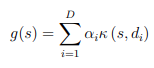This repository implements in TensorFlow 2 the Kernel-Based Activation Function KAF as described in Scardapane et al.. Moreover, results reproduction for some of the experiments carried out in the paper is attempted.
A KAF is a novel class of trainable activation functions defined as the following weighted sum:
where s is a scalar (the activation), k a 1D kernel method, D and d_i respectively the size of the dictionary and the dictionary elements whereas a_i the actual trainable parameters.
Experiments show KAFs as a promising class of trainable activation functions which can satify several desiderable properties as being universal appoximators for compact continuos functions, smooth over their entire domain, introducing only a linear number of parameters wrt the size of the layer in which they are applied. To the best of our knowledge no other trainable activation function guarantees all these properties. Furthermore, perhaps more importantly, accuracy of neural networks which make use of KAF consistently outperforms accuracy gained when using same architecture but "fixed" activation functions such as ReLU, ELU, tanh ecc. .
KAF performances are first evaluated in the context of Feed-forward neural networks using as a benchmark the SUSY dataset and then, similarly, for Convolutional neural networks using the CIFAR-10 dataset.
Theory, experiments and results are commented more in-depth in the relative notebooks.