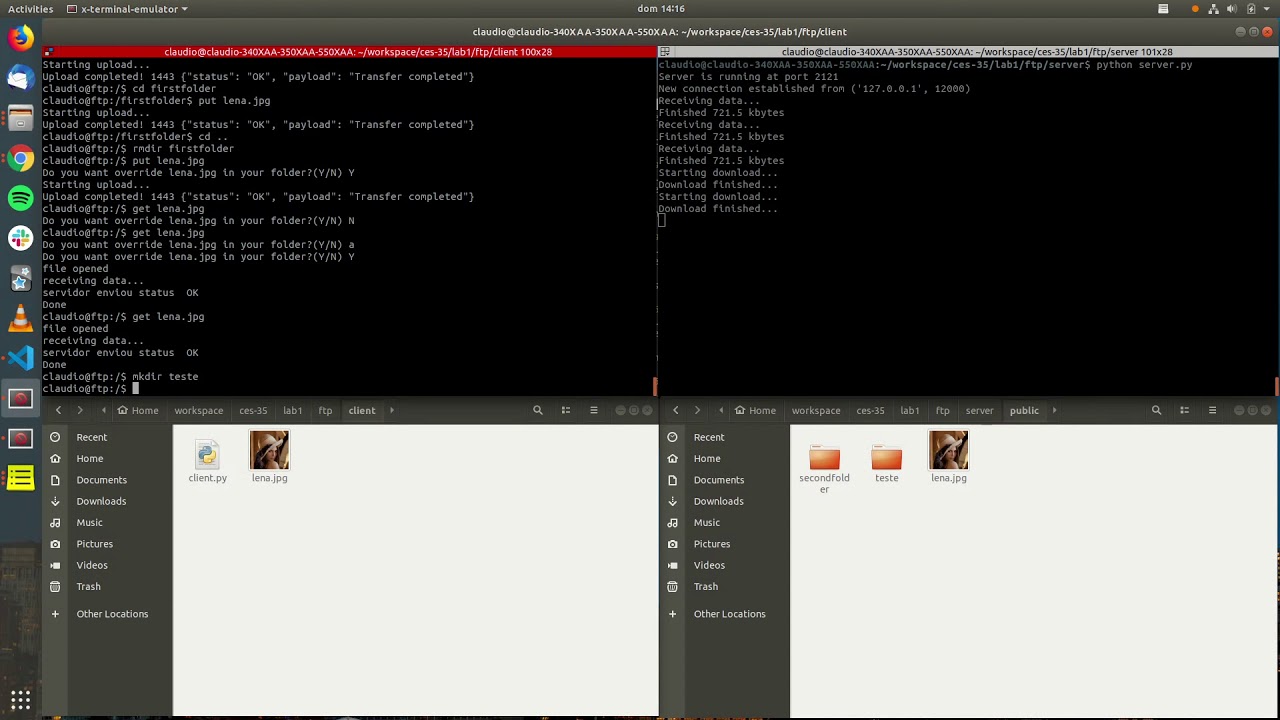
Application developed for computer network classes to illustrate the mechanism of protocols on application layer.
The system contains two main files: server.py and client.py. Both can be run by using the following commands:
$ python3 client.py [PORT]
$ python3 server.py
The optional parameter PORT when running client.py will be used to set the port used by client.py. The default port is 12000. The server always run on port 2121.
Two others files are imported by server.py: config.py and credentials.py. The first file has a path to the shared folder to be accessed by the client and the last has the client credentials. For now,this files has to edited by hand and credentials are in plaintext.
- open [SERVER_IP]
- close
- quit
- cd FOLDER_NAME
- mkdir FOLDER_NAME
- rmdir FOLDER_NAME
- delete FILENAME
- ls [DIRECTORY]
- pwd
- get FILENAME
- put FILENAME
The communication works on "ping-pong" style and do the file transfer using the same connection used for control. This is a difference from FTP because FTP do the file transfer "out-of-band".
Each amount of data transmited between server and client is limited in 51 bytes. Because of this limitation, a split of message is needed. There are three types of message:
- Content messages: This messages are strings containing one command of two uppercase characters and a sequence of characters representing a payload. This payload can be a argument of command or a status message sent by the server.
- Control messages: This messages are used to perform the "ping-pong" its use is generally a response message.
- File transfer
The transfer of content messages is limited to 2 characters on each transmission and large messages has to be splitted in pieces of two characters. The peer knows the end of a message using a "end of message" packet consisting of two space characters (" ").
The file transfer has to be splitted as well. The "end of file" is identified due to a special packet consisting of a sequence of bytes 0.
The following diagrams shows a overview of how the communication works. This diagrams are simplified because content messages are sent using a great amount of packets due to the split.