This is an implementation of unsupervised multiple kernel learning (U-MKL) for dimensionality reduction, which builds upon a supervised MKL technique by Lin et al (10.1109/TPAMI.2010.183).
By a combination of feature-based kernels, it allows optimally fusing heterogeneous information and weighting the contribution of each input to the final result.
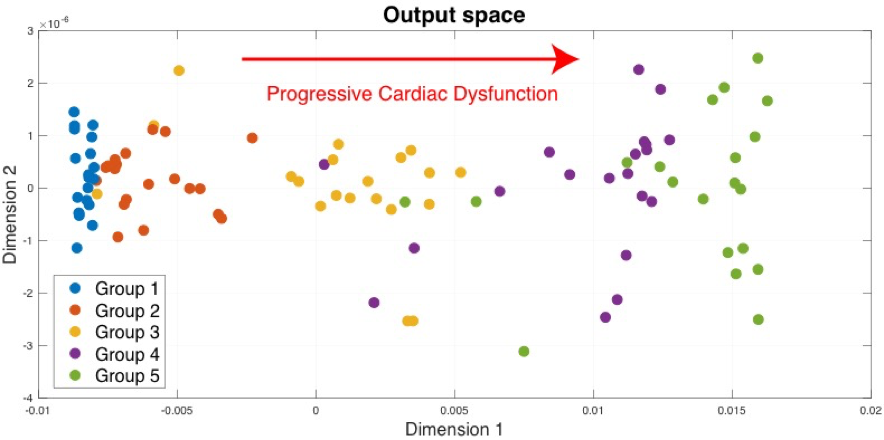
U-MKL handles heterogeneous descriptors and reduces their complexity into a simplified, low-dimensional representation, which highlights the main characteristics of the input data.
Further information can be found in Sanchez-Martinez et al. (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.06.007)
Published reports of research using this code (or a modified version) may cite the following article that describes the multiple kernel learning for dimensionality reduction approach:
- Y. Lin, T. Liu, and C. Fuh. Multiple kernel learning for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 33:1147–1160, 2011.
The present MATLAB implementation is the one detailed in:
- S. Sanchez-Martinez, N. Duchateau, T. Erdei, A.G. Fraser, B.H. Bijnens, and G. Piella. Characterization of myocardial motion patterns by unsupervised multiple kernel learning. Medical Image Analysis, 35:70-82, 2017.
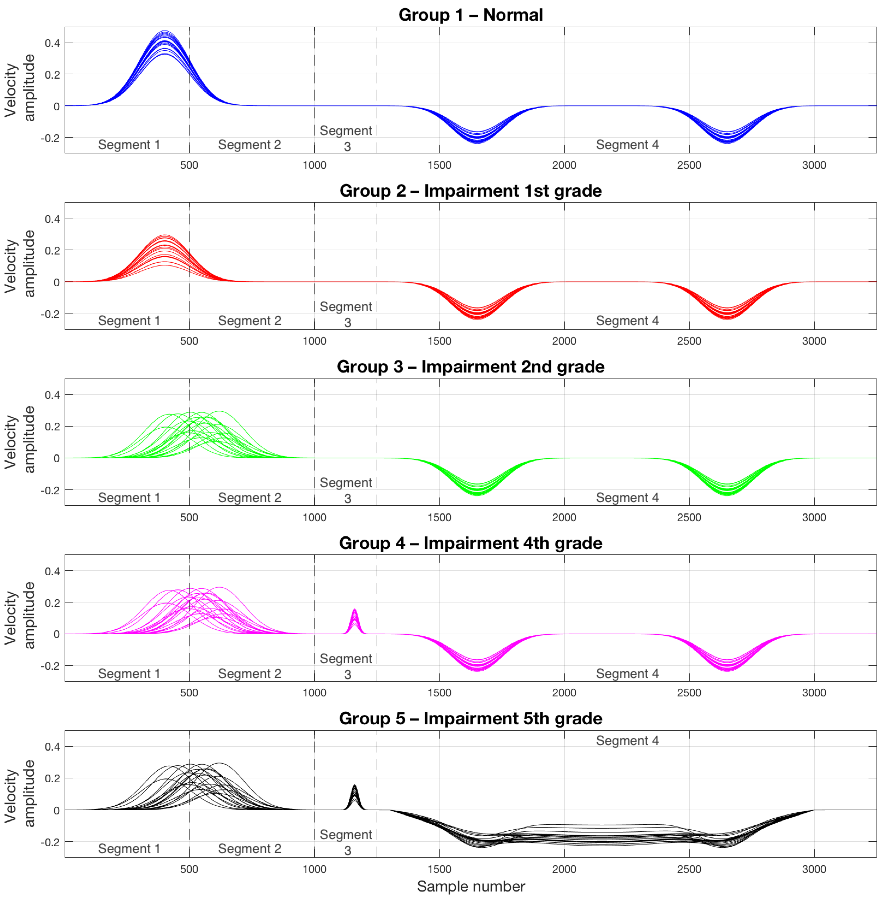
Synthetic left ventricular myocardial velocities that emulate the span of cardiac abnormalities that may be observed in a HFPEF population, ranging from completely normal subjects (Group 1) to subjects with a severely impaired cardiac function (Group 5). Four features of the velocity traces, extracted from physiological knowledge about impaired cardiac function, have been modified to create the synthetic curves, namely:
- Diminished systolic peak velocity
- Delay of the systolic peak velocity
- Appearance of a post-systolic event
- Fusion during diastole of the negative peaks corresponding to the left ventricular suction and the atrial contraction.
Twenty subjects have been created for each group, making a total of 100 subjects. The velocity curves are split in 4 segments, as depicted in the figure above. Each of these segments will be a feature to be used as input to the MKL algorithm.
| Segment number | Number of samples per segment |
|---|---|
| #1 | 500 |
| #2 | 500 |
| #3 | 250 |
| #4 | 2000 |
Clean version of the unsupervised Multiple Kernel Learning for dimensionality reduction code. A few remarks:
It is necessary to install the CVX toolbox to be able to run the algorithm. See the details in the CVX web.
The C scripts (computeENERGY.c, computeSWA.c and computeSWB.c) need to be compiled in Matlab. To do so just write in the Matlab command line:
mex computeENERGYmex computeSWAmex computeSWBIf any problem occurs during compilation, try:
mex -setupto change the configuration.
After this is done, run “Launch_MKL.m” function
Unsupervised Multiple Kernel Learning is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
Unsupervised Multiple Kernel Learning is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with Unsupervised Multiple Kernel Learning. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.