Header only library. Requires c++17.
Features a class to calculate with time and multiple timer classes for recording and profiling.
Please use clang-tidy if you want to contribute: easy installation
- adding/substracting while considering the unit: 1[s] + 1[s] -> ok; 1[s] + 1[s^2] -> error
- division/multiplication with
- a) int/double/etc
- b) PreciseTime class while keeping track of the unit: 1[s] * 1[s] = 1[s^2]
- calculateing the square root of a PreciseTime keeping track of the unit: sqrt(4[s^2]) = 2[s].
- Comparisons: {==, !=, <=, >=, <, >}
- Nice print output: std::cout << my_precise_time << std::endl;
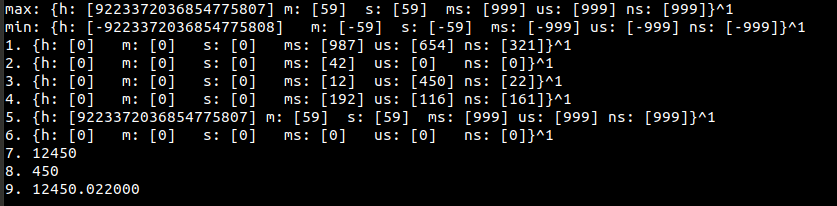
- Max Time: h: [9223372036854775807] m: [59] s: [59] ms: [999] us: [999] ns: [999]
- Min Time: h: [-9223372036854775808] m: [-59] s: [-59] ms: [-999] us: [-999] ns:[-999]
- Constexpr construction and arithmetic (appart from sqrt)
- A dynamic PreciseTime where the user can specify the needed resolution and the max time span to optimize calculation
- Optimize: get rid of the internal seconds
- Record multiple times (e.g. in a loop) the execution time of e.g. a function.
- As many (named) timers as you like, held in one instance of the CollectingTimer class.
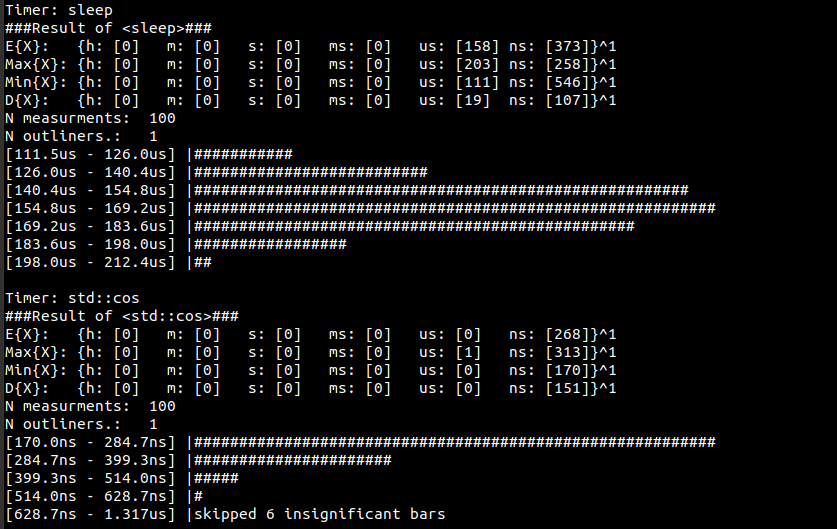
- On demand output of max, min, mean, median, standard deviation for all timers.
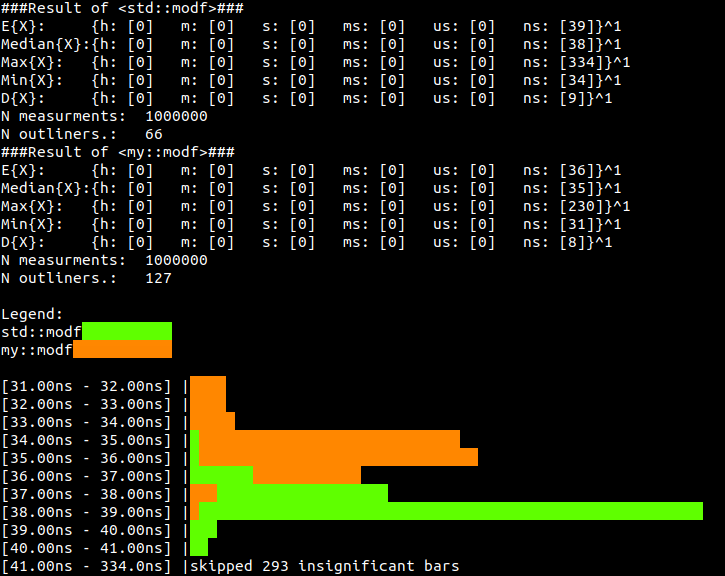
- Print Histogram of measurements into console
- Write multiple histograms on top of each other for better comparison in console.
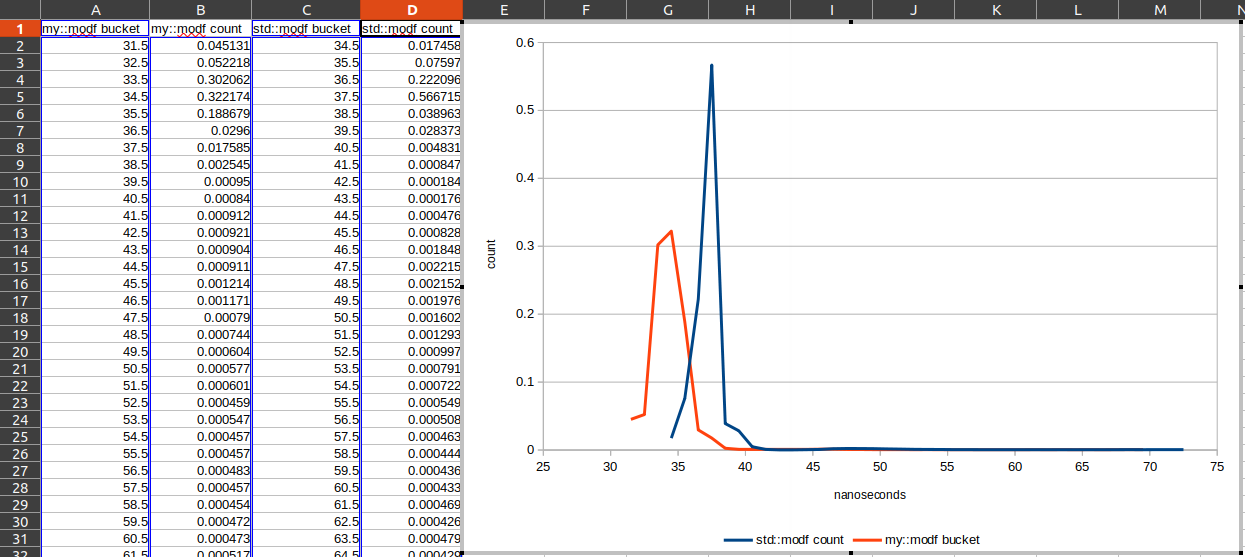
- Write measurements to file for further investigation in your favorite table calculation or MATLAB/Octave
- Print histogram to file for further investigation in your favorite table calculation (choose X-Y-Plot) or MATLAB/Octave.
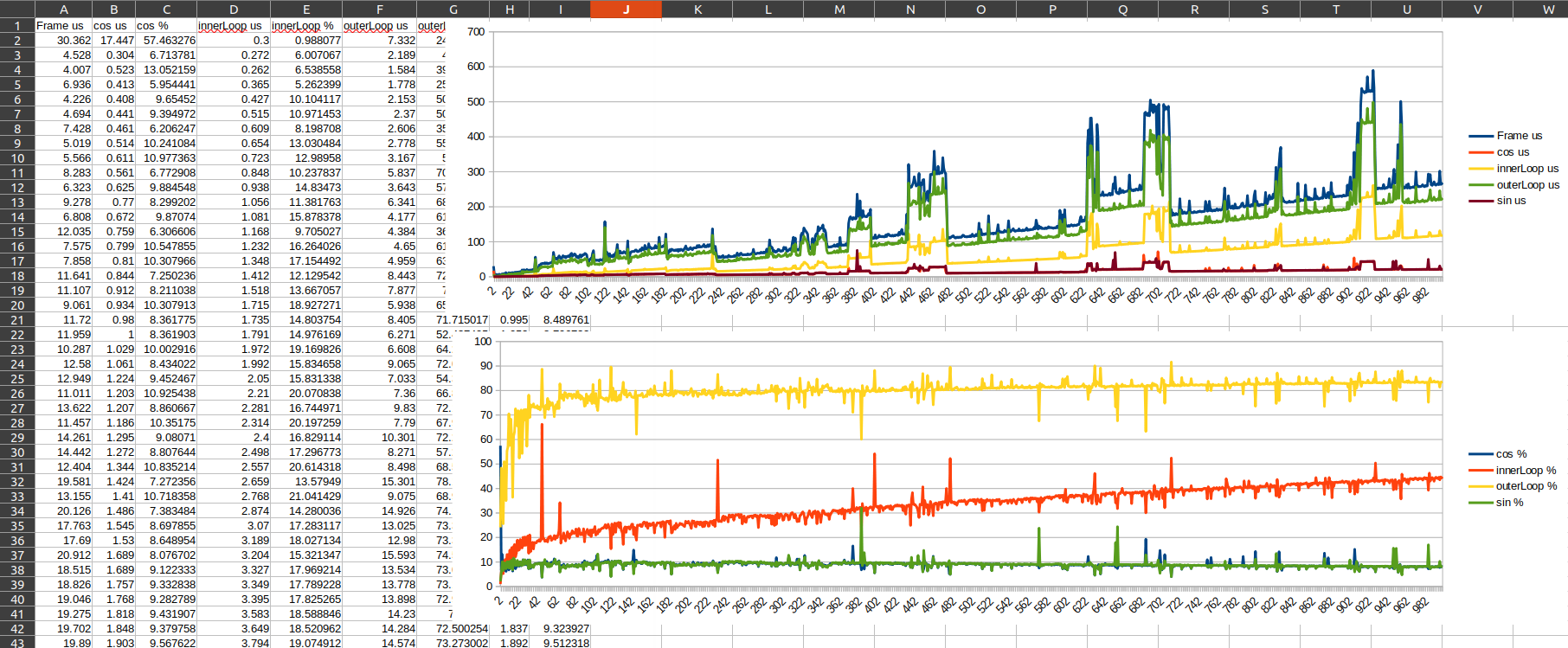
- To be used in a loop: For every loop/frame record the execution time of multiple functions (via named timers) called (multiple times) in that loop.
- Print for every frame the total execution time of a (named) timer into a file for further investigation in your favorite table calculation or MATLAB/Octave
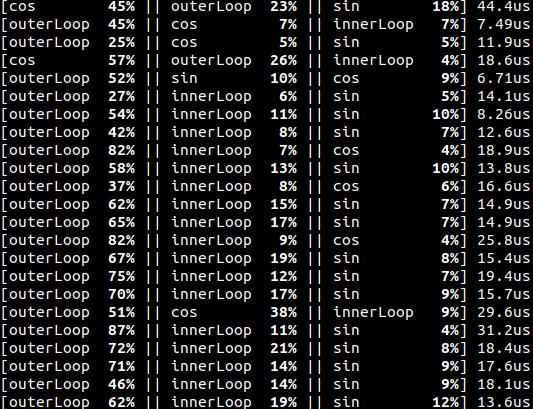
- simple console debug output showing the 3 longest running functions in the last frame.
- LiveStream every Frame via tcp/ip socet into a GUI to have a live graph
- At the moment only the accumulated time per frame per timer is available in the output file. Maybe show every call and duration as a rectangle in a timeline for every function.
- Starts the timer on creation and stops it on destruction. A callback function to report the result must be provided.
- Start/Reset/getTime nothing more.
- If you use CMake to build your project place this repro inside 'path' and use add_subdirectory(path/ timer) and target_link_libraries(your_lib timer_lib)
- Or just include the header
- To run the tests run
scripts/debug_build.sh
#include "include/precise_time.hpp"
int main() {
constexpr PreciseTime max_pt = PreciseTime::max();
constexpr PreciseTime min_pt = PreciseTime::min();
std::cout << "max: " << max_pt << "\n"
<< "min: " << min_pt << "\n";
using ns = std::chrono::nanoseconds;
using us = std::chrono::microseconds;
using ms = std::chrono::milliseconds;
using s = std::chrono::seconds;
using m = std::chrono::minutes;
using h = std::chrono::hours;
// construction
PreciseTime my_time1(ns(987654321));
std::cout << "1. " << my_time1 << "\n";
PreciseTime my_time2(ms(42));
std::cout << "2. " << my_time2 << "\n";
constexpr PreciseTime my_time3 = ns(22) + us(450) + ms(12);
std::cout << "3. " << my_time3 << "\n";
constexpr std::array<long, 6> seperated_times = my_time3.getSeperatedTimeComponents();
const std::array<std::string, 6> info = {
"nanoseconds.", "microseconds.",
"milliseconds.", "seconds.",
"minutes.", "hours."};
for(size_t i = 0; i < 6; i++){
std::cout << seperated_times[i] << " " << info[i] "\n";
}
// calculations: add/substract times
my_time1 = my_time1 + my_time1;
my_time1 -= my_time2;
// calculations: multiply/divide by factor
my_time2 *= 1.5;
my_time2 = my_time2 / 3.3;
// calculations: s*s = s^2
PreciseTime timeSquared = my_time1 * my_time2;
// This throws a runtime error if build in debug mode.
// calculations: s^2 + s: can't mix units
// PreciseTime corruptedTime = timeSquared + my_time1;
// Takeing the square root only works with usints s^n where n is even.
PreciseTime normalTime = PreciseTime::sqrt(timeSquared);
std::cout << "4. " << normalTime << "\n";
// overflow protection
constexpr auto my_time4 = max_pt * 5; // my_time4 is still max_pt
std::cout << "5. " << my_time4 << "\n";
// constexpr arithmetic
constexpr auto zero_t = max_pt - my_time4;
std::cout << "6. " << zero_t << "\n";
// coversations
typedef std::chrono::microseconds exampleType;
// This gets the time in exampleType ! this might result in resolution loss
// if the time is 22ns and 450us and 12ms, This returns exact 12450us
constexpr exampleType us = my_time3.convert<exampleType>();
std::cout << "7. " << us.count() << "\n";
// if the time is 22ns and 450us and 12ms, This returns exact 450us
constexpr exampleType part_us = my_time3.get<exampleType>();
std::cout << "8. " << part_us.count() << "\n";
// if the time is 22ns and 450us and 12ms, This returns exact* 12450.022
// double precision exact
constexpr double floatingPoint = my_time3.toDouble<exampleType>();
std::cout << "9. " << std::fixed << floatingPoint << "\n\n";
return 0;
}#include "include/collecting_timer.hpp"
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <random>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
CollectingTimer timer;
std::random_device rd;
std::default_random_engine generator(rd());
const double mean = 1.;
const double deviation = 0.15;
std::normal_distribution<double> distribution(mean, deviation);
const std::string timer_cos("std::cos");
const std::string timer_sleep("sleep");
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
const double sleep = distribution(generator);
timer.start(timer_sleep);
usleep(sleep * 100);
timer.stop(timer_sleep);
timer.start(timer_cos);
std::cos(static_cast<double>(i) / 100.);
timer.stop(timer_cos);
}
std::cout << timer << "\n";
return 0;
}#include "include/collecting_timer.hpp"
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <random>
#include <unistd.h>
// from https://github.com/google/benchmark/blob/main/include/benchmark/benchmark.h
#define BENCHMARK_ALWAYS_INLINE __attribute__((always_inline))
template <class Tp>
inline BENCHMARK_ALWAYS_INLINE void DoNotOptimize(Tp const& value) {
asm volatile("" : : "r,m"(value) : "memory");
}
template <class Tp>
inline BENCHMARK_ALWAYS_INLINE void DoNotOptimize(Tp& value) {
#if defined(__clang__)
asm volatile("" : "+r,m"(value) : : "memory");
#else
asm volatile("" : "+m,r"(value) : : "memory");
#endif
}
constexpr double fastModF(double x, double& full) noexcept {
full = static_cast<double>(static_cast<long long>(x));
return x - full;
}
int main() {
CollectingTimer timer;
std::random_device rd;
std::default_random_engine generator(rd());
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> distr(-1000000000000000000., 100000000000000000000.);
constexpr int num_tests = 1000000;
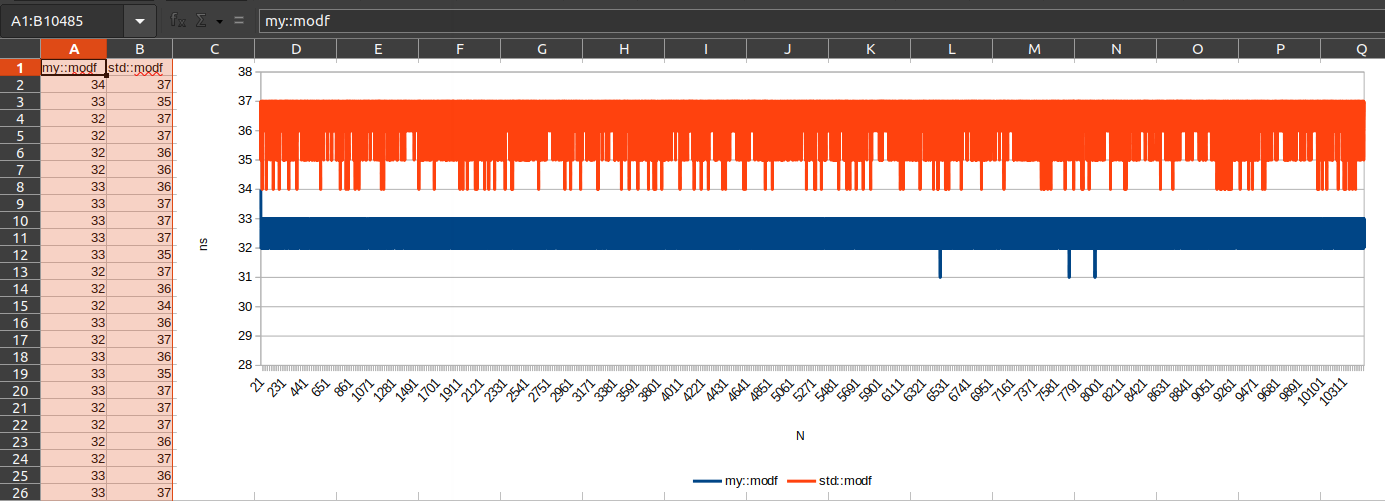
const std::string timer_std_modf("std::modf");
const std::string timer_my_mod_f("my::modf");
for(int i = 0; i < num_tests; i++){
const double d = distr(rd);
timer.start(timer_std_modf);
double full = 0.;
const double decimals = std::modf(d, &full);
timer.stop(timer_std_modf);
DoNotOptimize(full);
DoNotOptimize(decimals);
timer.start(timer_my_mod_f);
double full_mine = 0.;
const double decimals_mine = fastModF(d, full_mine);
timer.stop(timer_my_mod_f);
DoNotOptimize(full_mine);
DoNotOptimize(decimals_mine);
}
// save in file
timer.histogramToFile<std::chrono::nanoseconds>("/tmp/histo.csv", ';');
timer.measurementsToFile<std::chrono::nanoseconds>("/tmp/measure.csv", ';');
// print to console
std::vector<CollectingTimer::Result>results(2);
timer.getResult(timer_std_modf, results[0]);
timer.getResult(timer_my_mod_f, results[1]);
std::cout << results;
return 0;
}#include <timer/frame_timer.hpp>
FrameTimer ft;
std::string t1("innerLoop");
std::string t2("outerLoop");
std::string t3("cos");
std::string t4("sin");
int f1(int i) {
const auto t = ft.startScopedTimer(t1);
int a = 0;
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
a += j;
}
return a;
}
int f2(int i) {
const auto t = ft.startScopedTimer(t2);
int a = 0;
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
a += f1(j);
}
return a;
}
int f3(int i) {
const auto t = ft.startScopedTimer(t3);
int a = 0;
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
a += std::cos(j);
}
return a;
}
int f4(int i) {
const auto t = ft.startScopedTimer(t4);
int a = 0;
for (int j = i; j > 0; --j) {
a += std::sin(j);
}
return a;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> erg;
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; ++i) {
ft.frameStart<true>();
erg.push_back(f2(i));
erg.push_back(f3(i));
erg.push_back(f4(i));
}
ft.measurementsToFile<std::chrono::microseconds>("/tmp/frames.csv", ';');
return erg[0];
}