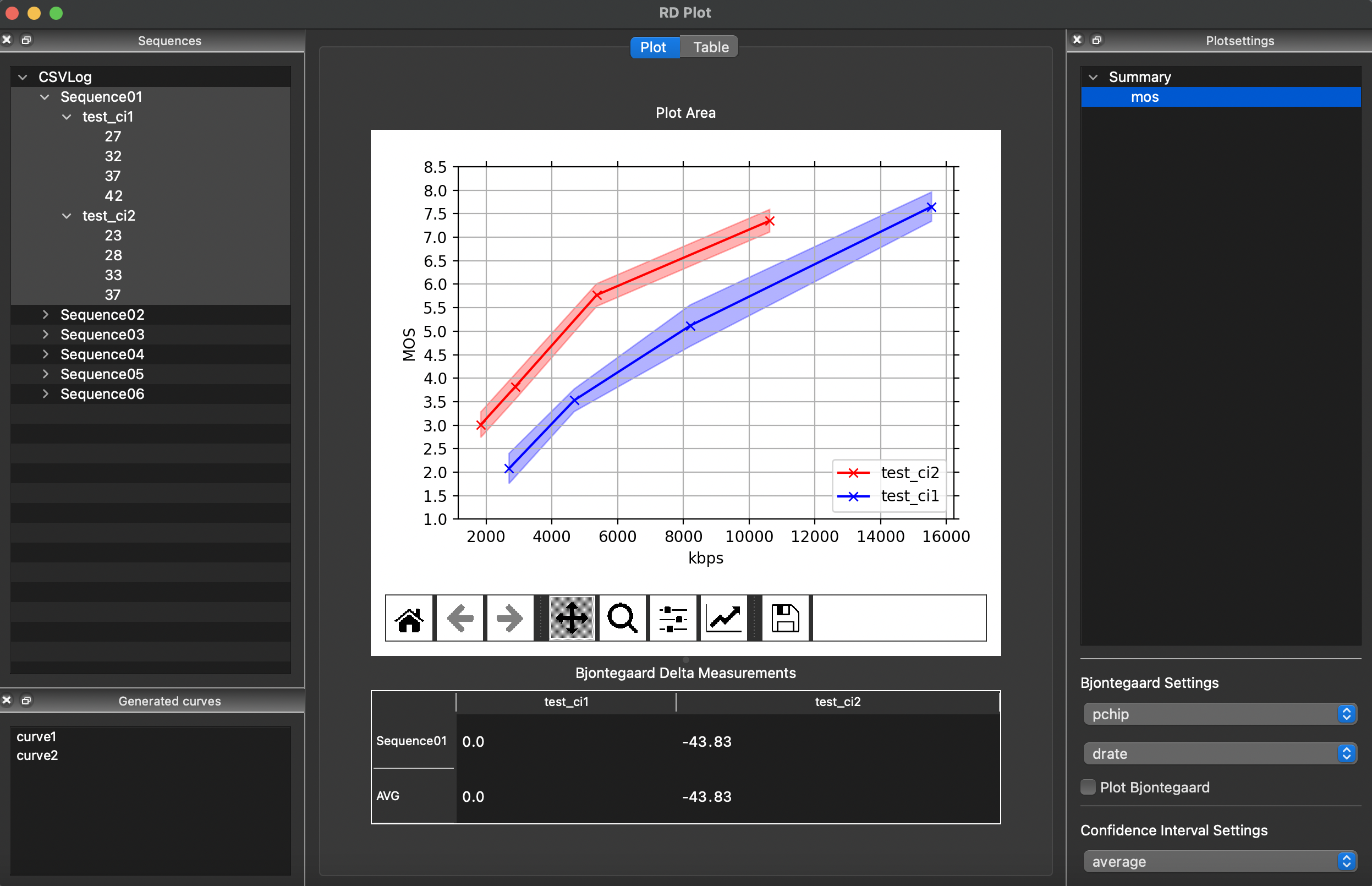
RDPlot is a tool for plotting rate distortion curves. In particular, it can
- Parse the output of reference software such as HM, SHM, or VTM.
- Parse data points from xml-formatted files.
- Parse data from csv-formatted files.
- Calculate Bjontegaard Delta statistics.
- Export plots and BD statistics for camera ready presentation.
It was developed along the design principle of easy extensibility. If no parser for your data is available, you can consider to introduce a new parser. If you feel like your parser would be of interest for others, please submit a PR.
RDPlot was presented as a Demo on VCIP 2021. Please consider citing the corresponding demo paper when using RDPlot for the evaluation of your simulations.:
@inproceedings{ScSaWi21,
author = {Schneider, J. and Sauer, J. and Wien, M.},
title = {{RDP}lot -- An Evaluation Tool for Video Coding Simulations},
booktitle = {Visual Communications and Image Processing {VCIP}~'21},
address = {Munich},
year = {2021},
month = {12},
publisher = {{IEEE}, Piscataway},
}
| AppVeyor | GitHub Actions |
|---|---|
In the following sections different installation strategies are outlined:
RDPlot is available on PyPi. Therefore, you can directly install RDPlot via pipx:
pipx install rdplot
This should work on all platforms. However, on Apple silicon you might have to fiddle a bit and use Rosetta.
For Windows an installer is available on the release page. The installer will install a released version. If you want to install the most recent (unreleased) version, you can download the installer from Appveyor's artifacts.
We assume that you are familiar to Python development for the following sections. If you run into any problems, don't hesitate to use the Issue tracker.
If you need system packages that conflict with the packages required for RDPlot, you can use a python virtual environment (see below).
When you are inside a virtual environment, python ignores all system packages and instead uses a dedicated environment, allowing you to install packages with pip that would otherwise conflict with system packages and/or different versions. The pitfall is that you need to activate the environment each time you want to use the program.
You can find more info on virtual environments at https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/.
venv is included in python since version 3.3. If your python version is older consider upgrading, or install venv using:
sudo pip install virtualenv
Download RDPlot. Make sure you do this at a place where it can stay:
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/IENT/RDPlot cd RDPlot
Create a virtualenv named "env" inside the RDPlot directory:
python3 -m venv env
Activate the venv and install dependencies:
source env/bin/activate pip3 install --upgrade pip gitpython
Build and install RDPlot:
python3 setup.py sdist pip3 install --no-binary rdplot --upgrade dist/rdplot-*.tar.gz
Leave the environment:
deactivate
Remember to activate the environment every time you want to run RDPlot:
cd RDPlot source env/bin/activate rdplot deactivate
To uninstall, simply delete the RDPlot directory.
Note: things are not tested for Mac. You may have to fiddle a little bit. Please contribute, if you have ideas for improvements.
First of all you need to install python3. You can get it here. If you are using Homebrew you can alternatively install python3 via console:
brew install python@3.9
Moreover, install all the requirements:
cd src/rdplot pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Additionally install py2app:
pip3 install py2app
Then navigate back to the top level and build an app in alias mode:
cd ../.. python3 setup.py py2app -A
Now you should have an app in the dist folder.
Note: This app contains hard links to the directory with the source. It is strongly recommended to clone the whole directory to your Applications folder. Then you can simply build the app and launch it from the internal search. Another possibility is to put an alias in your Applications folder and/or attach it to the Dock.
If you want to update the app, it is fairly easy: Navigate to the local copy of the repository (now most probably in your Applications folder) and then:
git pull python3 setup.py py2app -A
Done!
Uninstall is also simple: Just delete the local copy of the repositories and all aliases.
If you want to help improving RDPlot, you most probably need to run it directly from source for development and testing.
You can start RDPlot from the command line with:
PYTHONPATH=~PATH_TO_RDPLOT/src/ python3 PATH_TO_RDPLOT/src/rdplot/__main__.py
If you want to start the tool out of an IDE, make sure that you have set the PYTHONPATH environment variable correctly.