This project is work-in-progress and starts as a tool to access the CAN buses available on my Mazda3, for reverse engineering and for fun.
Development is done on an ESP32 DevKitC V4 board, which includes an ESP32-WROOM-32D module.
Built and tested with ESP-IDF v5.1.
- ✔ CAN connection with vehicle
- Tested CAN transceivers: SN65HVD230, MCP2551 (with 5V -> 3.3V RX voltage translation)
- ✔ Linux SocketCAN compatibility with
slcandriver - ✔ Bluetooth
slcanover Bluetooth Classic Serial Port Profile (SPP)- legacy pairing PIN is 0000
- note: this connection method is unreliable, dropped messages caused by ESP32 Bluetooth driver congestion are highly likely
- ❔ WiFi: softAP and/or STAtion
- is there some standard protocol for CAN over TCP/UDP? not really...
- GVRET is undocumented (though an implementation exists)
- socketcand is too complex and out of scope
- other proprietary protocols... are proprietary
- SLCAN over TCP:
- ESP32 side: expose TCP server with SLCAN
- client side: use
socatto bind a virtual serial port to the TCP socket, use the virtual serial port withslcandor directly with SavvyCAN
- is there some standard protocol for CAN over TCP/UDP? not really...
- ❔ logging to SD card
- same file format as
candump?
- same file format as
- ❔ OBD/UDS diagnostics
- ❔ reverse engineered Mazda-specific messages
- ❔ custom protocol for better efficiency?
- ❔ ...
Use the VSCode ESP-IDF extension.
Check idf.openOcdConfigs in your settings.json (currently set up for J-Link).
- Pair device via GUI or with
bluetoothctl sudo rfcomm bind rfcomm0 aa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ffwhereaa:bb:cc:dd:ee:ffis the Bluetooth address of your ESP32 (found while pairing or in ESP32 logs)
This adapter implements the LAWICEL SLCAN protocol as expected by the slcan SocketCAN driver, so that it can be used with can-utils' slcand and other utilities like cansniffer.
Set up CAN interface:
sudo slcand -o -c -s6 -S 921600 /dev/ttyUSB0 slcan0 # add -F to run in foreground, use /dev/rfcomm0 for Bluetooth serial portExpose with socketcand:
sudo socketcand -v -i slcan0Sniff bus in real time:
sudo ip link set up slcan0
cansniffer slcan0Dump to file:
candump -l slcan0Replay from file:
sudo ip link add dev vcan0 type vcan
sudo ip link set up vcan0
# Replay slcan0 dump on vcan0 in infinite loop
canplayer vcan0=slcan0 -li -I ./candump-*.logBroadcast request ID: 0x7DF
ECU-specific request ID: 0x7E0-0x7E7
ECU-specific response ID: 0x7E8-0x7EF
OBD format: (8 data bytes) ...
0x7DF - 2 0x01 0x00 0xCC 0xCC 0xCC 0xCC 0xCC
Ethernet twisted pair cable should help with signal integrity (it's designed to carry differential signals).
| Ethernet twisted pair | Signal | OBD-II connector pin |
|---|---|---|
| blue + white blue | +12V | 16 |
| brown + white brown | ground | 4 |
| white orange | HS CANH (500kbps) | 6 |
| orange | HS CANL (500kbps) | 14 |
| white green | MS CANH (125kbps) | 3 |
| green | MS CANL (125kbps) | 11 |
| Card pin | SPI mode | SD 1-bit mode | SD 4-bit mode | ESP32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | DAT2 | (12) |
| 2 | CS | CD | DAT3 | (13) |
| 3 | MOSI | CMD | CMD | 15 |
| 4 | 3V3 | 3V3 | 3V3 | 3V3 |
| 5 | SCLK | CLK | CLK | 14 |
| 6 | GND | GND | GND | GND |
| 7 | MISO | DAT0 | DAT0 | 2 |
| 8 | - | - | DAT1 | (4) |
Notes:
- For SD 1-bit mode, CMD, CLK and DAT0 lines must be pulled up (10KOhm). CD/DAT3 should also be pulled up (10KOhm) on the card side
- GPIO2 (DAT0) conflicts with ESP32 serial download mode, possible solutions: disconnect GPIO2 from SD or jumper GPIO0 and GPIO2 (auto-reset should work)
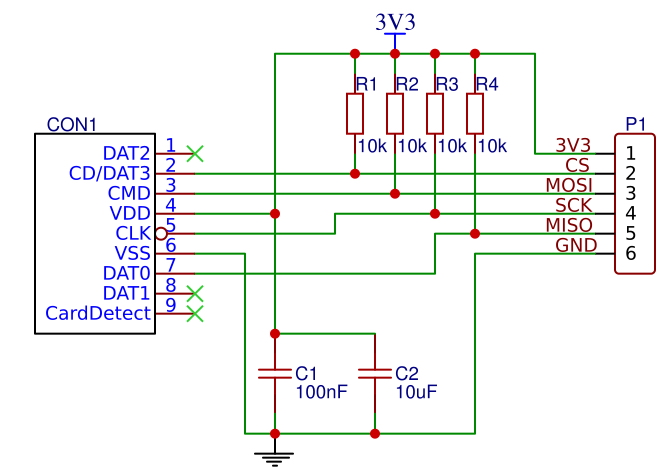
Schematic of the microSD breakout board I'm using:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OBD-II_PIDs
- https://x-engineer.org/automotive-engineering/internal-combustion-engines/diagnostics/on-board-diagnostics-obd-modes-operation-diagnostic-services/
- https://www.mazdaclub.it/forum/viewtopic.php?f=52&t=23307&p=272187&hilit=extra#p272187
GUI tools:
Message databases:
- https://github.com/majbthrd/MazdaCANbus
- https://github.com/commaai/opendbc
- https://github.com/silverchris/Mazda3_Canbus_Messages
Message database conversion:
Other tools:
Blogs:
- http://she-devel.com/Mazda3_Controller_Area_Network_Experimentation.html
- http://www.madox.net/blog/projects/mazda-can-bus/
- http://opengarages.org/index.php/Mazda_CAN_ID
- https://mx5things.blog/2017/02/18/can-bus-sniffer/
- https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/networking/can.txt
- https://elinux.org/CAN_Bus
- https://elinux.org/Bringing_CAN_interface_up
- https://github.com/linux-can/can-utils
- https://python-can.readthedocs.io/en/master/interfaces/slcan.html
- https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/drivers/net/can/slcan.c
- https://github.com/darauble/lawicel-slcan
- http://www.can232.com/docs/can232_v3.pdf
- http://www.can232.com/docs/canusb_manual.pdf