Includes BFS, DFS, Dijkstra, WFI, Bellman Ford
BFS describes a strategy for searching a graph, but it does not say that you must search for anything in particular. Works on a Queue (FIFO) basis
Performance: O(E + V),
where V - vertices
and E - edges
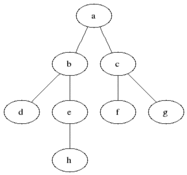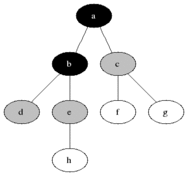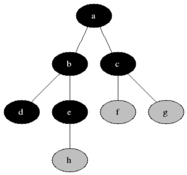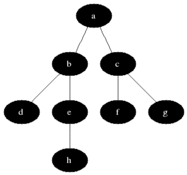
(0)
/ | \
(1) (2) (3)
|
(4)
Output BFS: 0 1 2 3 4
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Similar to BFS but works on a Stack (LIFO) basis
Performance: O(E + V),
where V - vertices
and E - edges
(0)
/ | \
(1) (2) (3)
|
(4)
Output DFS: 0 1 4 2 3
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
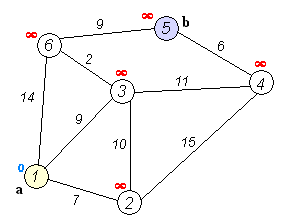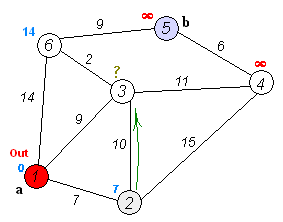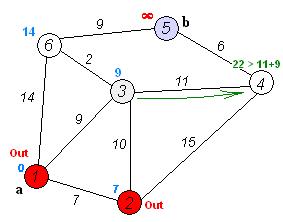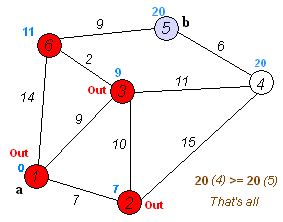
Dijkstra's algorithm adapts BFS to let you find single-source shortest paths. Doesn't work with negative weight
- Set all Vertex distance to Integer.MAX_VALUE (Infinity). After that, update startVertex distance (distance = 0)
- Add startVertex to TreeSet
- While TreeSet is not empty:
- pollFirst from TreeSet
- For each vertex near, try to do relaxation (if it happend, add vertex to the TreeSet)
- Your result will be nearest distance from startVertex to each in graph
-
At each performed relaxation add pointer (pointer at first is startVertex, then pointer is pollFirst from TreeSet) to paths array (for key use
relaxedvertex) -
Than using stack (because you need to reverse path), print it out. Exemple for viewing all pathes from startVertex:
Stack<Integer> realPath = new Stack<>(); for(Vertex vertex : vertices) { if(vertex.dist != Integer.MAX_VALUE) { System.out.print("Path from " + startPoint + " to " + vertex.id + ": " + startPoint); for (int v = vertex.id; v != startPoint; v = paths[v]) realPath.push(v); while (!realPath.isEmpty()) System.out.print("->" + realPath.pop()); System.out.println(); }else System.out.println("No way for "+vertex.id); }
Performance: O(E + VlogV) Θ(ElogV),
where V - vertices
and E - edges
(0)
⁵/ ¹| ³\
(1) (4) (2)
¹\⁶/
(3)
Output: 0 5 3 6 1
Path from 0 to 3: 0->1->3
Path from 0 to 4: 0->4
No way for 5
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Kind of BFS where weight can be only 0 or 1
-
Works like Dijkstra but with some code changes (when we can do relaxation):
if(edge_weight[pointer][edge] == 0) deque.addFirst(edge); else deque.addLast(edge);
- At each performed relaxation add pointer (pointer at first is startVertex, then pointer is pollFirst from TreeSet) to paths array (for key use
relaxedvertex) - Than using stack (because you need to reverse path), print it out. Exemple for viewing all pathes from startVertex:
Performance: O(E + V),
where V - vertices
and E - edges
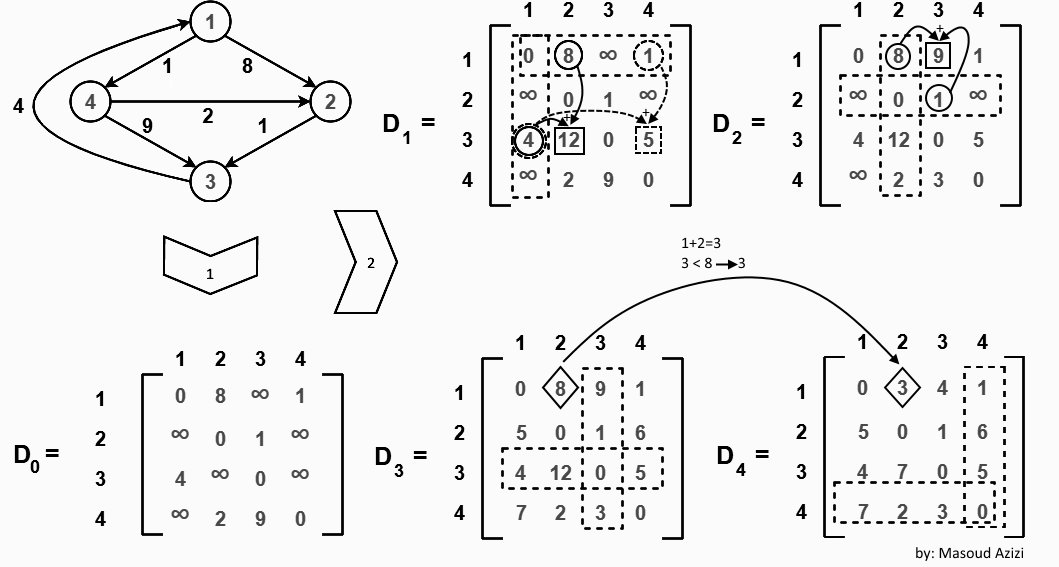
Also known as Floyd's algorithm, the Roy–Warshall algorithm, the Roy–Floyd algorithm.
WFI means
Warshall Floyd Ingerman
(Warshall, Floyd, Roy - idea; Peter Ingerman - algorithm)
It find distance each for each vertex
-
Create adjacency matrix with weight as values. Set diagonal of 0-s (vertex can not be connected to itself). For no connection use
∞Example:A B C A 0 2 3 B ∞ 0 1 C ∞ ∞ 0 -
Use the formula bellow to get result:
matrix[i][j] = Math.min(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j]); -
Write some code:
for(int k = 0; k < n; k++) for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) matrix[i][j] = Math.min(matrix[i][j], matrix[i][k] + matrix[k][j]);
Performance: O(V³) Θ(V²),
where V - count of Vertices
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Work with negative cycles. Doesn't work with undirected and at the same time negative edge
- Set distance that equals Integer.MAX_VALUE for all verteces. Then set distance of startVertex to 0
- For every vertex, do relaxation for others
- At the end you can check if graph contains negative weight cycle
Performance: O(VE) Θ(VE),
where V - count of Vertices
and E - edges
CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons