Arktos is an open source project designed for large scale cloud compute infrastructure. It is evolved from the open source project Kubernetes codebase with core design changes.
Arktos aims to be an open source solution to address key challenges of large-scale clouds, including system scalability, resource efficiency, multitenancy, edge computing, and the native support for the fast-growing modern workloads such as containers and serverless functions.
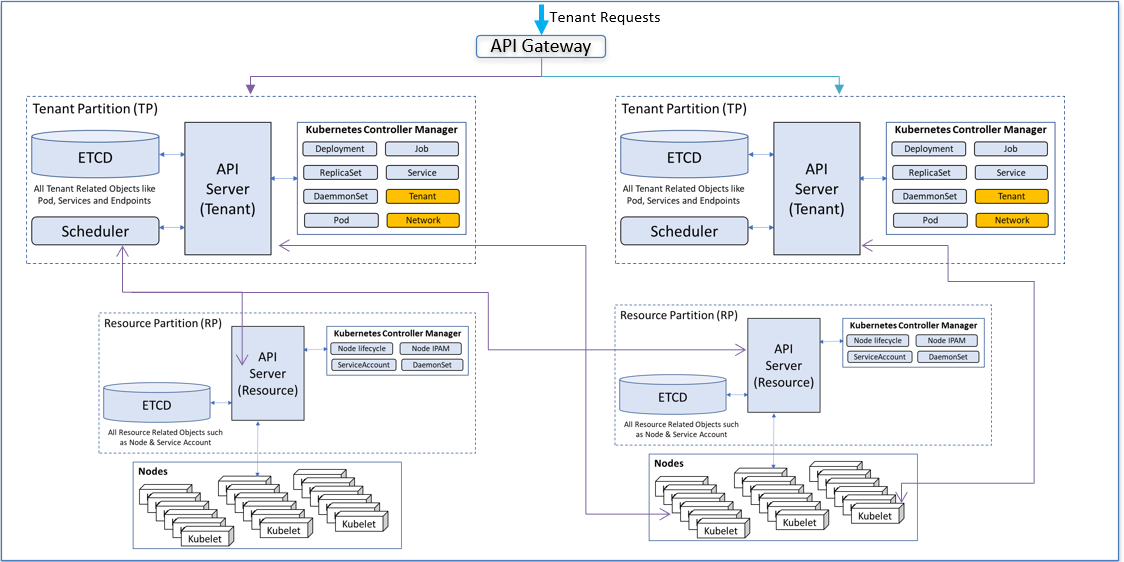
Arktos achieves a scalable architecture by partitioning and scaling out components, including API Server, storage, controllers and data plane. The eventual goal of Arktos is to support 300K nodes with a single regional control plane.
Arktos implements a hard multitenancy model to meet the strict isolation requirement highly desired by public cloud environment. It's based on the virtual cluster idea and all isolations are transparent to tenants. Each tenant feels it's a dedicated cluster for them.
In addition to container orchestration, Arktos implements a built-in support for VMs. In Arktos a pod can contain either containers or a VM. They are scheduled the same way in a same resource pool. This enables cloud providers use a single converged stack to manage all cloud hosts.
There are more features under development, such as cloud-edge scheduling, in-place vertical scaling, etc. Check out our releases for more information.
Arktos requires a few dependencies to build and run, and a bash script is provided to install them.
After the prerequisites are installed, you just need to clone the repo and run "make":
Note: you need to have a working Go 1.13 environment. Go 1.14 and above is not supported yet.
mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com
git clone https://github.com/CentaurusInfra/arktos
cd arktos
make
The easiest way to run Arktos is to bring up a single-node cluster in your local development box:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/arktos
./hack/arktos-up.sh
The above command shows how to set up arktos with default network solution, bridge. With release 1.0, an advanced network solution, Mizar, is introduced into Arktos. The integration with Mizar allows tenant pods/services to be truely isolated from pods/services in another tenant. To start Arktos cluster with Mizar, make sure you are using Ubuntu 18.04+, run the following command:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/arktos
CNIPLUGIN=mizar ./hack/arktos-up.sh
After the Arktos cluster is up, you can access the cluster with kubectl tool released in Arktos just like what you do with a Kubernetes cluster. For example:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/arktos
./cluster/kubectl.sh get nodes
To setup a multi-node cluster, please refer to Arktos Cluster Setup Guide. And this guide gives detailed instructions if you want to enable partitions in the cluster.
To setup an Arktos scale out cluster in Google Cloud, please refer to Setting up Arktos scale out environment in Google Cloud.
To setup an Arktos scale out cluster in local dev environment, follow the instructions on Setting up local dev environment for scale out.
Pacific Time: Tuesday, 6:00PM PT (Weekly). Please check our discussion page here for the latest meeting information.
Resources: Meeting Link | Meeting Agenda | Meeting Summary
The design document folder contains the detailed design of already implemented features, and also some thoughts for planned features.
The user guide folder provides information about these features from users' perspective.
To report a problem, please create an issue in the project repo.
To ask a question, please start a new discussion here.