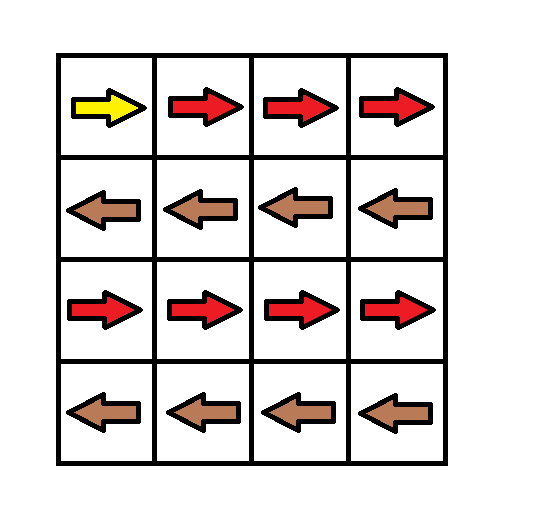
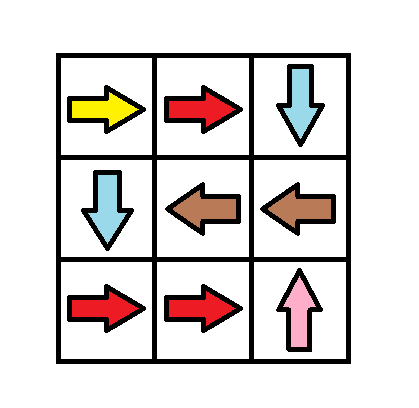
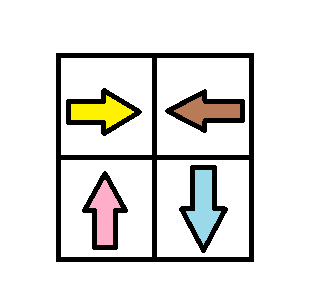
Given an m x n grid. Each cell of the grid has a sign pointing to the next cell you should visit if you are currently in this cell. The sign of grid[i][j] can be:
1which means go to the cell to the right. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i][j + 1])2which means go to the cell to the left. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i][j - 1])3which means go to the lower cell. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i + 1][j])4which means go to the upper cell. (i.e go fromgrid[i][j]togrid[i - 1][j])
Notice that there could be some signs on the cells of the grid that point outside the grid.
You will initially start at the upper left cell (0, 0). A valid path in the grid is a path that starts from the upper left cell (0, 0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1) following the signs on the grid. The valid path does not have to be the shortest.
You can modify the sign on a cell with cost = 1. You can modify the sign on a cell one time only.
Return the minimum cost to make the grid have at least one valid path.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2],[1,1,1,1],[2,2,2,2]] Output: 3 Explanation: You will start at point (0, 0). The path to (3, 3) is as follows. (0, 0) --> (0, 1) --> (0, 2) --> (0, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (1, 3) --> (1, 2) --> (1, 1) --> (1, 0) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (2, 0) --> (2, 1) --> (2, 2) --> (2, 3) change the arrow to down with cost = 1 --> (3, 3) The total cost = 3.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1,3],[3,2,2],[1,1,4]] Output: 0 Explanation: You can follow the path from (0, 0) to (2, 2).
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,2],[4,3]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1001 <= grid[i][j] <= 4
BFS using deque.
class Solution:
def minCost(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [[0, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1], [1, 0], [-1, 0]]
q = deque([(0, 0, 0)])
vis = set()
while q:
i, j, d = q.popleft()
if (i, j) in vis:
continue
vis.add((i, j))
if i == m - 1 and j == n - 1:
return d
for k in range(1, 5):
x, y = i + dirs[k][0], j + dirs[k][1]
if 0 <= x < m and 0 <= y < n:
if grid[i][j] == k:
q.appendleft((x, y, d))
else:
q.append((x, y, d + 1))
return -1class Solution {
public int minCost(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
Deque<int[]> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
q.offer(new int[]{0, 0, 0});
int[][] dirs = {{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int i = p[0], j = p[1], d = p[2];
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) {
return d;
}
if (vis[i][j]) {
continue;
}
vis[i][j] = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= 4; ++k) {
int x = i + dirs[k][0], y = j + dirs[k][1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n) {
if (grid[i][j] == k) {
q.offerFirst(new int[]{x, y, d});
} else {
q.offer(new int[]{x, y, d + 1});
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}function minCost(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length,
n = grid[0].length;
let ans = Array.from({ length: m }, v => new Array(n).fill(Infinity));
ans[0][0] = 0;
let queue = [[0, 0]];
const dirs = [
[0, 1],
[0, -1],
[1, 0],
[-1, 0],
];
while (queue.length) {
let [x, y] = queue.shift();
for (let step = 1; step < 5; step++) {
let [dx, dy] = dirs[step - 1];
let [i, j] = [x + dx, y + dy];
if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) continue;
let cost = ~~(grid[x][y] != step) + ans[x][y];
if (cost >= ans[i][j]) continue;
ans[i][j] = cost;
if (grid[x][y] == step) {
queue.unshift([i, j]);
} else {
queue.push([i, j]);
}
}
}
return ans[m - 1][n - 1];
}class Solution {
public:
int minCost(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> vis(m, vector<bool>(n));
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
deque<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push_back({0, 0});
while (!q.empty())
{
auto p = q.front();
q.pop_front();
int i = p.first / n, j = p.first % n, d = p.second;
if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) return d;
if (vis[i][j]) continue;
vis[i][j] = true;
for (int k = 1; k <= 4; ++k)
{
int x = i + dirs[k][0], y = j + dirs[k][1];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n)
{
if (grid[i][j] == k) q.push_front({x * n + y, d});
else q.push_back({x * n + y, d + 1});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
};func minCost(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
q := doublylinkedlist.New()
q.Add([]int{0, 0, 0})
dirs := [][]int{{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}
vis := make([][]bool, m)
for i := range vis {
vis[i] = make([]bool, n)
}
for !q.Empty() {
v, _ := q.Get(0)
p := v.([]int)
q.Remove(0)
i, j, d := p[0], p[1], p[2]
if i == m-1 && j == n-1 {
return d
}
if vis[i][j] {
continue
}
vis[i][j] = true
for k := 1; k <= 4; k++ {
x, y := i+dirs[k][0], j+dirs[k][1]
if x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n {
if grid[i][j] == k {
q.Insert(0, []int{x, y, d})
} else {
q.Add([]int{x, y, d + 1})
}
}
}
}
return -1
}