-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Example Code for Arduino
Before using the Arduino's example code, make sure that the logic levels match. If you are using a 5V Arduino, you could use a logic level converter or voltage division as listed below.
It is recommended to use a dedicated bi-directional LLC for a reliable connection if you are using a 5V Arduino microcontroller:
Fingerprint Scanner (Pin #) <-> Logic Level Converter <-> 5V Arduino w/ Atmega328P
UART_TX (3.3V TTL)(Pin 1) <-> LV4 <-> HV4 <-> RX (pin 4)
UART_RX (3.3V TTL)(Pin 2) <-> LV1 <-> HV1 <-> TX (pin 5)
GND (Pin 3) <-> GND <-> GND <-> GND
Vin (3.3V~6V) (Pin 4) <-> HV <-> 5V
LV <-> 3.3V
After wiring the circuit up, it should look like this:
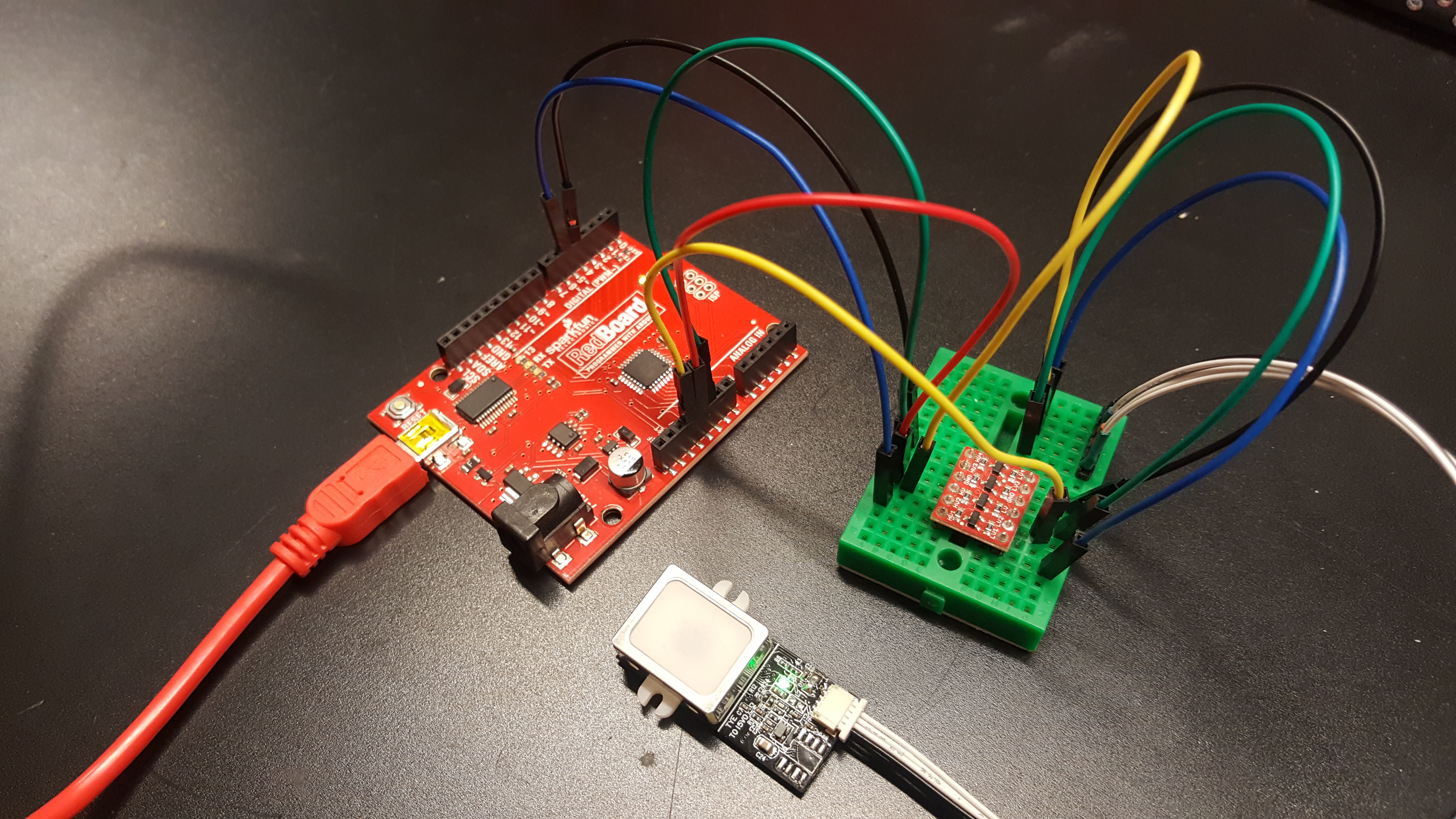
Otherwise, you could use 3x 10kOhm resistors to divide the voltage from a 5V Arduino down to 3.3V FPS similar to the "Uni-Directional" application circuit on our old logic level converter as shown below:
![SparkFun Logic Level Converter [BOB_11978]](https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/b/0/e/1/0/522637c6757b7f2b228b4568.png)
Below is the connection between the FPS, 5V Arduino, and resistors for voltage division:
Voltage Divider <-> Fingerprint Scanner(Pin #) <-> Voltage Divider <-> 5V Arduino w/ Atmega328P
<-> UART_TX (3.3V TTL) (Pin 1) <-> <-> RX (pin 4)
GND <-> 10kOhm <-> 10kOhm <-> UART_RX (3.3V TTL) (Pin 2) <-> 10kOhm <-> TX (pin 5)
GND <-> GND (Pin 3) <-> GND <-> GND
<-> Vin (3.3V~6V) (Pin 4) <-> <-> 5V
Note: You can add the two 10kOhm resistors in series for 20kOhms. =)
After wiring the circuit up, it should look like this:
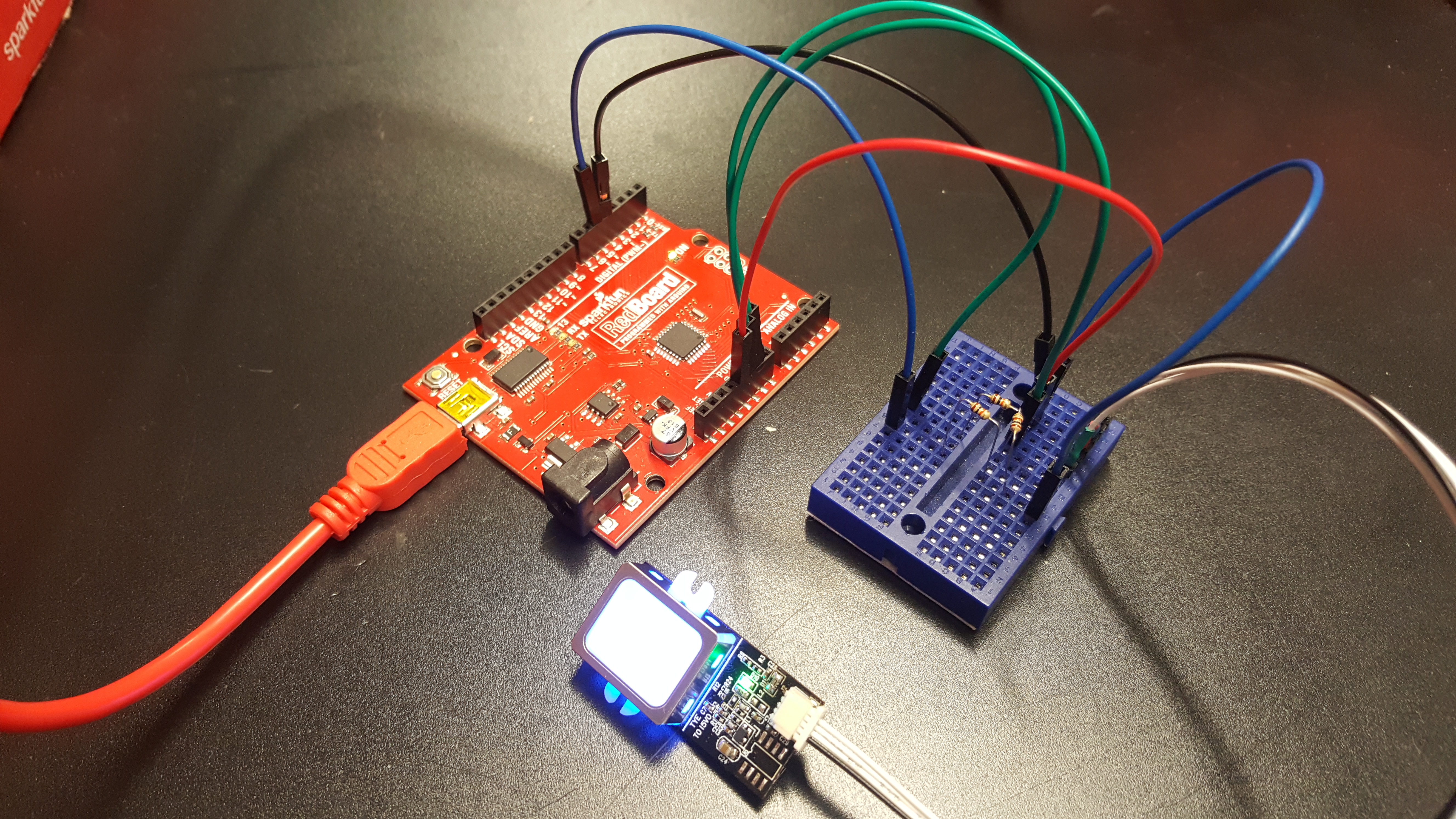
Testing this with a Arduino Uno based microcontroller (i.e RedBoard Programmed with Arduino or Arduino Uno ) and the serial passthrough code, I was able to connect to the SDK demo software provided on the fingerprint scanner's product page. This might be another alternative if you do not have a 3.3V FTDI to connect to your fingerprint scanner.
To use the SDK demo with an Arduino microcontroller connected to the fingerprint scanner, you need to :
- Build a circuit between the Arduino and scanner using logic level translation. This is assuming that you are using a 5V Arduino.
- In the Arduion IDE, upload the FPS_Serial_Passthrough.ino sketch to your Arduino.
- In the SDK_demo.exe labeled Serial Port Number , select a COM port that is lower than COM10 (COM3 should be the lowest that you can use).
- Select a baud rate of 9600 .
- After uploading the serial passthrough code or powering the Arduino for the first time during the session, you will need to reset the Arduino. Press the RESET button.
- After the Arduino initializes, press on the "Open" button in the SDK
The image below shows the SDK_Demo before it is opened with an Arduino on COM7 and a baud of 9600 :
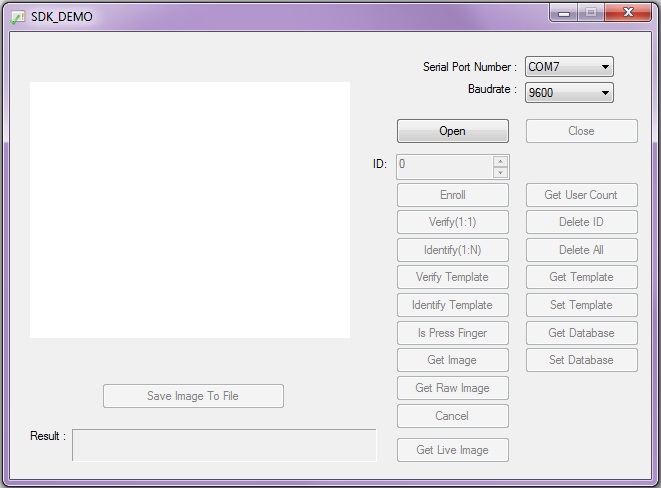
To utilize the features of the fingerprint scanner with an Arduino, you would need to write code based off ADH-Tech's demo SDK software and the protocol commands. Luckily, there was someone in the community that wrote a library and example code. Hawley's code does most of the leg work for you and handles a lot of the complicated protocol commands. This library is limited in functionality compared to the SDK_Demo.exe and it would require more code to utilize all the fingerprint scanner's features used in the SDK. If you look at the comments in the FPS_GT511C3's library, certain functions were not implemented due to the Atmega328P's memory restrictions. Certain functions were also not needed when it was originally written. The FPS_GT511C3 library and example code works with the GT511C3 and GT511C1R models.
Three features were simplified in each of the examples code to:
- Blinks the blue LED.
- Enroll a fingerprint.
- Attempt to identify the fingerprint against the local database.
The FPS_Blink.ino sketch is a basic test to see if the Arduino is able to talk with the fingerprint scanner through the serial UART. As a basic sanity check, it is recommended to test this code to make sure that your connections are correct and the fingerprint is able to send/receive commands. The code sets up a the Arduino's hardware serial UART for debugging and tells the scanner to send serial debug messages. The code also initializes the connection with the fingerprint scanner.
Once the setup is complete, the Arduino will tell the fingerprint scanner to toggle the blue LED. By opening the serial monitor with 9600 baud, you should see this output:
FPS - Open
FPS - SEND: "55 AA 01 00 00 00 00 00 01 00 01 01"
FPS - RECV: "55 AA 01 00 00 00 00 00 30 00 30 01"
FPS - LED on
FPS - SEND: "55 AA 01 00 01 00 00 00 12 00 13 01"
FPS - RECV: "55 AA 01 00 00 00 00 00 30 00 30 01"
FPS - LED off
FPS - SEND: "55 AA 01 00 00 00 00 00 12 00 12 01"
FPS - RECV: "55 AA 01 00 00 00 00 00 30 00 30 01"
The code will repeat and toggle the LED while printing to the serial monitor.
The FPS_Enroll.ino is used for enrolling a fingerprint each time the Arduino is reset. The fingerprint will save in a template within the scanner's local database. The code will initialize like the FPS_Blink.ino sketch. Instead of toggling the LED, the LED will remain on to scan a fingerprint. Before the end of the setup() function, it will jump to the Enroll() function. The Enroll() function will look for an empty template ID and begin enrolling your fingerprint.
Below is what to expect in the serial monitor when enrolling a finger successfully:
Press finger to Enroll #3
Remove finger
Press same finger again
Remove finger
Press same finger yet again
Remove finger
Enrolling Successful
The scanner will reject a fingerprint if the scanner is not able to recognize your finger at anytime during the enrollment process. If your finger is not placed in the same position like the other scans, the template will not be saved. When this happens, you will need to restart the enrollment process.
Below is what to expect when the scanner fails if the first scan does not match the second scan.
Press finger to Enroll #4
Remove finger
Press same finger again
Failed to capture second finger
Try enrolling a fingerprint by uploading the code and following the serial monitor's output. To enroll more than one fingerprint, just reset the Arduino.
The FPS_IDFinger.ino sketch checks to see if a finger is on the scanner. Once a finger has been placed on the scanner, it checks the fingerprint against any of the fingerprints saved in the local database. You will be notified through the serial monitor if the fingerprint matches an ID, if the fingerprint is not found, or when it fails to read the fingerprint. After checking and lifting your finger, it will request for another fingerprint to check.
Below is what you would expect when using this example:
Verified ID:0
Finger not found
Finger not found
Verified ID:0
Verified ID:0
Please press finger
Please press finger
Please press finger
Verified ID:2
Please press finger
Verified ID:2
Please press finger
Looking at the output, "Finger not found" usually means that: the fingerprint does not match any of the template IDs or when the the scanner is not able to clearly read the fingerprint. If the finger has been enrolled, you would need to make sure that you place the fingerprint on the scanner just like when you scanned the finger.
Depending on what model you are using, make sure to change number of IDs in the condition statement. By default, the code uses 200 since the GT-511C3 can hold up to 200 fingerprint templates. If you are using the GT-511C1R, you would need to change the number to 20. Try testing the scanner with the code to see if the scanner is able to read the fingerprints that were enrolled.
The demo code was originally designed for the ATmega328P on the Arduino Uno. If you were using it with ATmega2560 (i.e. Arduino Mega 2560) or ATmega32U4 (i.e. Arduino Leonardo, Pro Micro 5V/16MHz, Pro Micro 3.3V/8Mhz, FioV3, etc.), you would need to re-configure the software serial pin definitions and adjust the connections. Not all the pins can support change interrupts for a serial Rx pin depending on what Arduino microcontroller is used. For more information, try looking at the reference language for the Software Serial library.
To use the FPS on an Arduino Mega 2560 or Arduino Leonardo, you would just need to comment out the line where it says:
SoftwareSerial fps(4, 5); // (Arduino SS_RX = pin 4, Arduino SS_TX = pin 5)
and uncomment out the line here:
SoftwareSerial fps(10, 11); // (Arduino SS_RX = pin 10, Arduino SS_TX = pin 11)
Once you change the code, make sure to rewire your connections to follow the pin definitions.
Caution: The FPS_GT511C3 library might not work for all microcontrollers using the Arduino IDE. As you move away from the ATmega328P family, you may need to modify the code or port the library over to get it working. It would be easier and faster to just have a RedBoard handle the FPS code. To use the fingerprint scanner, you could just write additional code to have the ATmega328P send serial data to the other microcontroller.)