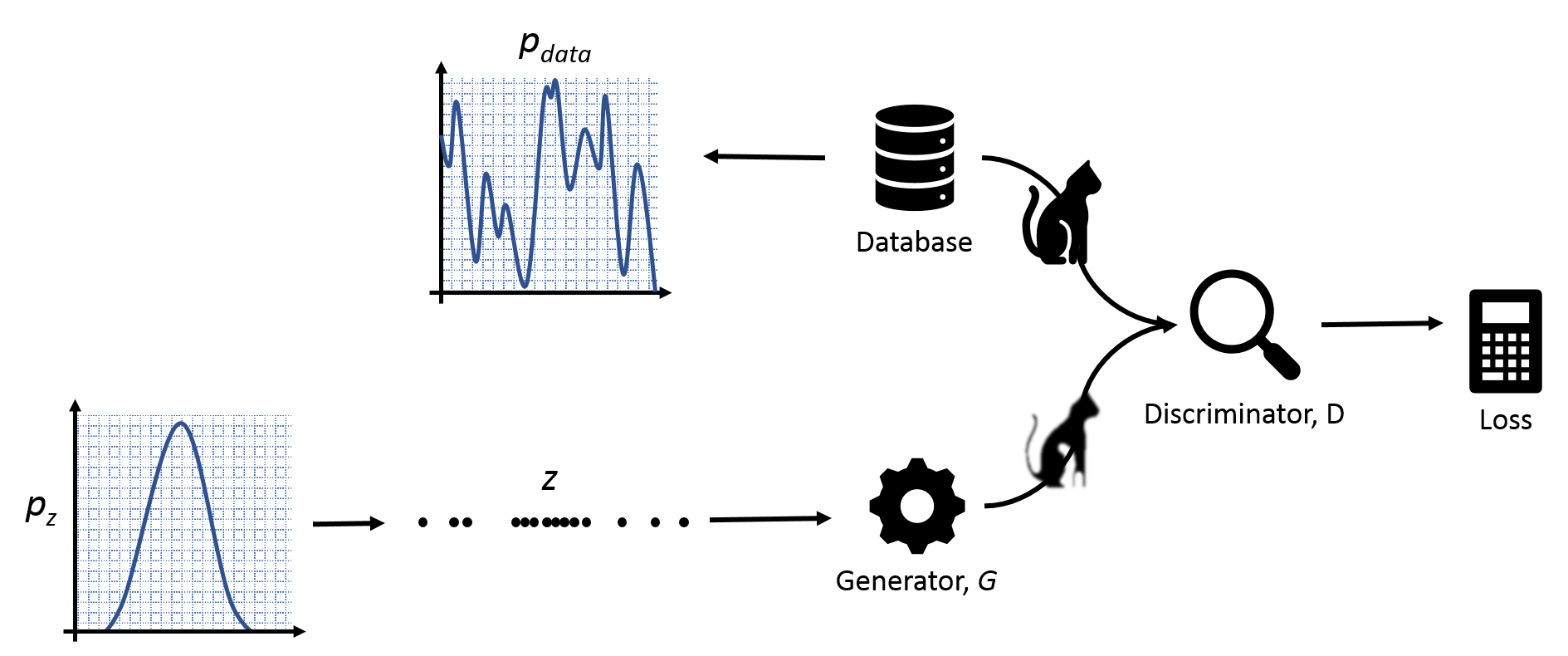
The following diagram shows the basic concept of GAN network. In the picture, the generator tries to produce synthetic images to fool the discriminator where as the discriminator tries to tell synthetic images from real images.
Training a CNN for Deep Learning typically requires a large amount of labeled training image data, which remains a challenge in the biomedical domain because of the expense of expert annotation. Although researchers have reported successful training of Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) models to generate synthetic images as a potential solution to solve the training set bottleneck, training CNNs and GANs in a timely manner could require demanding programming experience and skill sets from domain experts. Our aim is to provide end users a streamlined workflow to facilitate rapid utilization of GAN networks to produce synthetic radiology images for DL training.
We firstly ported a GAN network implementation to tensorFlow for wider and easier adoption. Secondly we wrapped the GAN implementation as a python module such that users can start GAN training for synthetic training in a few lines of code. Finally we containerized the workflow such that users are freed from tedious software environment setup just in order to start DL training.
GAN network architecture, figures, etc.
-
Python ‘regan’ library
-
Docker version
-
Instructions to build, install, and use the ‘regan’ library
-
Instructions to use the docker version (the python library warped in the docker container for easier usage, for example, the container has all necessary libraries so users don’t have to setup environments on their own computers (they only need a GPU and video card driver)
This repository reflects our efforts at the NCBI Hackathon (Bethesda, MD) 10-12 Sep, 2018.
- Xinlian Liu, FNLCR
- Yanling Liu, FNLCR
- Samar Samarjeet, NIH
- Chun-Hung Lin, USDA