A Non-Cryptocurrency Public Chain is a transformed public chain framework based on an existing public chain. Gas Credit transfers are not permitted between standard wallets. There are no cryptocurrency incentives for mining or participating in consensus. On Spartan Network, there are three Non-Cryptocurrency Public Chains at launch. We except to add more in the foreseeable future.
As a clear demonstration, all commands in this document are run with root permission. These commands can also be run under normal user permissions, please set the file storage and configure the parameters properly.
This document is a guide to install, configure and run a full node in the Spartan-III Chain(Powered by NC-PolygonEdge) public blockchain.
Spartan-III Chain (Powered by NC PolygonEdge) network has two identifiers, a network ID and a chain ID. Although they often have the same value, they have different uses. Peer-to-peer communication between nodes uses the network ID, while the transaction signature process uses the chain ID.
Spartan-III Chain Network Id = Chain Id = 5566
Below is the instruction for Linux.
It is recommended to build Spartan-III Chain full nodes on Linux Server with the following requirement.
- 2 CPU
- Memory: 2GB
- Disk: 100GB SSD
- Bandwidth: 20Mbps
- 4 CPU
- Memory: 16GB
- Disk: 512GB SSD
- Bandwidth: 20Mbps
In this chapter, we will build a full node by commands. If you prefer to build the node by Docker Images, please go to chapter 4 Full Node Installation by Docker.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Golang | 1.17+ |
| GCC | latest |
| Git | 1.8.3.1+ |
| tree (optional) | 1.6.0 |
There are 2 methods to install NC PolygonEdge Node: building from source and installing by Docker. Please refer to the installation method that is most applicable in your specific case.
Go 1.17 or above is recommended for building and installing the Spartan-III Chain node software. Install go by the following steps:
Download and untar the installation file
wget https://go.dev/dl/go1.18.5.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -C /usr/local -zxvf go1.18.5.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Change environment variables, for example in bash:
vi /etc/profile
Insert the parameter at the bottom of the file:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/binThen, save the change and make the /etc/profile file take effect:
source /etc/profile
Now, check whether go is correctly installed:
go version
Install gcc by the following command:
yum install gcc
Check the version
gcc -v
Install gcc by the system command
yum install git
Check the version
git version
Download the source code of Spartan NC PolygonEdge from github (git has been installed):
git clone https://github.com/BSN-Spartan/NC-PolygonEdge.git
cd NC-PolygonEdge/
make build
cp polygon-edge /usr/bin
Execute the following commands to check the version of Spartan NC PolygonEdge:
polygon-edge version
Create a new directory node1/:
mkdir node1
Copy genesis.json and config.json files from spartan/ directory to node1/ directory:
cp ./spartan/genesis.json ./spartan/config.json node1/
genesis.json defines the genesis block data and specifies the system parameters.
Refer to below template to configure your config.json file:
{
"chain_config": "./genesis.json",
"secrets_config": "",
"data_dir": "./data",
"block_gas_target": "0x0",
"grpc_addr": "0.0.0.0:9632",
"jsonrpc_addr": "0.0.0.0:8545",
"telemetry": {
"prometheus_addr": ""
},
"network": {
"no_discover": false,
"libp2p_addr": "0.0.0.0:1478",
"nat_addr": "",
"dns_addr": "",
"max_peers": -1,
"max_outbound_peers": -1,
"max_inbound_peers": -1
},
"seal": true,
"tx_pool": {
"price_limit": 1000000000,
"max_slots": 2500
},
"log_level": "INFO",
"restore_file": "",
"block_time_s": 5,
"headers": {
"access_control_allow_origins": [
"*"
]
},
"log_to": "",
"dev": true,
"json_rpc_batch_request_limit":100
}
Edit below parameters of config.json:
data_diris the directory used to store the ledger, secret key file and other information. To change the data storage configuration, please refer to: https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/validator-hosting
grpc_addr is the gRPC port of the node. As the management function, it is not recommended to open this interface to the Internet.
jsonrpc_addr is the transaction API. You can set it public to your user or forward it to users.
no_discover Set to false by default to make the node discoverable in the network. For VDCs, it is required to set this parameter to "false", otherwise the health check of the node cannot be performed.
libp2p_addr is the listening address of P2P. For VDCs, it is required to open this port, otherwise the health check of the node cannot be performed.
nat_addr is the public IP address of the server. For VDCs, it is required to set, otherwise the health check of the node cannot be performed.
log_tois the output file of the log. For detailed log configuration, please refer to:https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/validator-hosting#log-files
To learn more about config.json, check out the following link:
https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/configuration/sample-config
Start the node in node1/ directory with the command below:
polygon-edge server --config config.json
You can see the blocks are synchronized to the node:

Or you can execute in the background via nohup:
nohup polygon-edge server --config config.json > output.log 2>&1 &
You can check the process of block synchronization from the log:
tail -f output.log
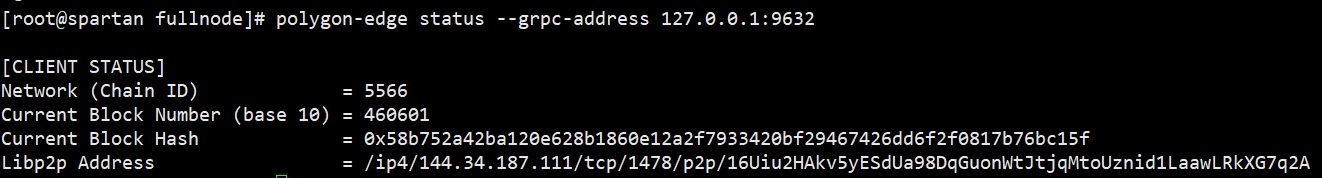
Confirm the node status:
polygon-edge status --grpc-address 127.0.0.1:9632
In this chapter, we will build a full node by docker images. If you have built a node by commands, you can skip this chapter and move forward.
| Software | Version |
|---|---|
| Docker-ce | 18+ |
| Run the following command to install the Docker image: |
wget -qO- https://get.docker.com/ | sh
Grant user permission to execute Docker commands:
sudo usermod -aG docker your-user
Now, check the docker version:
docker versionOfficial Docker images are hosted under the hub.docker.com registry. Run the following command to pull them to the server:
docker pull bsnspartan/nc-polygon-edge:latest
Refer to chapter 3.3 Configuring the Node, make sure you have created node1 directory, and copy genesis.json and config.json into it. You can also configure the ports in config.json file if needed.
Access to node1/ directory and start the node:
docker run -d -p 8545:8545 -p 1478:1478 -p 9632:9632 -v $PWD:/opt/ --restart=always --name spartan-nc-polygon-edge bsnspartan/nc-polygon-edge:latest server --config config.json
Confirm the node status:
docker exec spartan-nc-polygon-edge polygon-edge status --grpc-address 127.0.0.1:9632
When joining the Spartan Network as a Data Center, the Data Center Operator will be rewarded a certain amount of NTT Incentives based on the quantity of the registered node. To achieve this, the Data Center Operator should first provide the signature of the full node to verify the node's ownership.
Execute the following command in the node's data directory after the node is started.
Remember to configure NAT for your node and enable node discovery.
polygon-edge secrets validate --data-dir data --grpc-address 127.0.0.1:9632 --json
-
data-diris the data directory of the node. If you use local key management, you should specify this directory to store the data file of the node. -
configis the key configuration file, if you use remote key management, you should specify this parameter. -
grpc-addressis the node address that generates the signature, which is usually the current node address.
Execute below command:
docker exec spartan-nc-polygon-edge polygon-edge secrets validate --data-dir data --grpc-address 127.0.0.1:9632
After executing the above commands, you will get the following information. Please submit it to the locally installed Data Center Management System when registering the node.
{
"nodeId":"16Uiu2HAmTCgocz1Y25YDzQdqgHtBzh6UxnycXTwnhmxCFHy6xQPS",
"address":"/ip4/10.0.51.109/tcp/1478/p2p/16Uiu2HAmTCgocz1Y25YDzQdqgHtBzh6UxnycXTwnhmxCFHy6xQPS",
"signature":"AN1rKvtQYxuPqNffZ6Y3F5CZYAeRjWNKLZMB4FakqhJs3yp2GU4NcH6fgpRUpkxcDcQFPT8WvNRStCd5HJTbmCFqMqEUeGz2H"
}
You can use the following command to stop the running node and delete it, and also clear the node data by deleting the data directory.
If the node has been registered in the Data Center, you can back up the libp2p.key file stored in node1/data/libp2p/ directory, so that you can recover this registered node when needed.
Use the following command to stop the running node:
pkill -INT polygon-edge
Use the following command to stop the running container and delete the container and the image file:
docker stop spartan-nc-polygon-edge
docker rm spartan-nc-polygon-edge
docker rmi bsnspartan/nc-polygon-edge:latest
If you need to completely delete all data of the node, you can use the following command to delete the datadir directory.
rm -rf node1/
NC-PolygonEdge is compatible with ETH JSON RPC interface, please refer to the detailed interface list from below link:
https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/get-started/json-rpc-commands
NC-PolygonEdge provides a wealth of CLI commands for managing your nodes. For a detailed command list, please refer to the link below :
https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/get-started/cli-commands
Polygon Edge can report and serve the Prometheus metrics, which in their turn can be consumed using Prometheus collector(s).
The following is a detailed description reference:
https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/configuration/prometheus-metrics
This guide goes into detail on how to back up and restore a Polygon Edge node instance. It covers the base folders and what they contain, as well as which files are critical for performing a successful backup and restore.
For detailed operation, please refer to the link below:
https://docs.polygon.technology/docs/edge/working-with-node/backup-restore