30 minutes, Intermediate, Start Building
This example shows how to use Google Cloud Functions with the Node.js DataStax Cassandra Driver to set up a basic REST API for a Cassandra database via HTTP Endpoints. The Serverless Framework is used to facilitate the setup and deployment of the functions.
- How to use the DataStax Cassandra Driver with Google Cloud Functions
- How to use the Serverless Framework to set up Google Cloud Functions HTTP Endpoints
The Serverless Framework handles the packaging and deployment of the functions to the Google Cloud resources. Once the functions are deployed, the DataStax Cassandra Driver establishes the connection to the database and returns the results via the Google Cloud HTTP Endpoints which can be accessed to interact with the database.
To build and play with this app, follow the build instructions that are located here: https://github.com/DataStax-Examples/google-cloud-functions-nodejs
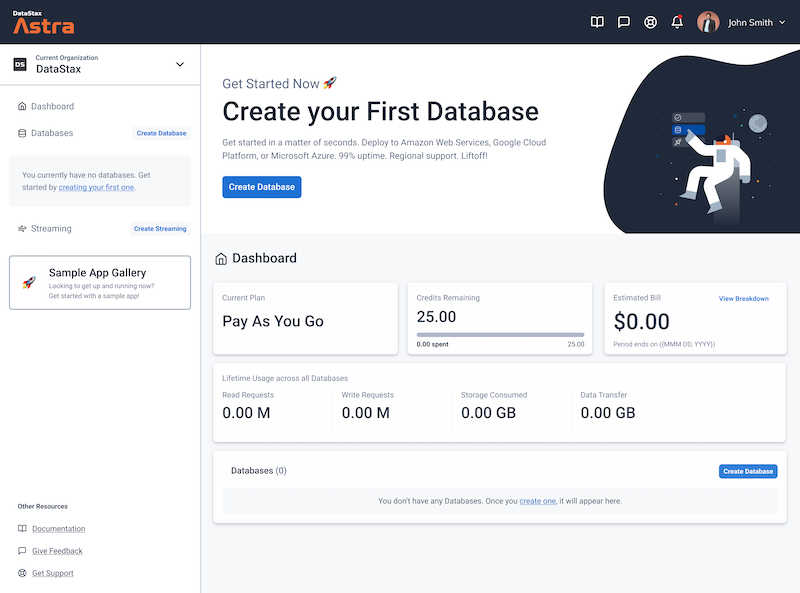
Let's do some initial setup by creating a serverless(!) database.
-
Create a DataStax Astra account if you don't already have one:
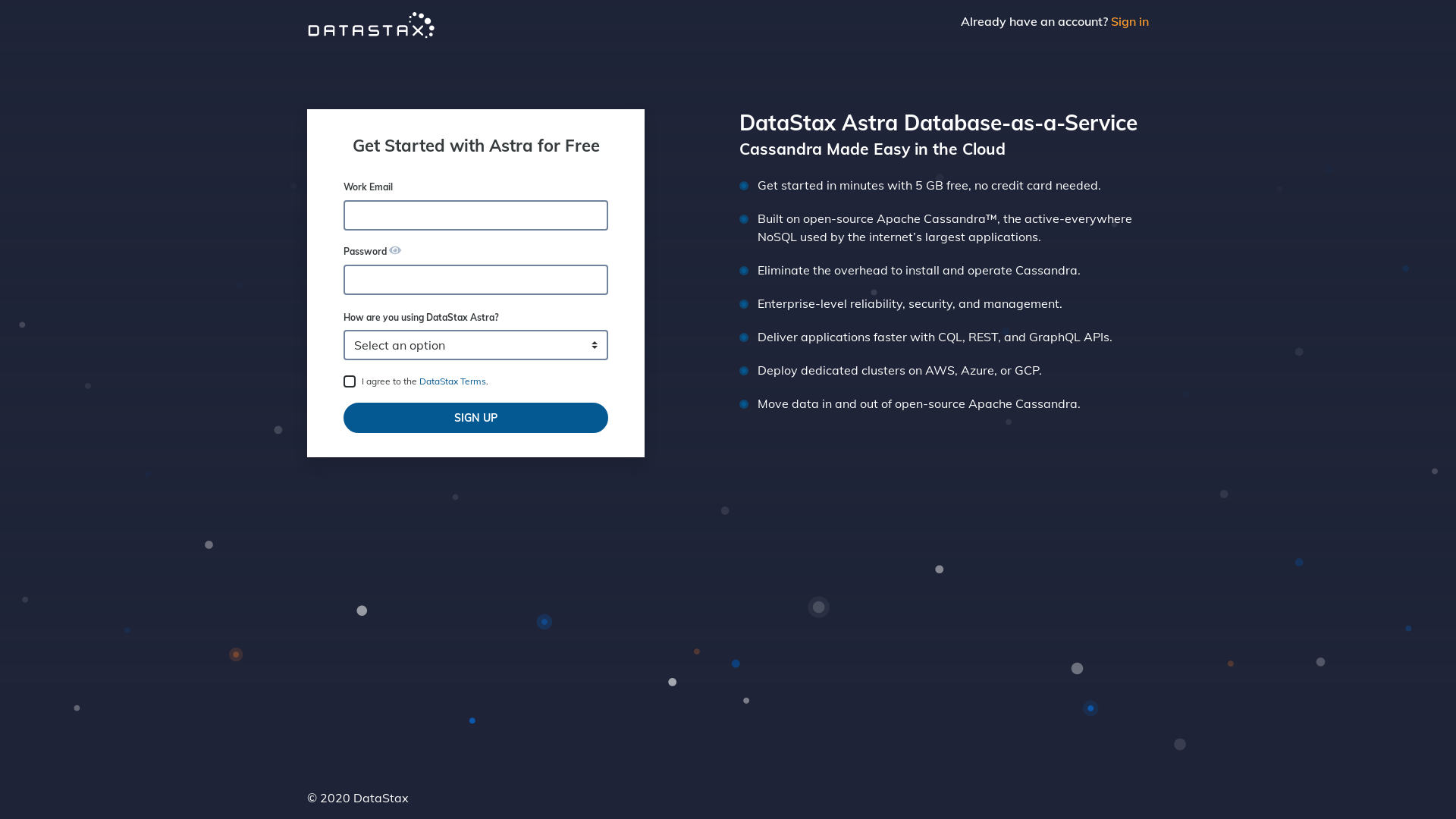
-
Define a database name, keyspace name and select a database region, then click create database.
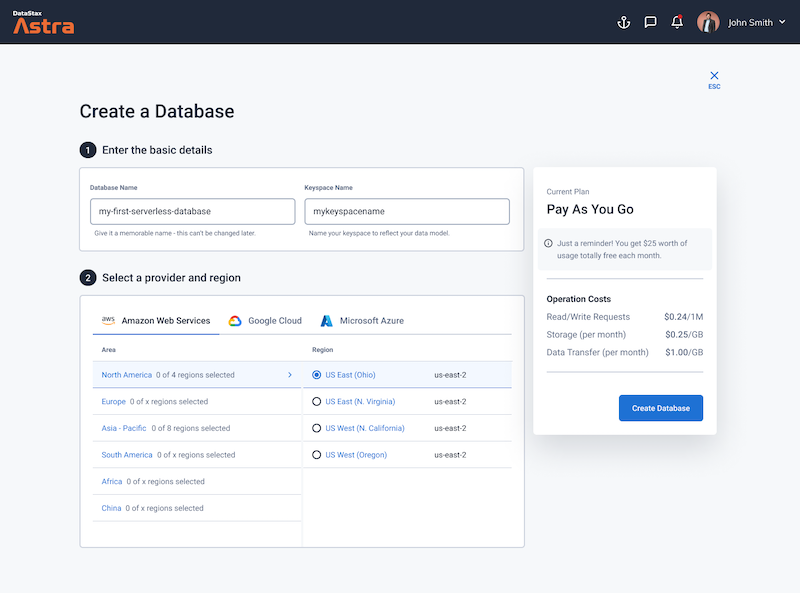
-
Your Astra DB will be ready when the status will change from
PendingtoActive💥💥💥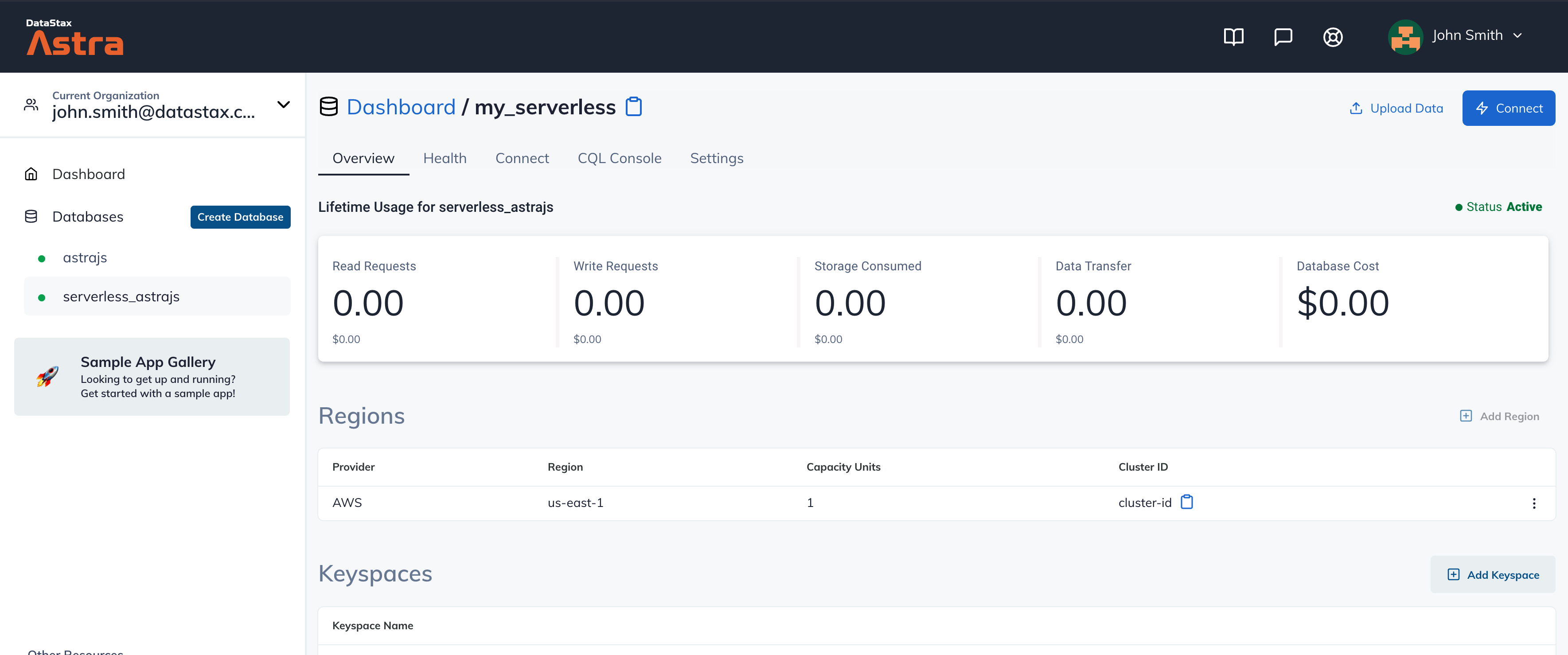
-
After your database is provisioned, we need to generate an Application Token for our App. Go to the
Settingstab in the database home screen.
-
Select
Admin Userfor the role for this Sample App and then generate the token. Download the CSV so that we can use the credentials we need later.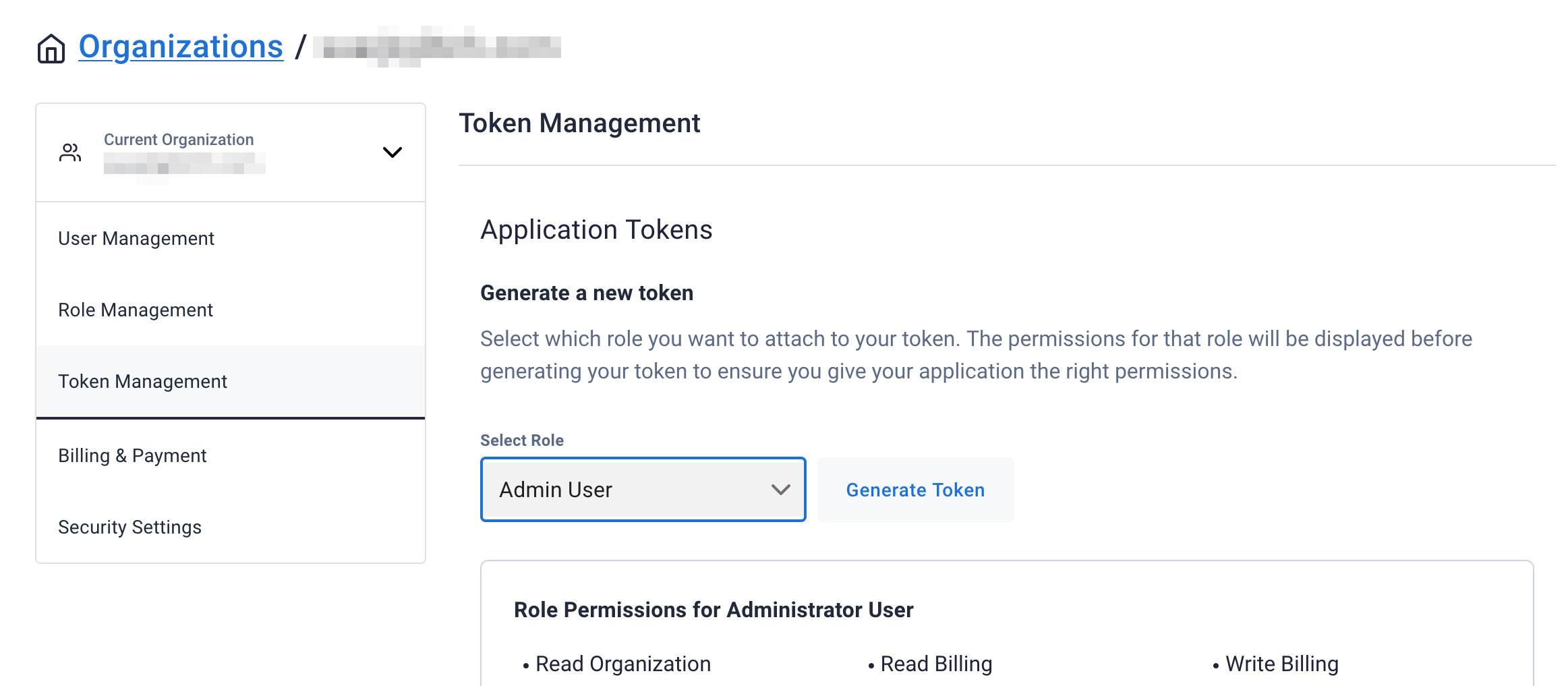
-
After you have your Application Token, head to the database connect screen and select the driver connection that we need. Go ahead and download the
Secure Bundlefor the driver.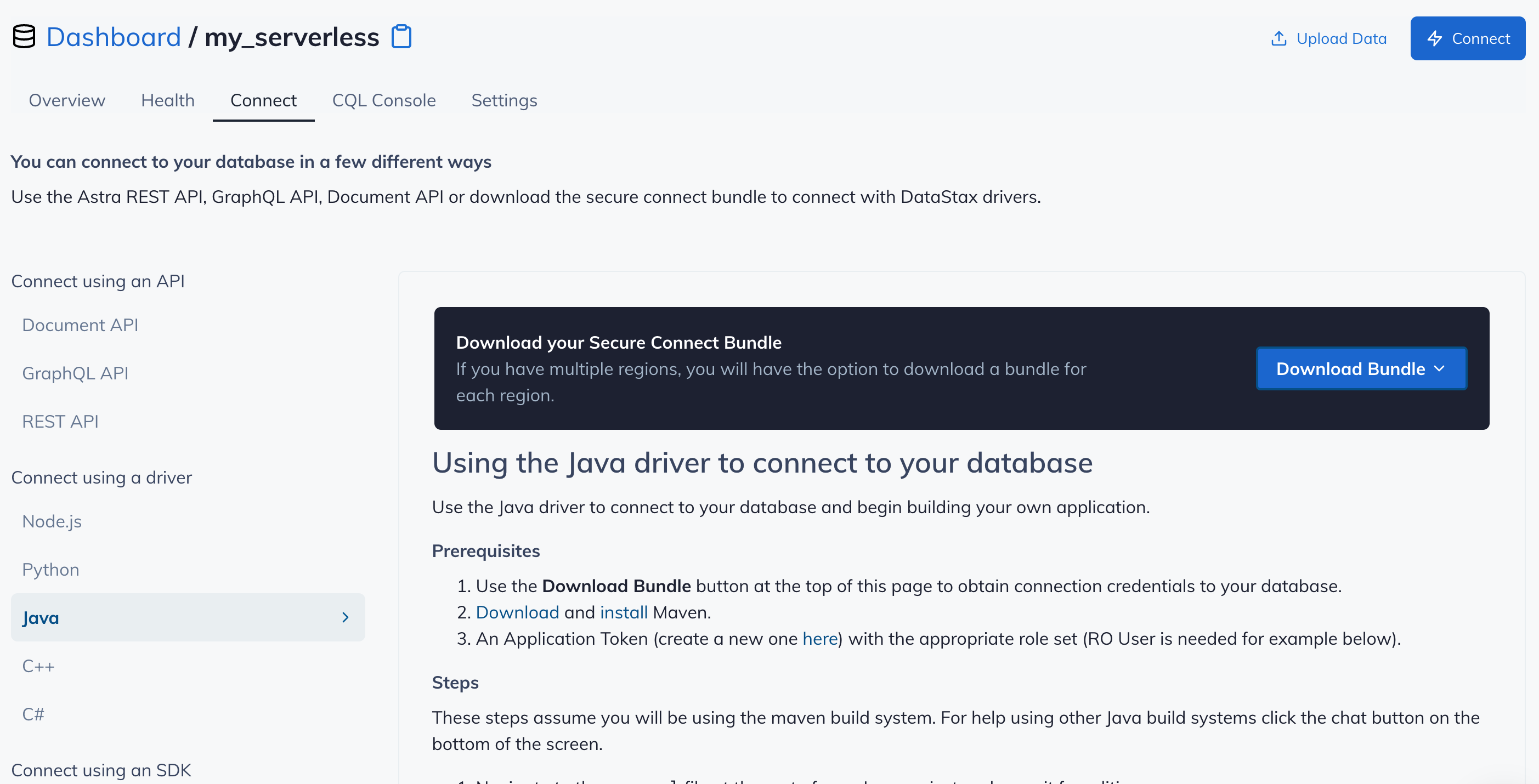
-
Make note of where to use the
Client IdandClient Secretthat is part of the Application Token that we generated earlier.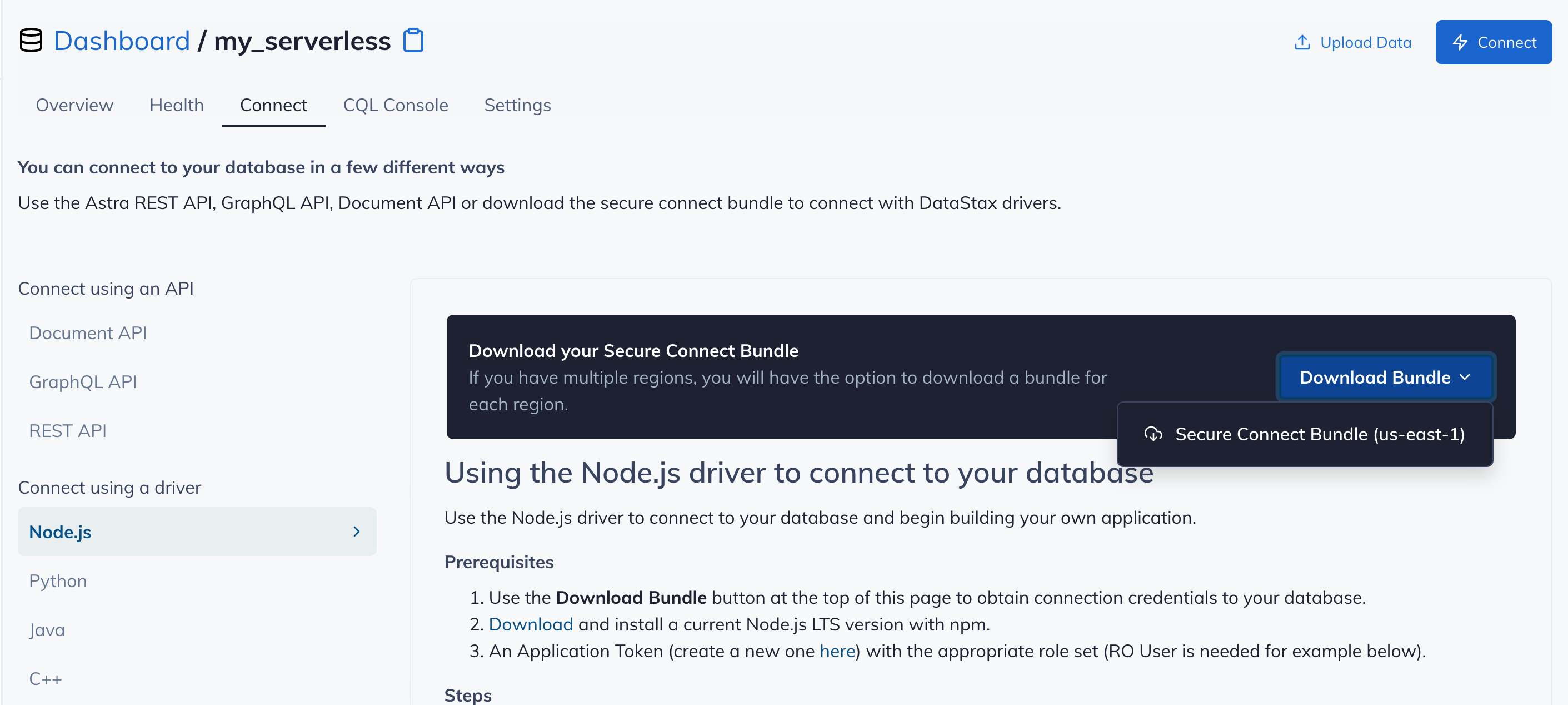
-
Click
Use this templateat the top of the GitHub Repository: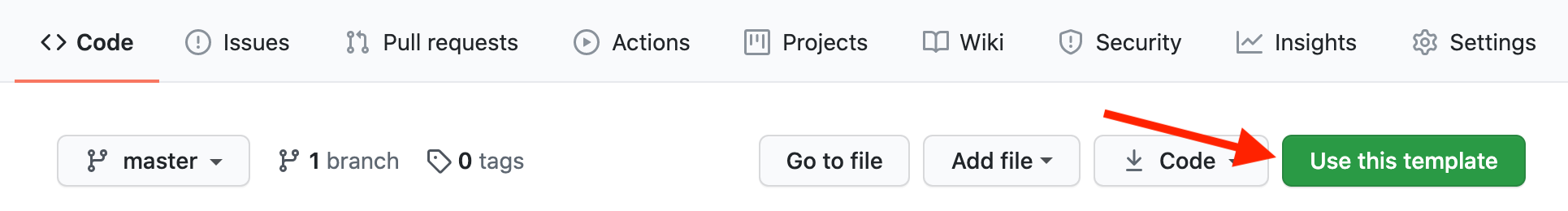
-
Enter a repository name and click 'Create repository from template':
Make sure you've completed the prerequisites before starting this step
Before running with this example, head over to the SETUP-README for instructions on how to
- launch an instance in Google Cloud
- install and start a Cassandra database
- setup your local development environment for Node.js and serverless
Once the above is completed, you will have all of the needed pieces in place to run this example.
- Install the DataStax Cassandra Driver
npm install cassandra-driver- Install serverless-google-cloudfunctions plugin
npm install serverless-google-cloudfunctions- Configure
serverless.ymlwith your project-id, credentials file, Contact Points ( public IP of GCP instance ), and Local Data Center ( likelydatacenter1)
From the project directory, deploy your function. This should output the endpoints that you can use to access the database.
sls deploy- When you are done, don't forget to clean things up with
sls remove
curl -X POST https://us-central1-<project-id>.cloudfunctions.net/createCatalogexpected output:
"Successfully created shopping.catalog schema"Note the -H "Content-Type:application/json" is required here.
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"item_id": 0, "name": "name_0", "description": "desc_0", "price": 10.1}' https://us-central1-<project-id>.cloudfunctions.net/addItemexpected output:
{"query":"INSERT INTO shopping.catalog (item_id, name, description, price) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)","item_id":0,"name":"name_0","description":"desc_0","price":10.1}curl -X GET https://us-central1-<project-id>.cloudfunctions.net/getItem/0expected output:
{"query":"SELECT name, description, price FROM shopping.catalog WHERE item_id = ?","item_id":["0"],"name":"name_0","description":"desc_0","price":"10.1"}