This script removes defined files from targeted folders. It is meant to be used by System Administrators, because it has many options and settings that can be configured to remove files in multiple and various ways. All data regarding file removal, target folders, file names, optional number of days files must be older then to be removed, if files in subfolders should be removed, and if files should be force removed, are written by user in Data.csv file. User can enter partial names of files in FileName column with a wildcard character, for example *.dat or Backup*. Script generates detailed log file, and report that is sent via email. In Settings.cfg file parameters are stored for email settings, and options to turn on or off console writing, loging, and email report as the user requires them.
Before running File Removal PowerShell Script user must configure the script settings in Settings.cfg file, and the data feeding the script must be entered in Data.csv file.
File Removal PowerShell Script can be configured in Settings.cfg file to write output to console, write permanent log and to send email when it is finished running. Email settings, log title and log separator are also configured in Settings.cfg file.
LogTitle- Define a string to be a title in logsLogSeparator- Define a string to be a separator in logs for clearer visibilityWriteTranscript- Set to true if writing transcript to console is wantedWriteLog- Set to true if writing a permanent log is wantedSendReport- Set to true if sending a report via email log is wantedLogFile- Relative path to permanent log fileReportFile- Relative path to report log fileSmtpServer- SMTP server FQDN or IP addressPort- SMTP port (25/465/587)To- Email address to send report log toFrom- Email address to send report log formSubject- Subject of the report log emailBody- First part of log email body
In Data.csv user enters target folders, target files and optionally number of days to remove files older than that.
| FolderPath | FileName | OlderThen | Recurse | Force |
|---|
-
FolderPath- In this column write the full path of the folder in which files are to be removed.- Example: C:\Folder\Folder\Folder
-
FileName- In this column write the name of the file which is to be removed. It can include a wild card character*so multiple files can be affected.- Example: * (Remove all files in target folder)
- Example: Cache.bat (Remove only the file named "Cache.bat")
- Example: *.bmp (Remove all files with ".bmp" extension)
- Example: Backup* (Remove all files with name starting with "Backup")
-
OlderThen- In this column write the number of days to remove files older than that in integer format- Example: 180 (Remove all files older than six months)
- Example: 0 (Remove all files regardless of file creation time)
-
Recurse- In this column enter true if file removal in subfolders is required.- Example: true (Remove all files even in subfolders of the target folder)
- Example: false (No files in subfolders of the target folder will be removed)
-
Force- In this column enter true if force removal of files is required.- Example: true (Force remove all selected files)
- Example: false (Selected files will not be removed by force)
All of the data parameters are taken in account while script is calculating which files will be removed. This is very convenient because it is possible to target multiple folders with different rulers for file removal with a single script.
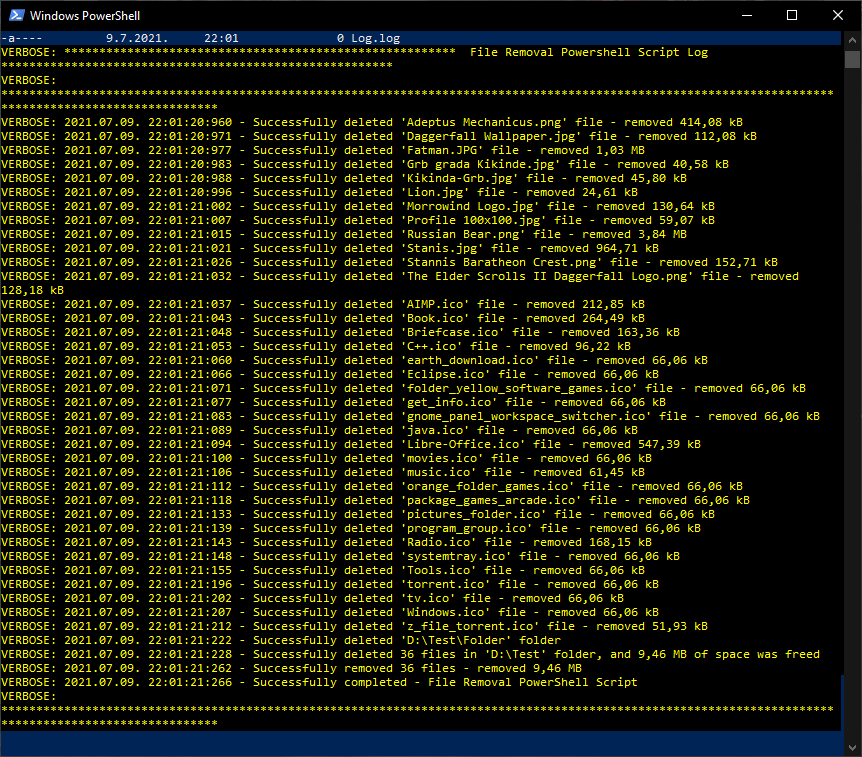
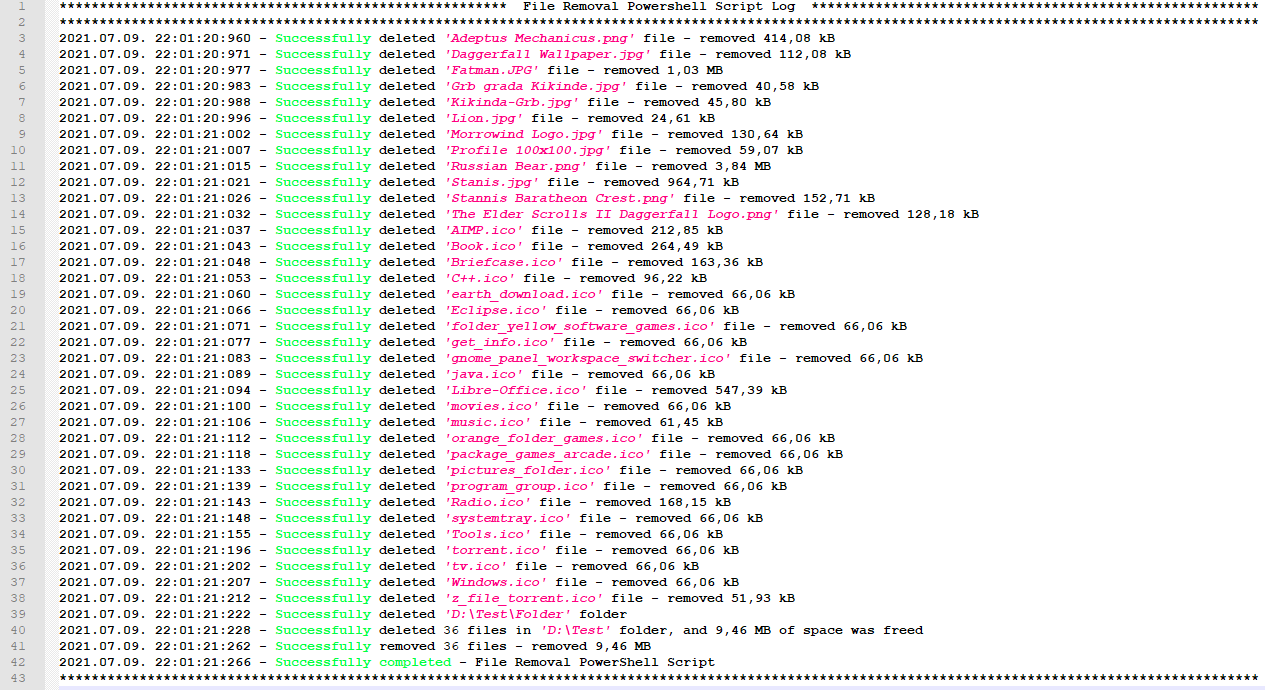
File Removal PowerShell Script can be run manually or with Task Scheduler.
File Removal PowerShell Script generates detailed log file and report, with time stamped log entry of every action and error, with files names which have been removed and disk space freed.
GNU General Public License Version 3
Script developer: Zoran Jankov