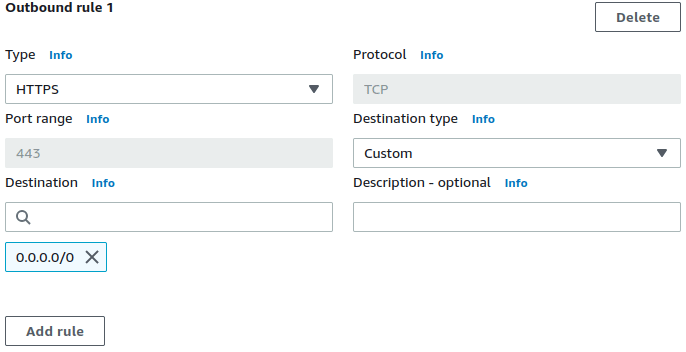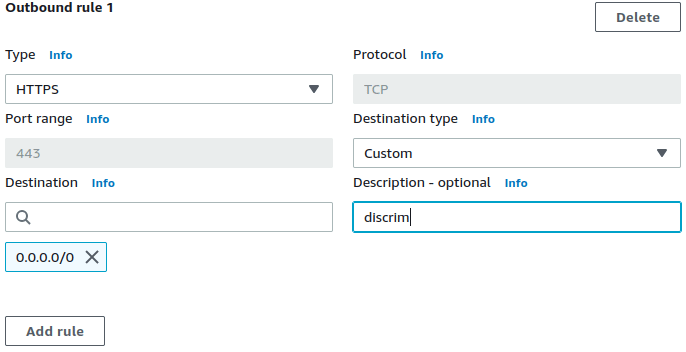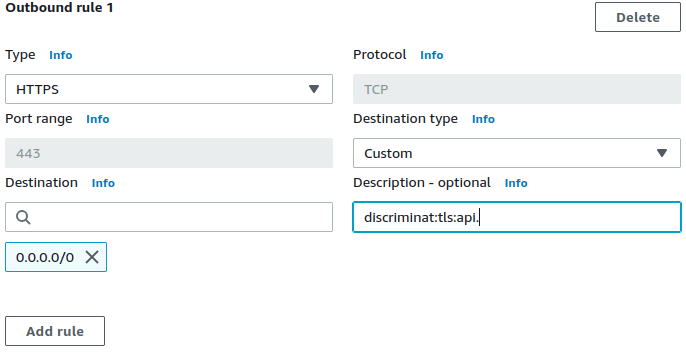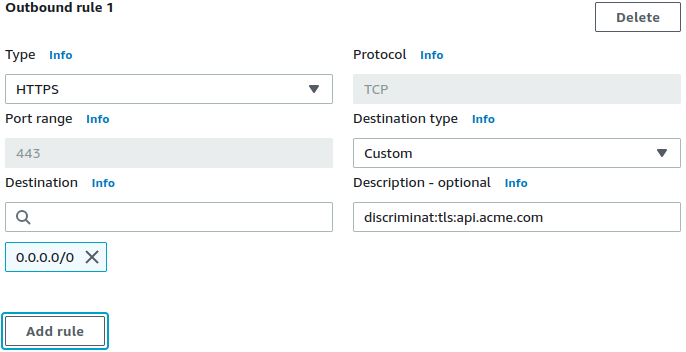
HTTPS, TLS, SSH, SFTP micro-segmentation firewall to filter VPC egress by hostnames. Simply specify allowed FQDNs within the respective apps' Security Groups' description fields. Apps will not require any proxy configuration.
2-minute Demo Video | Product Reviews at G2 | AWS Marketplace Subscription (required)
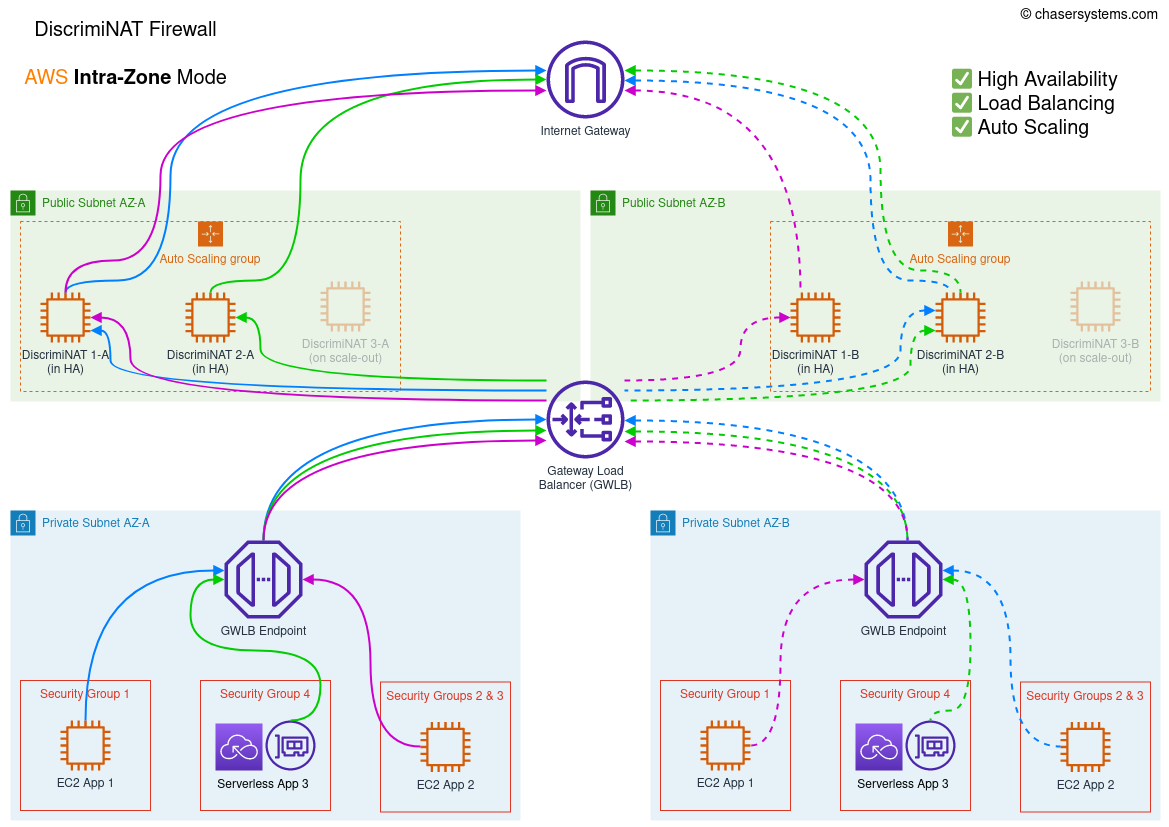
Architecture with Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) VPC Endpoints for Private Subnets' route table entries to the Internet, featuring:
🖧 High Availability
⚖ Load Balancing
🚀 Auto Scaling
Quick Allowlist Building
Standards & Compliance
Reference Architectures
Elastic IPs
Other VPC Requirements
Deployment Examples
Security Group Examples
Allowlist Building Examples
More Help
Automated System Health Reporting
Terraform Requirements
Terraform Inputs
Terraform Outputs
Terraform Resources
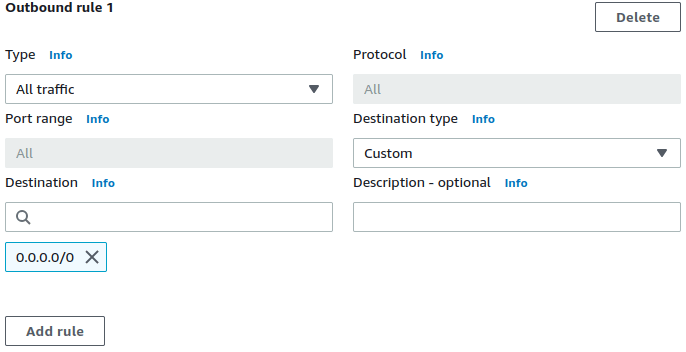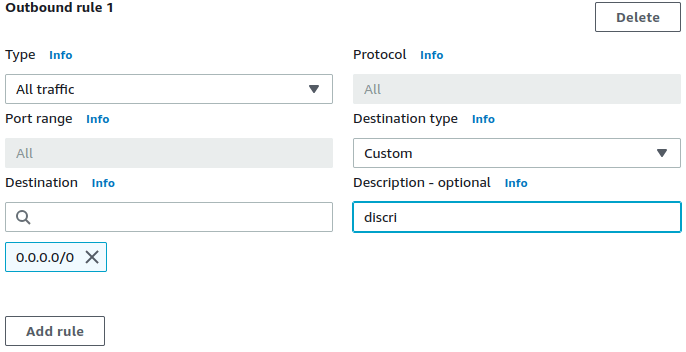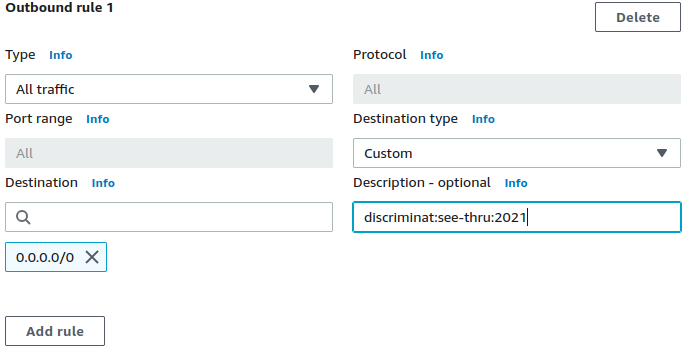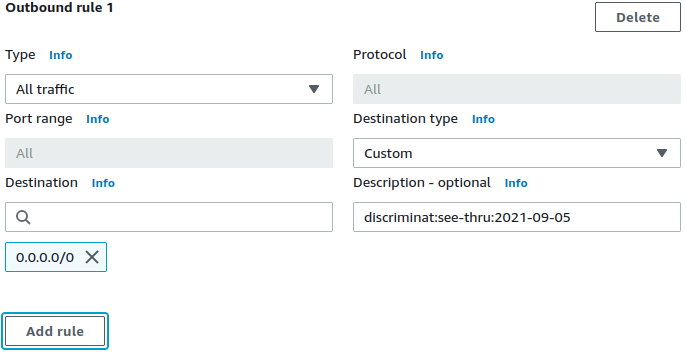
Use the see-thru mode to discover what needs to be in the allowlist for an app, by monitoring its outbound network activity first. Follow our building an allowlist from scratch recipe for use with CloudWatch.
Note
Terraform example of asee-thruSecurity Group is here.
The DiscrimiNAT Firewall helps your organisation achieve
💳 PCI DSS v4.0, Requirement 1.3.2
🇺🇸 NIST SP 800-53, AC-4 Information Flow Enforcement
🇺🇸 NIST SP 800-53, SC-7 Boundary Protection
✓✓ Out-of-band DNS Checks
⇄ Bidirectional TLS 1.2+ and SSH v2 Checks
In the cross-zone mode, the Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) will distribute traffic evenly across all deployed AZs. This reduces the number of DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances you will have to run for high-availability but increases data-transfer costs.
Note
Terraform variablehigh_availability_modeshould be set tocross-zone. This is also the default.
Warning
Minimum number of allocated Elastic IPs for high-availability (=2) with headroom for auto-scaling (+1) is 3 per region.
In the intra-zone mode, the GWLB will distribute traffic evenly across all DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances in the same AZ as the client. For effective high-availability, this mode will need at least two instances per deployed AZ. Please note this does not fully protect you against the failure of an entire AZ on the Amazon side, however your other services in the zone would potentially be impacted too and therefore not sending egress traffic.
Note
Terraform variablehigh_availability_modeshould be set tointra-zone.
Warning
Traffic will not be balanced to other zones, even in case of failure of all instances in one zone, therefore minimum high-availability numbers (=2) have to be configured per AZ.
Warning
Minimum number of allocated Elastic IPs for high-availability (=2) with headroom for auto-scaling (+1) is 3 per AZ; and therefore 6 for two AZs.
If a Public IP is not found attached to a DiscrimiNAT instance, it will look for any allocated but unassociated Elastic IPs that have a tag-key named discriminat (set to any value.) One of such Elastic IPs will be attempted to be associated with itself then.
Note
This allows you to have a stable set of static IPs to share with your partners, who may wish to allowlist/whitelist them.
The IAM permissions needed to do this are already a part of this module. Specifically, they are:
ec2:DescribeAddresses
ec2:AssociateAddress
Additionally, these permissions are constrained to work only for resources tagged appropriately, i.e. the tag discriminat is not null.
"Condition": {
"Null": {
"aws:ResourceTag/discriminat": false
}
}
Warning
An EC2 VPC Endpoint is needed for this mechanism to work though – since making the association needs access to the EC2 API. In the deployment example below, this is demonstrated by deploying the endpoint along with the VPC.
As noted in the Elastic IPs section above, an EC2 VPC Endpoint will be needed for DiscrimiNAT instances to associate an Elastic IP with themselves. This is demonstrated in the deployment example below.
📜 Entirely new VPC with DiscrimiNAT filtering for Private Subnets
# Allocating three Elastic IPs for high-availability and auto-scaling in the
# cross-zone mode.
resource "aws_eip" "nat" {
count = 3
tags = {
"discriminat" : "some-comment",
"Name" : "egress-ip-reserved"
}
lifecycle {
# change to `true` if this IP address has been shared with third parties
prevent_destroy = false
}
}
# Deploying a new VPC in two AZs with Public and Private Subnets.
module "aws_vpc" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws"
version = "> 3, < 6"
name = "discriminat-example"
cidr = "172.16.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
azs = ["eu-west-3a", "eu-west-3b"]
public_subnets = ["172.16.11.0/24", "172.16.21.0/24"]
private_subnets = ["172.16.12.0/24", "172.16.22.0/24"]
map_public_ip_on_launch = false
manage_default_security_group = true
default_security_group_ingress = []
default_security_group_egress = []
}
# Deploying an EC2 VPC Endpoint.
module "aws_vpc_endpoints" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/vpc/aws//modules/vpc-endpoints"
version = "> 3, < 6"
vpc_id = module.aws_vpc.vpc_id
endpoints = {
ec2 = {
service = "ec2"
private_dns_enabled = true
security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.vpce_ec2.id]
subnet_ids = module.aws_vpc.private_subnets
}
}
tags = {
"Name" : "ec2"
}
}
# A Security Group that allows the entire VPC to use the EC2 VPC Endpoint.
resource "aws_security_group" "vpce_ec2" {
name = "vpce-ec2"
description = "ingress from entire vpc to ec2 endpoint for connectivity to it without public ips"
vpc_id = module.aws_vpc.vpc_id
ingress {
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = [module.aws_vpc.vpc_cidr_block]
description = "only https standard port needed for ec2 api"
}
tags = {
"Name" : "vpce-ec2"
}
}
# Deploying DiscrimiNAT.
module "discriminat" {
source = "ChaserSystems/discriminat-gwlb/aws"
public_subnets = module.aws_vpc.public_subnets
private_subnets = module.aws_vpc.private_subnets
depends_on = [module.aws_vpc_endpoints]
}
# Updating route tables of Private Subnets with Gateway Load Balancer Endpoint
# routes for Internet access.
resource "aws_route" "discriminat" {
count = length(module.aws_vpc.private_subnets)
destination_cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
route_table_id = module.discriminat.target_gwlb_endpoints[count.index].route_table_id
vpc_endpoint_id = module.discriminat.target_gwlb_endpoints[count.index].id
}📜 Simple example with two allowed HTTPS FQDNs
# This Security Group must be associated with its intended, respective
# application – whether that is in EC2, Lambda, Fargate or EKS, etc. as long as
# a Security Group can be associated with it.
resource "aws_security_group" "foo" {
# You could use a data source or get a reference from another resource for the
# VPC ID.
vpc_id = module.aws_vpc.vpc_id
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "saas_monitoring" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.foo.id
type = "egress"
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
# The DiscrimiNAT Firewall will apply its own checks anyway, so you could
# choose to leave this wide open without worry.
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# You could simply embed the allowed FQDNs, comma-separated, like below. Full
# syntax at https://chasersystems.com/docs/discriminat/aws/config-ref
description = "discriminat:tls:app.datadoghq.com,collector.newrelic.com"
}📜 Complex example with HTTPS, SSH and two Security Groups
locals {
# You could store allowed FQDNs as a list...
fqdns_sftp_banks = [
"sftp.bank1.com",
"sftp.bank2.com"
]
fqdns_saas_auth = [
"foo.auth0.com",
"mtls.okta.com"
]
}
locals {
# ...and format them into the expected syntax.
discriminat_sftp_banks = format("discriminat:ssh:%s", join(",", local.fqdns_sftp_banks))
discriminat_saas_auth = format("discriminat:tls:%s", join(",", local.fqdns_saas_auth))
}
resource "aws_security_group" "foo" {
# You could use a data source or get a reference from another resource for the
# VPC ID.
vpc_id = module.aws_vpc.vpc_id
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "saas_auth" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.foo.id
type = "egress"
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Use of FQDNs list formatted into the expected syntax.
description = local.discriminat_saas_auth
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "sftp_banks" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.foo.id
type = "egress"
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# Use of FQDNs list formatted into the expected syntax.
description = local.discriminat_sftp_banks
}📜 Allow and log everything uptil and inclusive of a certain date.
# This Security Group must be associated with its intended, respective
# application – whether that is in EC2, Lambda, Fargate or EKS, etc. as long as
# a Security Group can be associated with it.
resource "aws_security_group" "monitor" {
# You could use a data source or get a reference from another resource for the
# VPC ID.
vpc_id = module.aws_vpc.vpc_id
}
resource "aws_security_group_rule" "monitor_and_log" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.monitor.id
type = "egress"
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
# The `see-thru` mode accepts a valid date in YYYY-mm-dd format. Full syntax
# at https://chasersystems.com/docs/discriminat/aws/config-ref#see-thru-mode
description = "discriminat:see-thru:2022-12-31"
}Afterwards, with the Security Group ID of monitor at hand, go to CloudWatch -> Log Insights, select the DiscrimiNAT log group and execute the following query to get a list of all accessed FQDNs in a nicely formatted table.
Warning
You will have to update the Security Group ID in this query.
filter see_thru_exerted AND see_thru_gid = "sg-00replaceme00"
| stats count() by see_thru_exerted, see_thru_gid, dhost, proto, dpt
See our website for full documentation on building an allowlist from scratch.
- Contact our DevSecOps Support for help and queries at any stage of your journey. You will be connected with a highly-skilled engineer from the first interaction.
- Check out the full documentation on our website.
10 minutes after boot, at 0200 UTC every day and once at shutdown, each instance of DiscrimiNAT will collect its OS internals & system logs since instance creation, config changes & traffic flow information from last two hours and upload it to a Chaser-owned cloud bucket. This information is encrypted at rest with a certain public key so only relevant individuals with access to the corresponding private key can decrypt it. The transfer is encrypted over TLS.
Access to this information is immensely useful to create a faster and more reliable DiscrimiNAT as we add new features. We also aim to learn about how users are interacting with the product in order to further improve the usability of it as they embark on a very ambitious journey of fully accounted for and effective egress controls.
We understand if certain environments within your deployment would rather not have this turned on. To disable it, a file at the path /etc/chaser/disable_automated-system-health-reporting should exist. From our Terraform module v2.7.1 onwards, this can be accomplished by setting the variable ashr to false:
ashr = false
--
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| terraform | > 1.2, < 2 |
| aws | >= 4.38, < 6 |
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| public_subnets | The IDs of the Public Subnets to deploy the DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances in. These must have routing to the Internet via an Internet Gateway already. | list(string) |
n/a | yes |
| private_subnets | The IDs of the Private Subnets where the workload, of which the egress is to be filtered, resides. A Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) will be deployed in these, and a map of Private Subnets' Route Table IDs to VPC Endpoint IDs (GWLB) will be emitted in the target_gwlb_endpoints output field. |
list(string) |
n/a | yes |
| connection_draining_time | In seconds, the amount of time to allow for existing flows to end naturally. During an instance-refresh or a scale-in activity, a DiscrimiNAT Firewall instance will not be terminated for at least this long to prevent abrupt interruption of existing flows. | number |
150 |
no |
| tags | Map of key-value tag pairs to apply to resources created by this module. See examples for use. | map(any) |
{} |
no |
| high_availability_mode | cross-zone or intra-zone. In the cross-zone mode, the Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB) will distribute traffic evenly across all deployed AZs. This reduces the number of DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances you will have to run for high-availability but increases data-transfer costs. In the intra-zone mode, the GWLB will distribute traffic evenly across all DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances in the same AZ as the client. For effective high-availability, this mode will need at least two instances per deployed AZ. |
string |
"cross-zone" |
no |
| per_region_min_instances | In case of high_availability_mode set to cross-zone, this is the minimum number of instances across all AZs. This variable is IGNORED in case of high_availability_mode set to intra-zone. |
number |
2 |
no |
| per_region_max_instances | In case of high_availability_mode set to cross-zone, this is the maximum number of instances across all AZs following a scale-out or an instances-refresh event. This variable is IGNORED in case of high_availability_mode set to intra-zone. |
number |
3 |
no |
| per_az_min_instances | In case of high_availability_mode set to intra-zone, this is the minimum number of instances per AZ. This variable is IGNORED in case of high_availability_mode set to cross-zone. |
number |
2 |
no |
| per_az_max_instances | In case of high_availability_mode set to intra-zone, this is the maximum number of instances per AZ following a scale-out or an instances-refresh event. This variable is IGNORED in case of high_availability_mode set to cross-zone. |
number |
3 |
no |
| instance_size | The default of t3.small should suffice for light to medium levels of usage. Anything less than 2 CPU cores and 2 GB of RAM is not recommended. For faster access to the Internet and for accounts with a large number of VMs, you may want to choose a machine type with dedicated CPU cores. Valid values are t3.small , c6i.large , c6i.xlarge , c6a.large , c6a.xlarge . |
string |
"t3.small" |
no |
| key_pair_name | Strongly suggested to leave this to the default, that is to NOT associate any key-pair with the instances. In case SSH access is desired, provide the name of a valid EC2 Key Pair. | string |
null |
no |
| user_data_base64 | Strongly suggested to NOT run custom startup scripts on DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances. But if you had to, supply a base64 encoded version here. | string |
null |
no |
| ami_owner | Reserved for use with Chaser support. Allows overriding the source AMI account for the DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances. | string |
null |
no |
| ami_name | Reserved for use with Chaser support. Allows overriding the source AMI version for the DiscrimiNAT Firewall instances. | string |
null |
no |
| byol | If using the BYOL version from the marketplace, supply the licence key as supplied by Chaser Systems here. | string |
null |
no |
| ashr | Automated System Health Reporting. See note in README to learn more. Set to false to disable. Default is true and hence enabled. | bool |
true |
no |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cloudwatch_log_group_name | Name of the CloudWatch Log Group where DiscrimiNAT instances will log traffic flow and configuration changes. Useful for automating any logging routing configuration. |
| target_gwlb_endpoints | Map of Route Table IDs to VPC Endpoint IDs (Gateway Load Balancer) for setting as targets to 0.0.0.0/0 in routing tables of the Private Subnets. A Terraform example of using these in an aws_route resource can be found at https://github.com/ChaserSystems/terraform-aws-discriminat-gwlb#deployment-examples, under 'Entirely new VPC with DiscrimiNAT filtering for Private Subnets' |
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| aws_autoscaling_group.discriminat | resource |
| aws_autoscaling_lifecycle_hook.discriminat_wait_for_drain_and_warmup | resource |
| aws_autoscaling_policy.cpu | resource |
| aws_iam_instance_profile.discriminat | resource |
| aws_iam_policy.discriminat | resource |
| aws_iam_role.discriminat | resource |
| aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.discriminat | resource |
| aws_launch_template.discriminat | resource |
| aws_lb.discriminat | resource |
| aws_lb_listener.discriminat | resource |
| aws_lb_target_group.discriminat | resource |
| aws_security_group.discriminat | resource |
| aws_vpc_endpoint.discriminat | resource |
| aws_vpc_endpoint_service.discriminat | resource |
| aws_ami.discriminat | data source |
| aws_eips.discriminat | data source |
| aws_route_table.private_subnet | data source |
| aws_subnet.public_subnet | data source |
| aws_vpc.context | data source |