Alteza is a static site generator driven by PyPage.
Examples of other static site generators can be found here.
Alteza can be thought of as a simpler and more flexible alternative to static site generators like Jekyll, Hugo, Zola, Nextra, etc.
The differentiator with Alteza is that the site author (if familiar with Python) will have a lot more fine-grained control over the output, than what (as far as I'm aware) any of the existing options offer.
The learning curve is also shorter with Alteza. I've tried to follow xmonad's philosophy of keeping things small and simple. Alteza doesn't try to do a lot of things; instead it simply offers the core crucial functionality that is common to most static site generators.
Alteza also imposes very little required structure or a particular "way of doing things" on your website (other than requiring unique names). You retain the freedom to organize your website as you wish. The name Alteza comes from a word that may be translated to illustriousness in Español.
A key design aspect of Alteza is writing little scripts and executing such code to generate your website. Your static site can contain arbitrary Python that is executed at the time of site generation. PyPage, in particular, makes it seamless to include actual Python code inside page templates. (This of course means that you must run Alteza with trusted code, or in an isolated container. For example, in a GitHub action–see instructions below.)
-
The directory structure is generally mirrored in the generated site.
-
By default, nothing is copied/published to the generated site.
- A file must explicitly indicate using a
public: truevariable/field that it is to be published.- Therefore, directories with no public files do not exist in the generated site.
- Files reachable from marked-as-public files will also be publicly accessible.
- Here, reachability is discovered when a provided
linkfunction is used to link to other files.
- Here, reachability is discovered when a provided
- All files starting with a
.are ignored.
- A file must explicitly indicate using a
-
All file and directory names, except for index page files, at all depth levels must be unique. This is to simplify use of the
link(name)function. With unique file and directory names, one can simply link to a file or directory with just its name, without needing to disambiguate a non-unique name with its path. Note: Directories can only be linked to if the directory contains an index page. -
There are two kinds of files: static asset files, and PyPage (i.e. dynamic template/layout or content) files. PyPage files get processed by the PyPage template engine.
-
Static asset files are not read by Alteza. They are selectively either symlinked or copied to the output directory (you can choose which, with a command-line argument). Here, selectively means that they are exposed in the output directory only if they are linked to from a PyPage file using a special Alteza-provided
link(name)function. -
PyPage files are determined based on their file name extension. They are of two kinds:
- Markdown files (i.e. files ending with
.md). - Any file with a
.pybefore its actual extension (i.e. any file with a.pybefore the last.in its file name). These are Non-Markdown Pypage files.
- Markdown files (i.e. files ending with
-
There is an inherited "environment"/
env(this is just a collection of Python variables) that is injected into the lexical scope of every PyPage file, before it is processed/executed by PyPage. Thisenvis a little different for each PyPage invocation--a copy of the inherited isenvis created for each PyPage file. More onenvin a later point below. -
Non-Markdown Pypage files are simply processed with PyPage as-is (and there is no template application step for non-Markdown PyPage files). The
.pypart is removed from their name, and the output/result is copied to the generated site. -
Markdown files:
-
Markdown files are first processed with PyPage, with a copy of the inherited
env. -
After this, the Markdown file is converted to HTML using the Python-Markdown library.
-
Third, they have their "front matter" (if any) extracted using the Python-Markdown's library Meta-Data extension/feature.
- The first line with a
---in the Markdown file ends the front matter section. - The front matter is processed by Alteza as YAML using the PyYAML.
- The first line with a
-
The fields from the YAML front matter the fields are injected into the
env/environment. -
The HTML is injected into a
contentvariable inenv, and thisenvis passed to alayouttemplate specified in configuration, for a second round of processing by PyPage. (Note: PyPage here is invoked on the template.)-
Templates are HTML files processed by PyPage. The PyPage-processed Markdown HTML output is passed to the template/layout as the
contentvariable. The template itself is then executed by PyPage. -
The template/layout should use this
contentvalue via PyPage (with{{ content }}) in order to inject thecontentinto itself. -
The template is specified using a
layoutorlayoutRawvariable declared in a__config__.pyfile. (More on configuration files in a later point below.) -
A
layoutvariable's value must be the name of a template.-
For example, you can write
layout: ordinary-pagein the YAML front matter of a Markdown file. -
Or, alternatively, you can also write
layout = "ordinary_page"in a__config__.pyfile. If alayoutvariable is defined like this in a__config__.pyall adjacent and descendant files will inherit thislayoutvalue.-
This can be used as a way of defining a default layout/template.
-
Of course, the default can be overridden in a Markdown file by specifying a layout name in the YAML front matter, or with a new default in a descendant
__config__.py.
-
-
Lastly, alternatively, a
layoutRawcan also be defined whose value must be the entire contents of a template PyPage-HTML file. A convenience functionreadfileis provided for this. For example, you can write something likelayout = readfile('some_layout.html')in a config file. AlayoutRaw, if specified, takes precedence overlayout. Using thislayoutRawapproach is not recommended.
-
-
Layouts/templates may be overridden in descendant
__config__.pyfiles. Or, may be overridden in the Markdown file itself using YAML front matter (by specifying alayout: ...), or even in a PyPage multiline code tag (not an inline code tag) inside a PyPage file (with alayout = ...).
-
-
Markdown files result in a directory with the base name (i.e. without the
.mdextension), with anindex.htmlfile containing the Markdown's output.
-
-
The Environment (
env) and Configuration (__config__.py, etc.):-
Note: Python code in both
.mdand other.py.*files are run using Python's built-inexec(andeval) functions, and when they're run, we passed in a dictionary for theirglobalsargument. We call that dict the environment, orenv. -
Configuration is done through file(s) called
__config__.py.-
First, we recursively go through all directories top-down.
-
At each directory (descending downward), we execute an
__config__.pyfile, if one is present. After execution, we absorb any variables in it that do not start with a_into theenvdict.
-
-
The deepest
.md/.py.*files get executed first. After it executes, we check if aenvcontains a fieldpublicthat is set asTrue. If it does, we mark that file for publication. Other than recording the value ofpublicafter each dynamic file is executed, any modification toenvmade by a dynamic file are discarded (and not absorbed, unlike with__config__.py).- I would not recommend using
__config__.pyto setpublicasTrue, as that would make the entire directory and all its descendants public (unless that behavior is exactly what is desired). Reachability withlink(described below) is, in my opinion, a better way to make only reachable content publicly exposed.
- I would not recommend using
-
-
The Name Registry and the
linkfunction.-
The name of every file in the input content is stored in a "name registry" of sorts that's used by
link.-
Currently, names, without their file extension, have to be unique across input content. This might change in the future.
-
The Name Registry will error out if it encounters any non-unique names. (I understand this is a significant limitation, so I might support making this opt-out behavior with a
--nonuniqueflag in the future.)
-
-
Any non-dynamic content file that has been
link-ed to is marked for publication (i.e. copying or symlinking). -
A Python function named
linkis injected into the top levelenv.-
This function can be used to get relative links to any other file.
linkwill automatically determine and return the relative path to a file.- For example, one can do
<a href="{{link('some-other-blog-post')}}">, and the generated site will have a relative link to it (i.e. to its directory if a Markdown file, and to the file itself otherwise).
- For example, one can do
-
Reachability of files is determined using this function, and unreachable files will be treated as non-public (and thus not exist in the generated site).
-
-
A file name's extension must be omitted while using
link(including the.py*for any file with.pybefore its extension).- i.e., e.g. one must write
link('magic-turtle')for the filemagic-turtle.md, andlink('pygments-styles')for the filepygments-styles.py.css. - Directories containing index files should just be referred to by the directory name. For example, the index page
about-me/hobbies/index.md(orabout-me/hobbies/index.py.html) should just be linked to with alink('hobbies').
- i.e., e.g. one must write
-
-
Certain fields, with certain names, hold special meaning, and are called/used by Alteza. One such variable is
layout(andlayoutRaw), which points to the layout/template to be used to render the page (as explained in earlier points above). It can be overriden by descendant directories or pages.Built-in Description linkThe
linkfunction takes a name or an object, and returns a relative link to it. If a name is provided, it looks for that name in the NameRegistry (and throws an exception if the name wasn't found).The
linkfunction has the side effect of making the linked-to page publicly accessible, if the page that is creating the link is reachable from another publicly-accessible page. The root/index page is always public.Note: for Markdown pages, an extra
../is added at the beginning of the returned path to accomodate the fact that Markdown pages get turned into directories with the page rendered into anindex.htmlinside the directory.Availability:
Page Template Config Index ✅ ✅ ❌ ✅ pathThe
pathfunction is similar to thepathfunction above, except that:- it does not have the side effect of impacting the reachability graph, and making the linked-to page publicly accessible, and
- it also does not add an extra
../at the beginning of the returned path for Markdown pages.
This function is good for use inside templates, to reference parent/ancestor templates for injection. For example, writing something like
{{ inject(path('skeleton')) }}.Available everywhere.
dirThe
dirvariables points to aDirNodeobject representing the directory that the relevant file is in.This object has a fields like
dir.pages, which is a list of all the pages (a list ofPageNodeobjects) representing all the pages in that directory. Pages means Markdown files and HTML files. Some of the fields indirare:dir.subDirs: List ofFileNodeobjects of files in this directory.dir.files: List ofFileNodeobjects of files in this directory.dir.pages: List ofPageNodeobjects of Markdown files, non-Markdown PyPage files, and HTML files.dir.indexPage: APageNodeobject of the index page, i.e. aindex.mdor aindex.htmlfile. If there is no index page, this isNone.dir.title: A stringtitleobject of the index page, only if the index page specifies a title. If there is no index page or no title specified by it, this isNone.
In templates, the
dirpoints to the directory that the file being processed is in.Available everywhere.
Title The title is accessed with page.title. It is picked up either from PyPage code in the page or atitleYAML field in the file. If `title` is not defined by the page, thenpage.realNameof the file is used, which is the adjusted name of the file without its extension and idea date prefix (if present) removed. The title isn't properly available to Python inside the page itself, or from__config__.py, since the page has not been processed when these are executed. Ifpage.titleis accessed from these (the page or config), or if atitlewas never defined in the page, then the.realNameof the file would be returned.Note: the title can directly be accessed as
title(withoutpageObj.title) in the template (and inherited templates) for the page, since all environment variables from the page are passed on to the template, during template processing.Availability:
Page Template Config Index ❌ ✅ ❌ ✅ YAML fields & other vars YAML fields (and other variables defined in PyPage code) of a page are:
- Available directly to template(s) that the page uses/invokes.
- Stored in
pageObj.env, for future access. The index page, for example, can usepage.envto access these fields & variables. - Stored as attributes in the
PyPageNodepage object, as long as theenvvar does not conflict with an existing attribute ofPyPageNode.- This enables referring to a field or variable with just
page.fieldName(instead of having to writepage.env[fieldName], which is also valid).
- This enables referring to a field or variable with just
Availability (same as
title):Page Template Config Index ❌ ✅ ❌ ✅ Last Modified Date & Time This is only available on
PageNodeobjects.The last modified date & time for a given file is taken from:
a. The date & time of the last commit that modified that file, in git history, if the file is inside a git repo.
b. The last modified date & time as provided by the file system.
There's a
getLastModifiedObj()function which returns a Pythondatetimeobject. There's also agetLastModified(f: str = default_datetime_format)functon which returns astrwith the date & time formatted.The
default_datetime_formatis%Y %b %-d at %-H:%M %p.Note: This function calls spawns a
gitprocess, so is a tiny bit slow.Available everywhere.
Idea Date This is only available on
PageNodeobjects.The "idea date" for a given file is either:
a. For a Markdown file, a date prefix before the markdown file's name, in the form
YYYY-MM-DD.b. If not a Markdown file or there's no date prefix, and the file is in a git repo, then the idea date is the date of the first commit that introduced the file into git history. (Note: this breaks if the file was renamed or moved.)
c. If there is neither a date prefix and the file is not in a git repo, there is no idea date for that file (i.e. it's
Noneor"").There's a
getIdeaDateObj()function which returns a Pythondateobject (orNoneif there's no idea). There's also agetIdeaDate(f: str = default_date_format)functon which returns astrwith the date & time formatted or""if there's no idea date.The
default_date_formatis%Y %b %-d.Note: This function calls spawns a
gitprocess, if it's not a Markdown file or if there is no date prefix in the Markdown file's name.Available everywhere.
readfileThis is just a simple built-in function that reads the contents of a file (assuming utf-8encoding) into a string, and returns it. Available everywhere.shThis exposes the entire shlibrary. The current working directory (CWD) would be wherever the file being executed is located (regardless of whether the file is a regular page or index page or__config__.pyor template). If the file is a template, the CWD would be that of the page being processed.See
sh's documentation here: https://sh.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Available everywhere.
Alteza is available as a GitHub action, for use with GitHub Pages. This is the simplest way to use Alteza, if you intend to use it with GitHub Pages. Using the GitHub action will avoid needing to install or configure Alteza. You can easily create & deply an Alteza website onto GitHub Pages using this action.
To use the GitHub action, create a workflow file called something like
.github/workflows/alteza.yml, and paste the following in it:name: Alteza on: workflow_dispatch: push: branches: [ "main" ] jobs: build: name: Build Website runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: read pages: write id-token: write environment: name: github-pages url: ${{ steps.generate.outputs.page_url }} steps: - name: Generate Alteza Website id: generate uses: arjun-menon/alteza@v0.8.8 with: path: .
The last parameter
pathshould specify which directory in your GitHub repo should be rendered into a website. Also, note: make sure to set thebranchesforworkflow_dispatchcorrectly (to your branch) so that this action is triggered on each push.For an example of this GitHub workflow above in action, see alteza-test (yaml, runs).
You can install Alteza easily with pip:
pip install altezaTry running
alteza -hto see the command-line options available.If you've installed Alteza with pip, you can just run
alteza, e.g.:alteza -h
If you're working on Alteza itself, then run the
altezamodule itself, from the project directory directly, e.g.python3 -m alteza -h.The
-hargument above will print the list of available arguments:usage: __main__.py --content CONTENT --output OUTPUT [--clear_output_dir] [--copy_assets] [--seed SEED] [-h] options: --content CONTENT (str, required) Directory to read the input content from. --output OUTPUT (str, required) Directory to send the output to. WARNING: This will be deleted. --clear_output_dir (bool, default=False) Delete the output directory, if it already exists. --copy_assets (bool, default=False) Copy static assets instead of symlinking to them. --seed SEED (str, default={}) Seed JSON data to add to the initial root env. -h, --help show this help message and exitAs might be obvious above, you set the
contentto your content directory. The output directory will be deleted entirely, before being written to.To test against
test_content(and generate output totest_output), run it like this:python -m alteza --content test_content --output test_output --clear_output_dir
Feel free to send me PRs for this project.
I'm using
black. To re-format the code, just run:black alteza. Fwiw, I've configured my IDE (PyCharm) to always auto-format withblack.To ensure better code quality, Alteza is type-checked with five different type checking systems: Mypy, Meta's Pyre, Microsoft's Pyright, Google's Pytype, and Pyflakes; as well as linted with Pylint.
To run some type checks:
mypy alteza # should have zero errors pyflakes alteza # should have zero errors pyre check # should have zero errors as well pyright alteza # should have zero errors also pytype alteza # should have zero errors too
Or, all at once with:
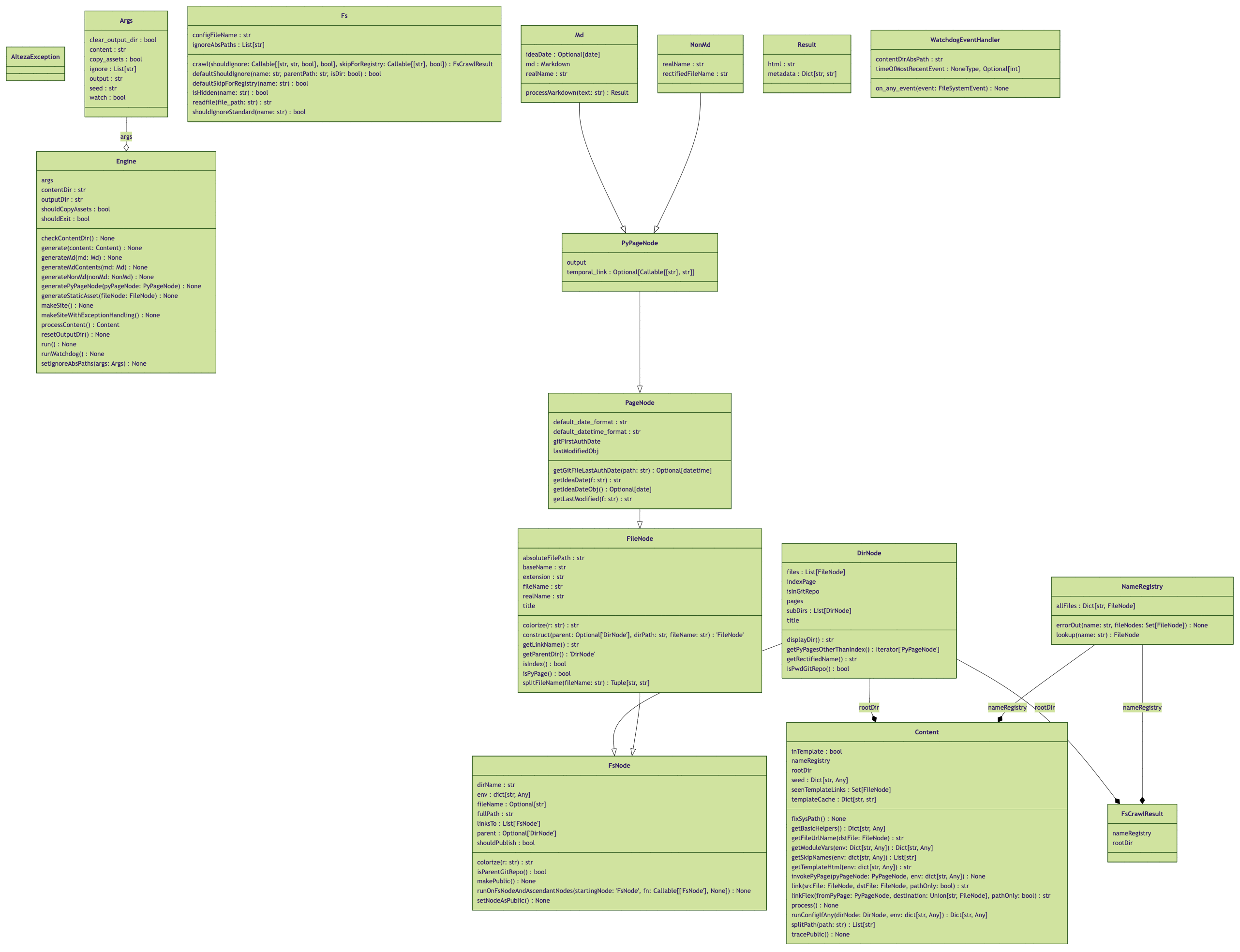
mypy alteza ; pyflakes alteza ; pyre check ; pyright alteza ; pytype alteza. Pytype is pretty slow, so feel free to omit it.Linting policy is very strict. Pylint must issue a perfect 10/10 score, otherwise the Pylint CI check will fail. On a side note, you can see a UML diagram of the Alteza code if you click on any one of the completed workflow runs for the Pylint CI check.
To test whether lints are passing, simply run:
pylint -j 0 altezaTo run it along with all the type checks (excluding
pytype), just run:mypy alteza ; pyre check ; pyright alteza ; pyflakes alteza ; pylint -j 0 alteza. I run this often.Of course, when it makes sense, lints should be suppressed next to the relevant line, in code. Also, unlike typical Python code, the naming convention generally-followed in this codebase is
camelCase. Pylint checks for names have mostly been disabled.Here's the Pylint-generated UML diagram of Alteza's code (that's current as of v0.8.0):
To install dependencies for development, run:
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt python3 -m pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
To use a virtual environment (after creating one with
python3 -m venv venv):source venv/bin/activate # ... install requirements ... # ... do some development ... deactive # end the venv
This project is licensed under the AGPL v3, but I'm reserving the right to re-license it under a license with fewer restrictions, e.g. the Apache License 2.0, and any PRs constitute consent to re-license as such.