This library allows a Z-Uno to control via the SPI interface a Sharp memory LCD display. It provides functions to display lines, rectangles, circles and text in various sizes. It has been optimized to use economically the limited resources of the Z-Uno devices, especially the stack and the dynamic memory.
The library provides the following functionalities:
- Communication to the LCD display via the Z-Uno SPI library
- Basic drawing functions: Line, rectangle and circle
- Character, string and integer write functions
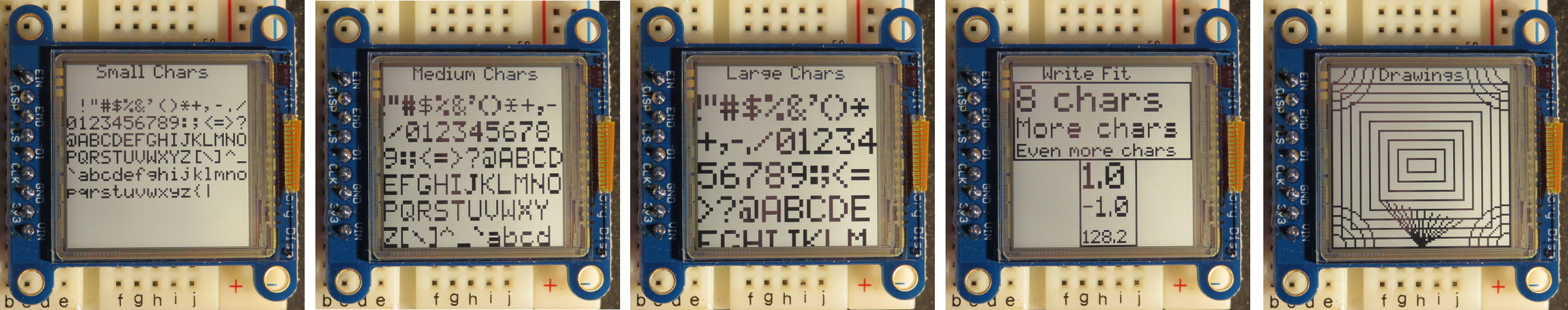
- 3 font sizes: 5x7, 8x11, 10x14
- Font patterns are stored in the code space (to reduce data space requirements)
- Write functions to fit strings and integers into specified areas, taking the biggest possible font
- Display can be oriented in 4 directions
The library has the following limitations and constraints:
- Only a single display can be controlled at the same time
- The display needs to be refreshed at least once per second by calling the method refresh
- The library has only been tested for a display size of 96x96 pixels
- An important amount of data space is required for the display buffer to store the full display content (1152 bytes for a 96x96 dot display)
- Getting started
- API - LCD display setup
- API - Display updates and refreshes
- API - Display buffer updates: Clear, line, rect, circle
- API - Display buffer updates: Write methods
- API - Auxiliary functions
- Release history
- License
Connect Sharp Memory LCD display properly to the Z-Uno device as specified in the following table:
| Adafruit | LS013B4DN04 | Z-Uno |
|---|
VIN | N/A | 5V (available for Adafruit display)
3v3 | VDDA/VDD | NC (3.3V if directly supplied)
GND | VSSA/VSS | GND
CLK | SCLK | SCK (pin 0)
DI | SI | MOSI (pin 2)
CS | SCS | SPI_CS (pin 8)
EMD | ExtMode | GND (=software clock for VCOM)
DISP | DISP | 5V (3.3v if directly supplied)
EIN | ExtComIn | NC (not connected)
Add the Sharp Memory LCD Display Library to the Z-Uno project. The library .h and .cpp files have to be stored in the Z-Uno project directory.
Include the LCD display library in the following way in your Z-Uno application:
- Include the LCD display library header file (.h)
- Create a sharpMemoryLCD class instance
- Call the method begin in the setup function
- Start each display update by clearing the display buffer with the method clear.
- Use the different drawing and writing functions to update the display data buffer. This will not yet update the physical display.
- Update the physical display with the method update.
- Ensure that the display is refreshed at least once every second by calling the method refresh (software VCOM clock).
/* 1 */ #include "SharpMemoryLCD.h"
/* 2 */ sharpMemoryLCD LCD=sharpMemoryLCD();
void setup() {
/* 3 */ LCD.begin();
}
void loop() {
/* 4 */ LCD.clear();
/* 5 */ LCD.circle(48,48,45);
LCD.writeS( 0, 0, "ABCD.1234 abcd!?");
LCD.rect(0, yp, 47, 95);
/* 6 */ LCD.update()
for (int c=0; c<60; c++) {
delay(1000);
/* 7 */ LCD.refresh();
}
}The Sharp Memory LCD Display Library .h and .cpp files have to be stored in the Z-Uno project directory. Include the library to the Z-Uno project:
#include "SharpMemoryLCD.h"The display size and the orientation are specified on the beginning of the .h include file. They can be changed to adapt to the size and orientation of the available display.
#define SMLCD_HEIGHT 96
#define SMLCD_WIDTH 96
#define SMLCD_ORIENTATION 270The .h include file defines in function of the display size a specific data type for coordinates as well as a constant for not applicable/available positions.
-
Small displays (heights and widths smaller than 256 pixels):
typedef byte xy_t; #define xy_tNA 255
-
Bigger displays (heights or widths equal or above 256 pixels):
typedef unsigned int xy_t; #define xy_tNA 0xffff
The following methods create a LCD display class instance and initialize it.
SharpMemoryLCD::SharpMemoryLCD();Creates an LCD display class instance. Only a single instance can be created per project. And therefore only a single physical display can be controlled.
--
--
sharpMemoryLCD LCD=sharpMemoryLCD();void SharpMemoryLCD::begin();Initializes the SPI interface including the CS pin as well as the class instance variables. This method has to be called inside the setup function.
--
--
void setup() {
LCD.begin();
}The following methods update and refresh the physical LCD display via the SPI interface. They don't update the local display buffer.
void SharpMemoryLCD::clearDisplay();Clears the physical display (but not the display buffer).
--
--
LCD.clearDisplay();void SharpMemoryLCD::update();Updates the physical display by transferring the data of the local display buffer to the display.
--
--
LCD.update();void SharpMemoryLCD::refresh()Refreshes the physical display by sending a toggle VCOM command. This method should be executed regularly at least once per second if no other physical display updates are performed. The method can be called without performance impact in much shorter intervals, since it skips display updates if they are requested in less than 750ms after the last refresh.
--
--
LCD.refresh();This group of methods provide basic drawing functionalities. They update the local display buffer but not the physical display itself.
void SharpMemoryLCD::clear();Clears the display buffer.
--
--
LCD.clear();void SharpMemoryLCD::setPixel(xy_t x,xy_t y);Sets a single pixel. Pixels that are outside of the display area are ignored.
- x - X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y - Y coordinate, type: xy_t
--
LCD.setPixel(48,48);void SharpMemoryLCD::line(xy_t x0, xy_t y0, xy_t x1, xy_t y1);Draws a line between the coordinates (x0,y0) and (x1,y1). The line endpoints can be situated outside of the display area.
- x0 - Start point X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y0 - Start point Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- x1 - End point X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y1 - End point Y coordinate, type: xy_t
--
x=LCD.line(10,20,50,80);void SharpMemoryLCD::rect (xy_t x0, xy_t y0, xy_t x1, xy_t y1);Draws a rectangle specified by 2 opposite corners (x0,y0) and (x1,y1).
- x0 - First corner X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y0 - First corner Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- x1 - Opposite corner X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y1 - Opposite corner Y coordinate, type: xy_t
--
LCD.rect(3,3,92,92);void SharpMemoryLCD::circle(xy_t x, xy_t y, xy_t radius);Draws a circle with the center (x,y) and the radius radius. A portion of the circle may be located outside of the display area.
- x - Circle center X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y - Circle center Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- radius - Circle radius, type: xy_t
--
x=LCD.circle(48,48,47);This group of methods allow writing characters, character strings and integer values using 3 different font sizes. The methods update the display buffer but not the physical display itself.
Different methods are provided for the 3 different font sizes:
- Small size 5x7 dot font - writeChrS, writeS
- Medium size 7x11 dot font - writeChrM, writeM
- Large size 10x14 dot font - writeChrL, writeL
The additional method writeFit scales the font size in a way that the text or integer value fits into a specified field.
The write methods support various options. Multiple options can be added together, or OR-combined.
| Value | Constant/Function | Description |
|---|
1 | SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT | Narrow writing, removes extra space between characters
2 | SMLCD_WRITE_CHECKONLY | Checks only the required space without writing the characters
4 | SMLCD_WRITE_CENTERY | Used by writeFit: Centers the characters in the vertical direction if a smaller font size is used
Pos<<4 | SMLCD_WRITE_DECIMALPOS(Pos) | Used by integer writes: Places a decimal separator at the specified location
xy_t writeChrS(xy_t x,xy_t y,char Chr,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeChrM(xy_t x,xy_t y,char Chr,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeChrL(xy_t x,xy_t y,char Chr,byte Options=0);Writes a single character. The X position to write a next character is returned.
- x - X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y - Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- Chr - Character to write, type: xy_t
- Options - Type: integer
- SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT (bit 0): Writes tightly, removes unnecessary space.
- SMLCD_WRITE_CHECKONLY (bit 1): Calculates just the space and returns the X position for the next character, without updating the display buffer.
X position for the next character. Type: xy_t
x=LCD.writeChrS(x,y,'!',SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT);xy_t writeS(xy_t x,xy_t y,char *Text,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeM(xy_t x,xy_t y,char *Text,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeL(xy_t x,xy_t y,char *Text,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeS(xy_t x,xy_t y,int Val,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeM(xy_t x,xy_t y,int Val,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeL(xy_t x,xy_t y,int Val,byte Options=0);Writes a character string or an integer. The X position to write a next character is returned.
- x - X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y - Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- Text - Character string to write, type: (char *)
- Val - Integer to write, type: integer
- Options - Type: integer
- SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT (bit 0): Writes tightly, removes unnecessary space.
- SMLCD_WRITE_CHECKONLY (bit 1): Calculates just the space and returns the updated X position for the next character, without updating the display buffer.
- SMLCD_WRITE_DECIMALPOS(Pos) (bit 4<<Pos): Option only available for the integer write methods. Adds an integer separator at the specified location.
X position for the next character. Type: xy_t
x=LCD.writeS(x,y,"Hello World",SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT);
x=LCD.writeS(x,y,MyValue,SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT|SMLCD_WRITE_DECIMALPOS(2));xy_t writeFit(xy_t x0,xy_t y0, xy_t x1,char *Text,byte Options=0);
xy_t writeFit(xy_t x0,xy_t y0, xy_t x1,int Val,byte Options=0);Writes a character string or an integer using the biggest possible font size to fit into a field that is limited by the X coordinates x0 and x1. The X position to write a next character is returned.
- x0 - Starting X coordinate, type: xy_t
- y - Y coordinate, type: xy_t
- x1 - End X coordinate, type: xy_t
- Text - Text to write, type: (char *)
- Val - Integer to write, type: integer
- Options - Type: integer
- SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT (bit 0): Writes tight, removes unnecessary space.
- SMLCD_WRITE_CHECKONLY (bit 1): Calculates just the space and returns the updated X position, without updating the display buffer.
- SMLCD_WRITE_DECIMALPOS(Pos) (bit 4<<Pos): Only the integer write method. Adds an integer separator at the specified location.
X position for the next character. Type: xy_t
x=LCD.writeFit(x,y,"Hello World",SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT|SMLCD_WRITE_CENTERY);
x=LCD.writeFit(x,y,MyValue,SMLCD_WRITE_TIGHT|SMLCD_WRITE_CENTERY);char *int2Str(int v, byte DecimalPos=0);Converts a integer into a string. Positive and negative values are supported. If DecimalPos is bigger than 0 a decimal separator (',') is added at the specified position. To reduce stack usage this function has not been defined as part of the LCD display class.
- Val - Integer value, type: int
- DecimalPos - Optional decimation separator position, type: byte
Pointer to converted character string. Type: (char *)
- 0.1
- Initial revision
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details