Resumable file upload in PHP using tus resumable upload protocol v1.0.0

Medium Article ⚡ Laravel & Lumen Integration ⚡ Symfony Integration ⚡ CakePHP Integration ⚡ WordPress Integration
tus is a HTTP based protocol for resumable file uploads. Resumable means you can carry on where you left off without re-uploading whole data again in case of any interruptions. An interruption may happen willingly if the user wants to pause, or by accident in case of a network issue or server outage.
- Installation
- Usage
- Extension support
- Events
- Middleware
- Setting up a dev environment and/or running examples locally
- Contributing
- Questions about this project?
- Supporters
Pull the package via composer.
$ composer require ankitpokhrel/tus-php
// Use v1 for dependencies that require Symfony 3 or 4.
$ composer require ankitpokhrel/tus-php:^1.2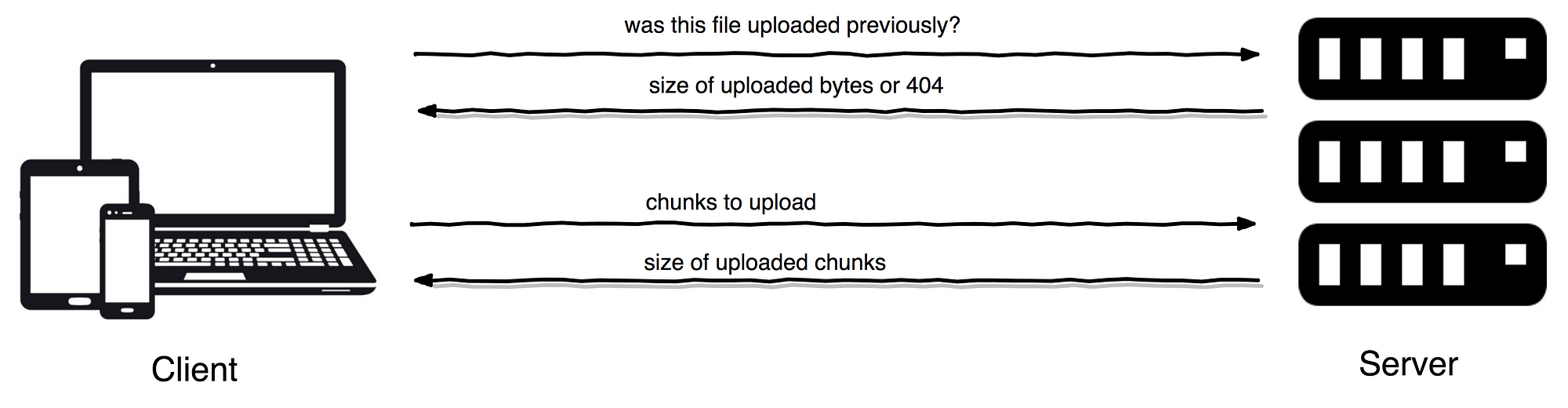 |
|---|
| Basic Tus Architecture |
This is how a simple server looks like.
// server.php
$server = new \TusPhp\Tus\Server('redis'); // Either redis, file or apcu. Leave empty for file based cache.
$response = $server->serve();
$response->send();
exit(0); // Exit from current PHP process.You need to rewrite your server to respond to a specific endpoint. For example:
# nginx.conf
location /files {
try_files $uri $uri/ /server.php?$query_string;
}A new config option fastcgi_request_buffering is available since nginx 1.7.11. When buffering is enabled, the entire request body is read from the client before sending the request to a FastCGI server. Disabling this option might help with timeouts during the upload. Furthermore, it helps if you’re running out of disc space on the tmp partition of your system.
If you do not turn off fastcgi_request_buffering and you use fastcgi, you will not be able to resume uploads because nginx will not give the request back to PHP until the entire file is uploaded.
location ~ \.php$ {
# ...
fastcgi_request_buffering off; # Disable request buffering
# ...
}A sample nginx configuration can be found here.
# .htaccess
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteRule ^files/?(.*)?$ /server.php?$1 [QSA,L]Default max upload size is 0 which means there is no restriction. You can set max upload size as described below.
$server->setMaxUploadSize(100000000); // 100 MB in bytesDefault redis and file configuration for server and client can be found inside config/server.php and config/client.php respectively.
To override default config you can simply copy the file to your preferred location and update the parameters. You then need to set the config before doing anything else.
\TusPhp\Config::set('<path to your config>');
$server = new \TusPhp\Tus\Server('redis');Alternately, you can set REDIS_HOST, REDIS_PORT and REDIS_DB env in your server to override redis settings for both server and client.
The client can be used for creating, resuming and/or deleting uploads.
$client = new \TusPhp\Tus\Client($baseUrl);
// Key is mandatory.
$key = 'your unique key';
$client->setKey($key)->file('/path/to/file', 'filename.ext');
// Create and upload a chunk of 1MB
$bytesUploaded = $client->upload(1000000);
// Resume, $bytesUploaded = 2MB
$bytesUploaded = $client->upload(1000000);
// To upload whole file, skip length param
$client->file('/path/to/file', 'filename.ext')->upload();To check if the file was partially uploaded before, you can use getOffset method. It returns false if the upload
isn't there or invalid, returns total bytes uploaded otherwise.
$offset = $client->getOffset(); // 2000000 bytes or 2MBDelete partial upload from the cache.
$client->delete($key);By default, the client uses /files as an API path. You can change it with setApiPath method.
$client->setApiPath('/api');By default, the server will use sha256 algorithm to verify the integrity of the upload. If you want to use a different hash algorithm, you can do so by
using setChecksumAlgorithm method. To get the list of supported hash algorithms, you can send OPTIONS request to the server.
$client->setChecksumAlgorithm('crc32');Uppy is a sleek, modular file uploader plugin developed by same folks behind tus protocol. You can use uppy to seamlessly integrate official tus-js-client with tus-php server. Check out more details in uppy docs.
uppy.use(Tus, {
endpoint: 'https://tus-server.yoursite.com/files/', // use your tus endpoint here
resume: true,
autoRetry: true,
retryDelays: [0, 1000, 3000, 5000]
})Tus-php server is compatible with the official tus-js-client Javascript library.
var upload = new tus.Upload(file, {
endpoint: "/tus",
retryDelays: [0, 3000, 5000, 10000, 20000],
metadata: {
name: file.name,
type: file.type
}
})
upload.start()Many cloud providers implement PHP streamWrapper interface that enables us to store and retrieve data from these providers using built-in PHP functions. Since tus-php relies on PHP's built-in filesystem functions, we can easily use it to upload files to the providers like Amazon S3 if their API supports writing in append binary mode. An example implementation to upload files directly to S3 bucket is as follows:
// server.php
// composer require aws/aws-sdk-php
use Aws\S3\S3Client;
use TusPhp\Tus\Server;
use Aws\Credentials\Credentials;
$awsAccessKey = 'AWS_ACCESS_KEY'; // YOUR AWS ACCESS KEY
$awsSecretKey = 'AWS_SECRET_KEY'; // YOUR AWS SECRET KEY
$awsRegion = 'eu-west-1'; // YOUR AWS BUCKET REGION
$basePath = 's3://your-bucket-name';
$s3Client = new S3Client([
'version' => 'latest',
'region' => $awsRegion,
'credentials' => new Credentials($awsAccessKey, $awsSecretKey)
]);
$s3Client->registerStreamWrapper();
$server = new Server('file');
$server->setUploadDir($basePath);
$response = $server->serve();
$response->send();
exit(0);- The Creation extension is mostly implemented and is used for creating the upload. Deferring the upload's length is not possible at the moment.
- The Termination extension is implemented which is used to terminate completed and unfinished uploads allowing the Server to free up used resources.
- The Checksum extension is implemented, the server will use
sha256algorithm by default to verify the upload. - The Expiration extension is implemented, details below.
- This Concatenation extension is implemented except that the server is not capable of handling unfinished concatenation.
The Server is capable of removing expired but unfinished uploads. You can use the following command manually or in a cron job to remove them. Note that this command checks your cache storage to find expired uploads. So, make sure to run it before the cache is expired, else it will not find all files that needs to be cleared.
$ ./vendor/bin/tus tus:expired --help
Usage:
tus:expired [<cache-adapter>] [options]
Arguments:
cache-adapter Cache adapter to use: redis, file or apcu [default: "file"]
Options:
-c, --config=CONFIG File to get config parameters from.
eg:
$ ./vendor/bin/tus tus:expired redis
Cleaning server resources
=========================
1. Deleted 1535888128_35094.jpg from /var/www/uploadsYou can use--config option to override default redis or file configuration.
$ ./vendor/bin/tus tus:expired redis --config=<path to your config file>The Server is capable of concatenating multiple uploads into a single one enabling Clients to perform parallel uploads and to upload non-contiguous chunks.
// Actual file key
$uploadKey = uniqid();
$client->setKey($uploadKey)->file('/path/to/file', 'chunk_a.ext');
// Upload 10000 bytes starting from 1000 bytes
$bytesUploaded = $client->seek(1000)->upload(10000);
$chunkAkey = $client->getKey();
// Upload 1000 bytes starting from 0 bytes
$bytesUploaded = $client->setFileName('chunk_b.ext')->seek(0)->upload(1000);
$chunkBkey = $client->getKey();
// Upload remaining bytes starting from 11000 bytes (10000 + 1000)
$bytesUploaded = $client->setFileName('chunk_c.ext')->seek(11000)->upload();
$chunkCkey = $client->getKey();
// Concatenate partial uploads
$client->setFileName('actual_file.ext')->concat($uploadKey, $chunkBkey, $chunkAkey, $chunkCkey);Additionally, the server will verify checksum against the merged file to make sure that the file is not corrupt.
Often times, you may want to perform some operation after the upload is complete or created. For example, you may want to crop images after upload or transcode a file and email it to your user. You can utilize tus events for these operations. Following events are dispatched by server during different point of execution.
| Event Name | Dispatched |
|---|---|
tus-server.upload.created |
after the upload is created during POST request. |
tus-server.upload.progress |
after a chunk is uploaded during PATCH request. |
tus-server.upload.complete |
after the upload is complete and checksum verification is done. |
tus-server.upload.merged |
after all partial uploads are merged during concatenation request. |
To listen to an event, you can simply attach a listener to the event name. An TusEvent instance is created and passed to all of the listeners.
$server->event()->addListener('tus-server.upload.complete', function (\TusPhp\Events\TusEvent $event) {
$fileMeta = $event->getFile()->details();
$request = $event->getRequest();
$response = $event->getResponse();
// ...
});or, you can also bind some method of a custom class.
/**
* Listener can be method from any normal class.
*/
class SomeClass
{
public function postUploadOperation(\TusPhp\Events\TusEvent $event)
{
// ...
}
}
$listener = new SomeClass();
$server->event()->addListener('tus-server.upload.complete', [$listener, 'postUploadOperation']);You can manipulate request and response of a server using a middleware. Middleware can be used to run a piece of code before a server calls the actual handle method. You can use middleware to authenticate a request, handle CORS, whitelist/blacklist an IP etc.
In order to create a middleware, you need to implement TusMiddleware interface. The handle method provides request and response object for you to manipulate.
<?php
namespace Your\Namespace;
use TusPhp\Request;
use TusPhp\Response;
use TusPhp\Middleware\TusMiddleware;
class Authenticated implements TusMiddleware
{
// ...
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public function handle(Request $request, Response $response)
{
// Check if user is authenticated
if (! $this->user->isLoggedIn()) {
throw new UnauthorizedHttpException('User not authenticated');
}
$request->getRequest()->headers->set('Authorization', 'Bearer ' . $this->user->token());
}
// ...
}To add a middleware, get middleware object from server and simply pass middleware classes.
$server->middleware()->add(Authenticated::class, AnotherMiddleware::class);Or, you can also pass middleware class objects.
$authenticated = new Your\Namespace\Authenticated(new User());
$server->middleware()->add($authenticated);If you wish to skip or ignore any middleware, you can do so by using the skip method.
$server->middleware()->skip(Cors::class, AnotherMiddleware::class);An ajax based example for this implementation can be found in examples/ folder. You can either build and run it using docker or use kubernetes locally with minikube.
Make sure that docker and docker-compose are installed in your system. Then, run docker script from project root.
$ bin/docker.shNow, the client can be accessed at http://0.0.0.0:8080 and server can be accessed at http://0.0.0.0:8081. Default API endpoint is set to/files
and uploaded files can be found inside uploads folder. All docker configs can be found in docker/ folder.
We also have some utility scripts to re-create docker images.
Please note that bin/rebuild.sh will delete tus-php related docker containers and images.
It will also delete uploads folder and re-create it. So that when you use bin/docker.sh
it will be like a fresh start. This command is useful when you start to make changes
to docker configurations, server configrations.
$ bin/rebuild.sh
$ bin/docker.shMake sure you have minikube and kubectl are installed in your system. Then, build and spin up containers using k8s script from project root.
$ bin/k8s.shThe script will set minikube docker env, build all required docker images locally, create kubernetes objects and serve client at port 30020. After successful build,
the client can be accessed at http://192.168.99.100:30020 and server can be accessed at http://192.168.99.100:30021.
The script will create 1 client replica and 3 server replicas by default. All kubernetes configs can be found inside k8s/ folder, you can tweak it as required.
You can use another helper script while using minikube to list all uploaded files, login to redis and clear redis cache.
# List all uploads
$ bin/minikube.sh uploads
# Login to redis
$ bin/minikube.sh redis
# Clear redis cache
$ bin/minikube.sh clear-cacheSince the server supports tus expiration extension, a cron job is set to run once a day at midnight to free server resources. You can adjust it as required in k8s/cron.yml.
- Install PHPUnit and composer if you haven't already.
- Install dependencies
$ composer install
- Run tests with phpunit
$ ./vendor/bin/phpunit # or $ composer test
- Validate changes against PSR2 Coding Standards
$ composer cs-fixer # or $ ./vendor/bin/php-cs-fixer fix <changes>
Note: There is an extra command composer test-coverage that will generate coverage
at project root. You can open coverage/index.html to checkout coverage report.
# Command to Generate Coverage
$ docker exec tus-php-server composer test-coveragePlease feel free to report any bug found. Pull requests, issues, and project recommendations are more than welcome!






