An Implementation of ProcessPLS in Python
Implementation by Sin Yong Teng. Radboud University Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
In this code implementation, the sklearn syntax is used. Furthermore, the ProcessPLS algorithm has been made to be represented in directed graphs data structure. This allows for more flexibility to be used with graph theory routines.
pip install processPLSfrom processPLS.model import *
from processPLS.datasets import *
X,Y,matrix=ValdeLoirData() #Get the data convinientlydf=pd.read_csv(r'.\ValdeLoirData.csv')
df=df.drop(columns=df.columns[0])
smell_at_rest=df.iloc[:,:5]
view=df.iloc[:,5:8]
smell_after_shaking=df.iloc[:,8:18]
tasting=df.iloc[:,18:27]
global_quality=df.iloc[:,27]
X={
'Smell at Rest':smell_at_rest,
"View":view,
"Smell after Shaking":smell_after_shaking,
"Tasting":tasting,
}
Y={"Global Quality":global_quality}
matrix = pd.DataFrame(
[
[0,0,0,0,0],
[1,0,0,0,0],
[1,1,0,0,0],
[1,1,1,0,0],
[1,1,1,1,0],
],
index=list(X.keys())+list(Y.keys()),
columns=list(X.keys())+list(Y.keys())
)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model = ProcessPLS()
model.fit(X,Y,matrix)
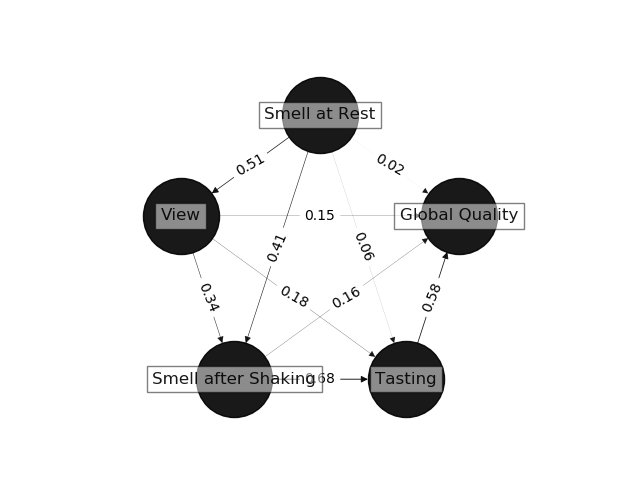
model.plot()
plt.show()Process_PLS(cv=RepeatedKFold(n_splits=5,n_repeats=2,random_state=999),scoring='neg_mean_squared_error',max_lv=30,overwrite_lv=False,inner_forced_lv=None,outer_forced_lv=None,name=None)
'''
This function sets up the processPLS model.
cv= cross validation method (follows sklearn syntax)
scoring= loss function/ scoring function (follows sklearn syntax)
max_lv= maximum numbers of latent variable (lv) for all SIMPLS models within ProcessPLS
overwrite_LV= (True/False) A boolean to set whether inner_forced_lv and outer_forced_lv should be used instead of automatically selecting latent variables
inner_forced_lv= (dict) a specific key value combination of number of LVs to forced into the inner model. Argument overwrite_LV must be set to True for this to be used. Example input:
inner_forced_lv={
'Smell at Rest':None,
"View":3,
"Smell after Shaking":6,
"Tasting":8,
"Global Quality":13
}
inner_forced_lv= (dict) a specific key value combination of number of LVs to forced into the outer model. Argument overwrite_LV must be set to True for this to be used. Example input:
outer_forced_lv={
'Smell at Rest':3,
"View":3,
"Smell after Shaking":2,
"Tasting":5,
"Global Quality":3
}
name: (string) Optional name of model.
'''
ValdeLoirData(original=False)
'''
This function gets the data for Valde Loir Dataset
original==False: The function returns X (dataframe in dict), Y (dataframe dict), and matrix (dataframe). matrix is the adjacency matrix for the graph connections.
original==True: The function returns the raw data (dataframe) with both X and Y combined within
'''y_pred= model.predict(Xnew)Colab Example Here
This implementation provides exactly the same output as the MATLAB version of ProcessPLS.
van Kollenburg, G., Bouman, R., Offermans, T., Gerretzen, J., Buydens, L., van Manen, H.J. and Jansen, J., 2021. Process PLS: Incorporating substantive knowledge into the predictive modelling of multiblock, multistep, multidimensional and multicollinear process data. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 154, p.107466.
For MATLAB Implementation, see this repository written by Tim Offermans. https://gitlab.science.ru.nl/toffermans/matlab-process-pls/-/tree/main/
S.Y. Teng. (2022). tsyet12/ProcessPLS:An Implementation of ProcessPLS in Python, Zenodo Release (zenodo). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7074754