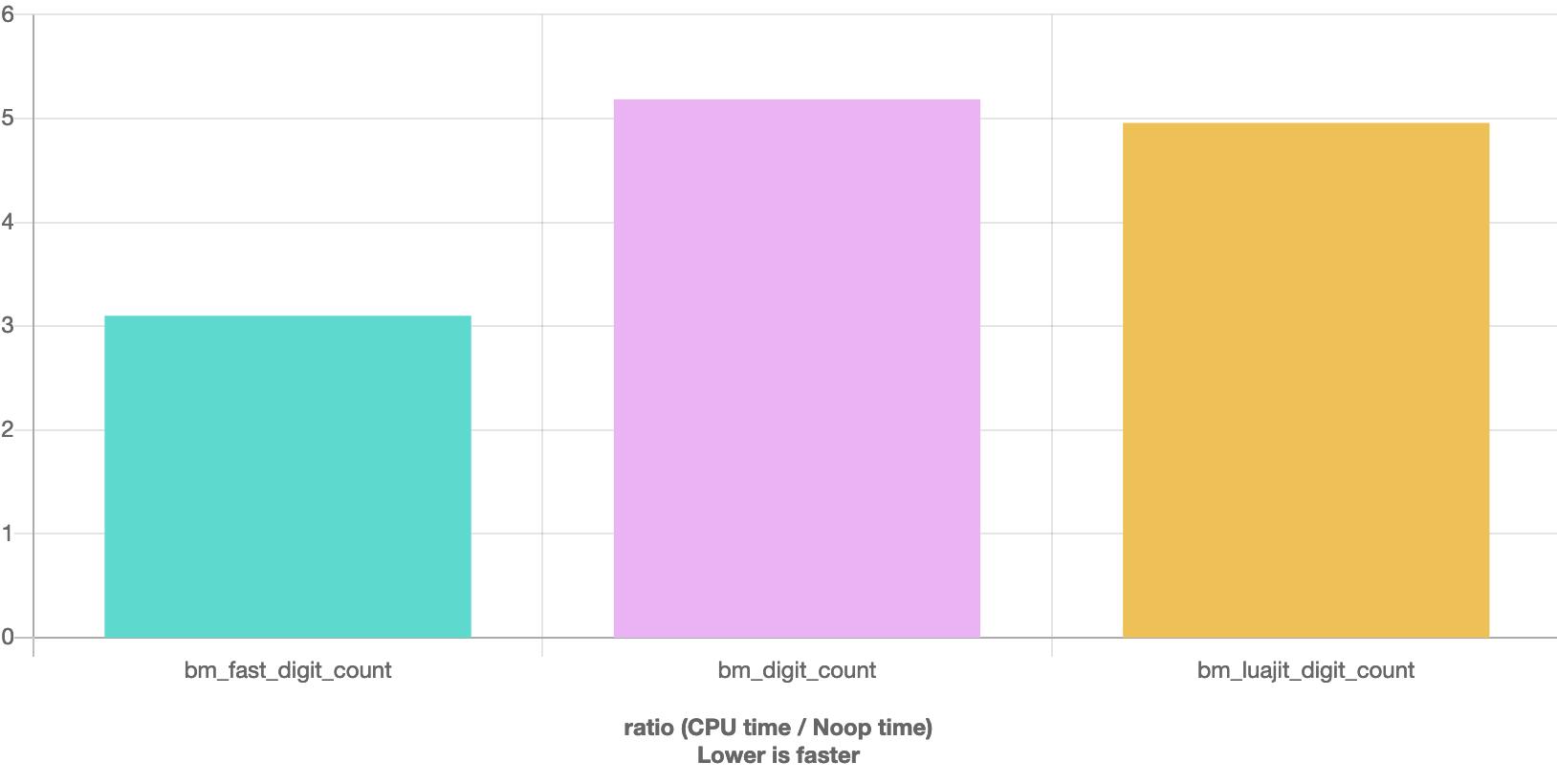| layout | title |
|---|---|
post |
第十五期 |
从reddit/hackernews/lobsters/meetingcpp摘抄一些c++动态。
每周更新
欢迎投稿,推荐或自荐文章/软件/资源等,请提交 issue
- Computing the number of digits of an integer quickly
- Computing the number of digits of an integer even faster
Daniel Lemire 整的新活,如何更快的计算一个数有几位,正常的算法就是除10
从数学角度就是取十的对数,这里考虑二进制,log10(X) = log2(X) / log2(10) 首先,不能用除,效率低,考虑乘和位移
log2(X)简单
int int_log2(uint32_t x) { return 31 - __builtin_clz(x|1); }然后考虑 log2(10) 简单估算是乘9除32 除以32可以改成位移
static uint32_t table[] = {9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999,
999999, 9999999, 99999999, 999999999};
int y = (9 * int_log2(x)) >> 5;
y += x > table[y];
return y + 1;luajit用到了类似的技巧 这里比乘9除32更精密一些
/* min(2^32-1, 10^e-1) for e in range 0 through 10 */
static uint32_t ndigits_dec_threshold[] = {
0, 9U, 99U, 999U, 9999U, 99999U, 999999U,
9999999U, 99999999U, 999999999U, 0xffffffffU
};
/* Compute the number of digits in the decimal representation of x. */
static MSize ndigits_dec(uint32_t x)
{
MSize t = ((lj_fls(x | 1) * 77) >> 8) + 1; /* 2^8/77 is roughly log2(10) */
return t + (x > ndigits_dec_threshold[t]);
}更进一步,ceil(log10(2j)) * 232 + 232 – 10ceil(log10(2j)) 考虑这种算法,生成的table又省了一些
int fast_digit_count(uint32_t x) {
static uint64_t table[] = {
4294967296, 8589934582, 8589934582, 8589934582, 12884901788,
12884901788, 12884901788, 17179868184, 17179868184, 17179868184,
21474826480, 21474826480, 21474826480, 21474826480, 25769703776,
25769703776, 25769703776, 30063771072, 30063771072, 30063771072,
34349738368, 34349738368, 34349738368, 34349738368, 38554705664,
38554705664, 38554705664, 41949672960, 41949672960, 41949672960,
42949672960, 42949672960};
return (x + table[int_log2(x)]) >> 32;
}table的数用脚本找的
最后,给个benchmark
这三个版本明显第三个要快一些
回顾SFINAE的几种写法,匹配失败不是错误,核心是匹配
基本写法
#include <iostream>
class MyType {
public:
using type = char;
};
class MyOtherType {
public:
using other_type = int;
};
template<typename T>
void foo(T bar, typename T::type baz)
{
std::cout << "void foo(T bar, typename T::type baz) is called\n";
}
template<typename T>
void foo(T bar, typename T::other_type baz)
{
std::cout << "void foo(T bar, typename T::other_type baz) is called\n";
}
int main()
{
MyType m;
MyOtherType mo;
foo(m, 'a');
foo(mo, 42);
// error: no matching function for call to 'foo(MyOtherType&, const char [3])'
// foo(mo, "42");
}
/*
void foo(T bar, typename T::type baz) is called
void foo(T bar, typename T::other_type baz) is called
*/decltype std::declval
#include <iostream>
class MyType {
public:
using type = char;
};
class MyOtherType {
public:
using other_type = int;
};
template<typename T>
decltype(typename T::type(), void()) foo(T bar)
{
std::cout << "decltype(typename T::type(), void()) foo(T bar) is called\n";
}
template<typename T>
decltype(typename T::other_type(), void()) foo(T bar)
{
std::cout << "decltype(typename T::other_type(), void()) is called\n";
}
int main()
{
MyType m;
MyOtherType mo;
foo(m);
foo(mo);
// error: no matching function for call to 'foo(MyOtherType&, const char [3])'
// foo(mo, "42");
}经典enable_if
template<typename T>
std::enable_if_t<std::is_integral<T>::value, T> f(T t){
//integral version
}
template<typename T>
std::enable_if_t<std::is_floating_point<T>::value, T> f(T t){
//floating point version
}concept
#include <concepts>
template<typename T>
class MyClass {
public:
void f(T x) {
std::cout << "generic\n";
}
void f(T x) requires std::floating_point<T> {
std::cout << "with enable_if\n";
}
};
比较经典的技巧了。
class foo {
private:
int data;
};
template<int foo::*Ptr>
int& get_data(foo& f) {
return f.*Ptr;
}
template<int foo::*Ptr>
struct foo_access {
friend int& get_data(foo& f) {
return f.*Ptr;
}
};
template struct foo_access<&foo::data>;
int& get_data(foo&);
int main() {
foo f{};
get_data(f) = 42; // access private data member
}得益于constexpr/consteval 可以编译时求质数。给了两种求质数的方法
一种常规
// \file compile-time-cpp/is-prime-17-constexpr-func.cc
#include <iostream>
constexpr bool is_prime(int v) {
for (int i = 2; i < v; i++) {
if (v % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
template<int v>
struct IsPrime {
static constexpr bool value = is_prime(v);
};
int main() {
std::cout << 7 << " : " << IsPrime<7>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << 2000 << " : " << IsPrime<2000>::value << std::endl;
std::cout << 2003 << " : " << IsPrime<2003>::value << std::endl;
return 0;
}一种是生成一个数组
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
template<int v>
consteval std::array<int, v + 1> sieve() {
std::array<int, v + 1> arr = {};
for(long long i = 2; i <= v; i++) {
if(arr[i]) {
continue;
}
for(long long j = i * i; j <= v; j+= i) {
arr[j] = 1;
}
}
return arr;
}
int main() {
auto sieve_array = sieve<12345>();
std::cout << 7 << " : " << sieve_array[7] << std::endl;
std::cout << 2000 << " : " << sieve_array[2000]<< std::endl;
std::cout << 2003 << " : " << sieve_array[2003]<< std::endl;
size_t i = 0;
std::cin >> i;
std::cout << sieve_array[i] << std::endl;
return 0;
}- [Compilation speed humps: std::tuple](https://marzer.github.io/md_blog_2021_05_31_compilation_speed_humps_std_tuple.html)
讨论了几种降低tuple编译时间的方法, 主要源头type_element,替代方案,自己实现type_list或者用type_pack_element
#ifdef __has_builtin
#if __has_builtin(__type_pack_element)
#define MZ_HAS_TYPE_PACK_ELEMENT
#endif
#endif
#ifdef MZ_HAS_TYPE_PACK_ELEMENT
template <typename... T, size_t N>
struct type_list_selector<type_list<T...>, N>
{
using type = __type_pack_element<N, T...>;
};
#else
// ... all the previous type_list_selectors ...
#endif小函数inline,但是在组合的函数里,函数的冷热程度不同,可能导致多余的inline
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline void do_thing(int input)
{
// this code is always inlined at the call site
}
void hot_code()
{
// the program spends >80% of its runtime in this function
while (condition) {
...
do_thing(y);
...
}
}
void cool_code()
{
// the program spends <5% of its runtime in this function
...
do_thing(a);
do_thing(b);
do_thing(c);
}
引入__attribute__((flatten)) 让上层来决定内部小函数inline
void do_thing(int input)
{
// this code is not always inlined at the call site
}
__attribute__((flatten)) void hot_code()
{
// the program spends >80% of its runtime in this function
while (condition) {
call_something(); // inlined!
do_thing(y); // inlined!
other_thing(); // also inlined!
}
}
void cool_code()
{
// the program spends <5% of its runtime in this function
...
do_thing(a); // not inlined!
do_thing(b); // not inlined!
do_thing(c); // guess!
}
非常好用
TODO: 看不懂
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/3LsRYnRDSRA" title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>结论是让你的简单类型尽可能简单,std::pair过于复杂
- https://github.com/Tencent/flare 腾讯出品的一个业务库,嵌入了各种常用客户端/rpc等等
- https://github.com/joaquintides/transrangers 更快的range
- oceanbase/oceanbase oceanbase又开源了
- https://github.com/jk-jeon/dragonbox/tree/1.0.0 高效的float-to-string算法,且合入了fmt库fmtlib/fmt#1882