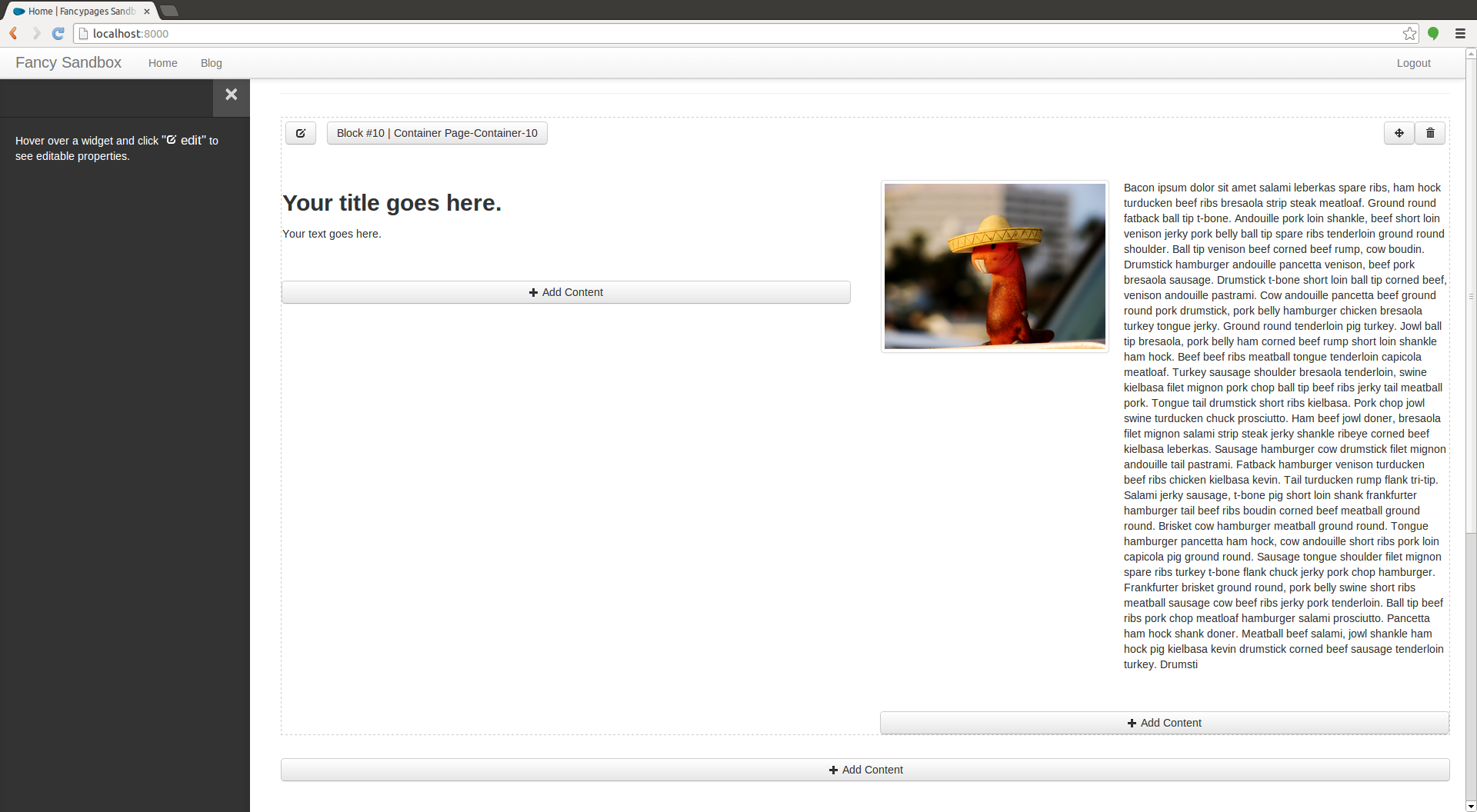
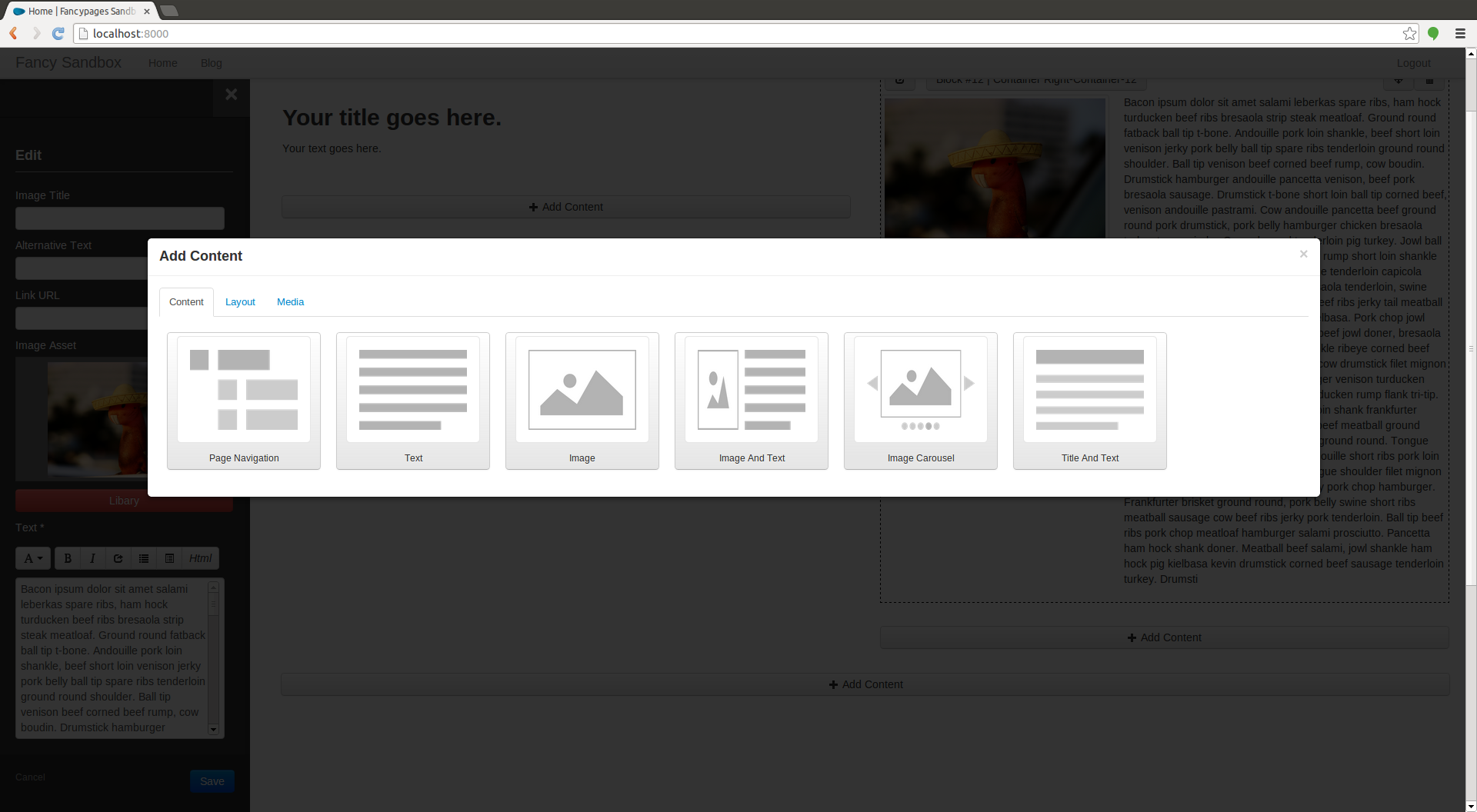
Fancypages provides easy inline page editing.
Another content management system, you ask? No it is not! Rather, it is a content enhancement system (CEnS) because it provides a user with the controlled ability to edit content on a page.
The way this Django app works is inspired by django-frontend-admin, django-content-blocks and other similar apps. Especially, the use of template tags to define customisable sections in a Django template is based on the ideas in the two apps mentioned above.
To use django-fancypages in your own project follow these steps:
Install via pip into you virtualenv (for now you have to install from the github repo because we haven't released it to PyPI yet):
$ pip install git+https://github.com/tangentlabs/django-fancypages.git
Add the required apps to your
INSTALLED_APPSby simply using the convenience functionget_appsin thefancypagesmodule:from fancyages import get_required_apps, get_fancypages_apps YOUR_OTHER_APPS = [ ... ] INSTALLED_APPS = YOUR_OTHER_APPS + get_required_apps() + get_fancypages_apps()Add the editor middleware that provides the editing panel to every fancypage or page that contains an FP container:
MIDDLEWARE_CLASSES = ( ... 'fancypages.middleware.EditorMiddleware', )Add the urls for
django-fancypagesto your project's mainurls.py. Make sure that it is at the end of you definitions otherwise the it will prevent your other URLs from working because it defines a rather generic URL pattern for its pages:urlpatterns = patterns('', ... url(r'^', include(fancypages.urls)), )Fancypages requires several default settings to be added. To make sure that you have all the default settings in your settings, you can use the defaults provided by fancypages itself. Add the following in your settings file before you overwrite specific settings:
... from fancypages.defaults import * ...
The CSS used by fancypages is generated by less using
django-compressor. This means you have to have lessc installed on your
system or in your virtualenv. You can either take care of that yourself or
use the requirements_less.txt file with pip to install both into your
virtualenv:
$ pip install -r requirements_less.txt
That's been a bit of work, hasn't it? Well done! Your should now be able to
access the fancypages dashboard after staring the Django server by running
./manage.py runserver or whatever else you do for that. A very basic
dashboard should now be available at: http://localhost:8000/dashboard/fancypages
- The Chocolate Box: https://www.chocolatebox.com.au
- Which Right Choice: https://www.whichrightchoice.com
- Freetix: https://www.freetix.com.au
- Agatha Christie: http://www.agathachristie.com
django-fancypages is released under the permissive New BSD license.