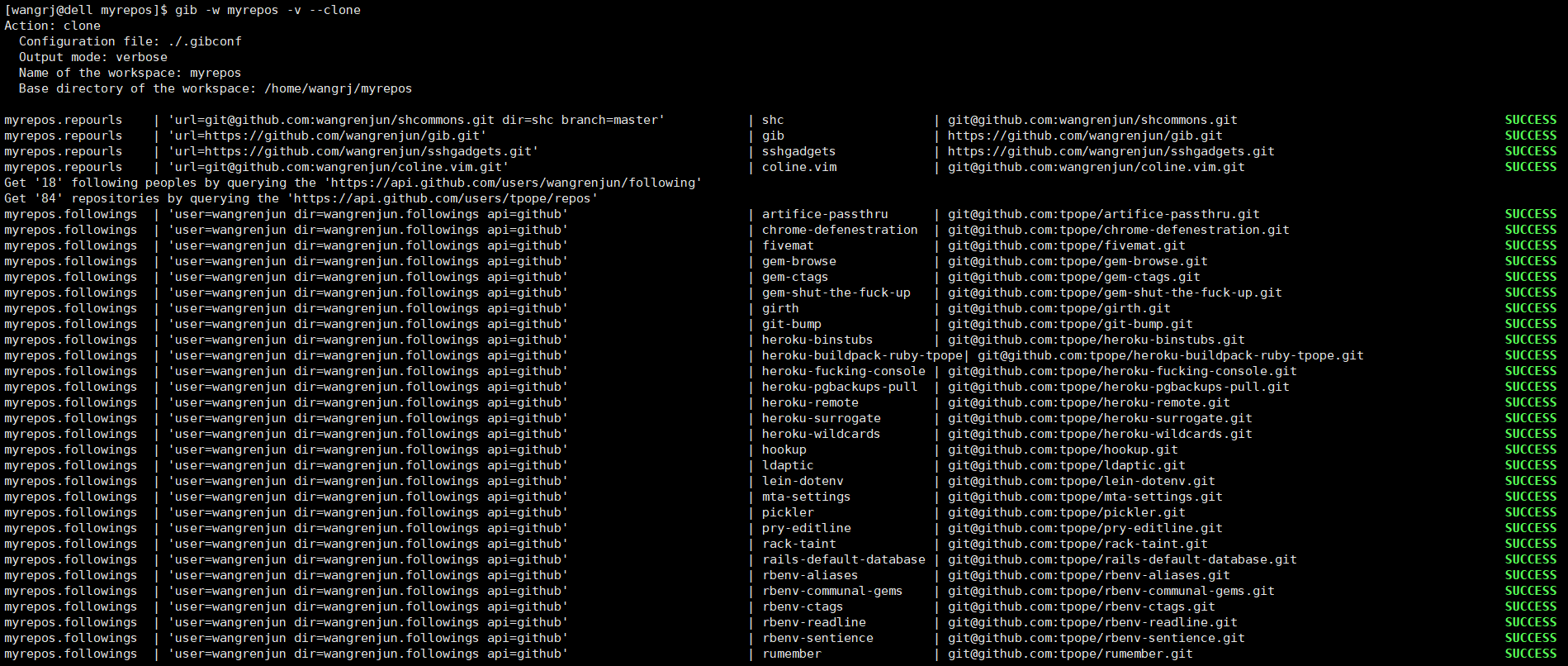
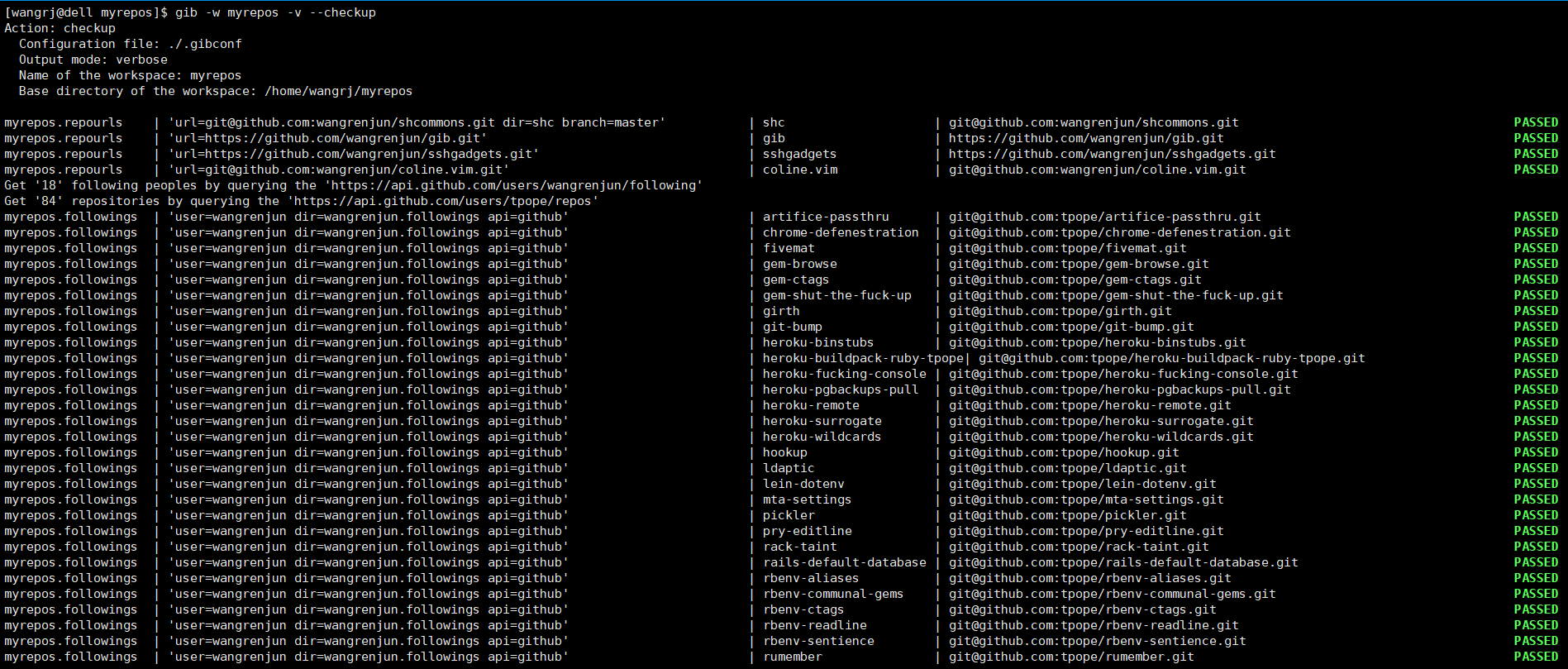
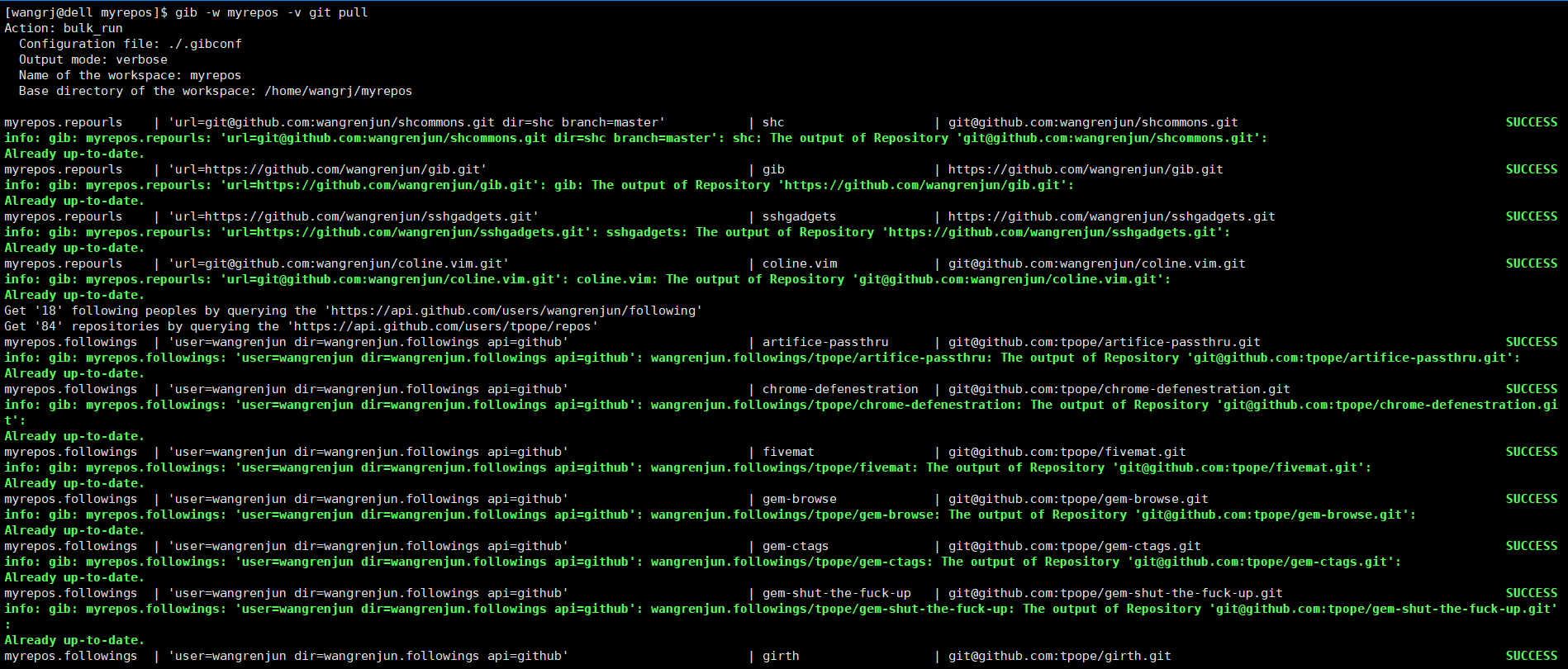
This shell script can simplify repository management when you have a lot of repositories or want to clone them, It can execute Git commands in many local repositories and also supports querying the APIs of Github and Gitlab to get repository URLs in bulk, So it can do a lot of batch operations, such as batch cloning my starred repositories on Github, batch git pull them, batch git commit, git grep in them, etc.
sudo sh -c "curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wangrenjun/gib/master/gib -o /usr/bin/gib && chmod +x /usr/bin/gib"- Batch clone or execute any command in the repositories from github via git url, account(username or organization name), user's starrings, user's watchings, user's followings.
- Batch clone or execute any command in the repositories from gitlab via git url, account(username or organization name).
USAGE: gib [-h | --help] [-v | --verbose] [-q | --quiet] [--force]
[--local] [--global] [--system] [-f <config file> | --file <config file>]
[-l | --list] [-w <workspace name> | --workspace <workspace name>]
[--repourls[=<url>]] [--repodirs[=<path>]] [--users[=<user>]]
[--orgs[=<organization>]] [--starrings[=<user>]] [--watchings[=<user>]] [--followings[=<user>]]
[--clone] [--checkup]
COMMAND
OPTIONS
-v, --verbose
Verbose output. Progress will be reported to stdout.
-q, --quiet
Operate quietly. Error message and progress is not reported to stdout and stderr.
--force
Enable forced mode to execute commands. Perform forced clone when it appears with the --clone option.
--local
Load the configuration file in the current directory ./.gibconf.
--global
Load user-wide configuration file ~/.gibconf.
--system
Load system-wide configuration file /etc/gibconf.
-f <config file>, --file <config file>
Use the given config file.
-l, --list
Output the configuration file. The format command is git config.
-w <workspace name>, --workspace <workspace name>
Specify the workspace name to operate. Each workspace contains the repositories, directories, users, Only one workspace can be specified per run.
--repourls[=<url>]
Specify the section of the repository urls.
--repodirs[=<path>]
Specify the section of the repository directories.
--users[=<user>]
Specify the section of the users.
--orgs[=<organization>]
Specify the section of the organizations.
--starrings[=<user>]
Specify the section of the starred by user.
--watchings[=<user>]
Specify the section of the watching by user.
--followings[=<user>]
Specify the section of the following by user.
--clone
Batch cloning or forced clone if the repository exists and --force option is used.
--checkup
Batch check the repositories, including their default branch and working tree status.
- default-workspace-name: Default workspace name when you omit the -w option.
- workspace-base-dir: Workspace base directory.
- repourls: URL of the Git repository, type is array.
- repodirs: Local directory of the Git repository, type is array.
- users: Username in Github or Gitlab, type is array.
- orgs: Organization name in Github or Gitlab, type is array.
- starrings: Which user has starring repositories in Github or Gitlab, type is array.
- watchings: Which user has watching repositories in Github or Gitlab, type is array.
- followings: Which user has following the peoples in Github or Gitlab, type is array.
- url: URL of the Git repository.
- dir: Directory of the repositories in this line.
- user: Username in Github or Gitlab.
- org: Organization name in Github or Gitlab.
- api: Tell me should query Github or Gitlab.
- branch: Git branch of the repositories in this line.
- token: Access token for Github or Gitlab API.