This is an overview of all github repositories associated with PuckerLab. Please find a list of the science communication projects, the developed bioinformatics tools, teaching activities, and project specific repositories below.
(1.1) MybMonday
Specific facts and research projects about MYB transcription factors are shared on a weekly basis via Twitter and LinkedIn using #MybMonday. All posts are collected in the #MybMonday github repository.

(1.2) FlavonoidFriday
Specific facts and research projects about the flavonoid biosynthesis are shared on a weekly basis via Twitter and LinkedIn using #FlavonoidFriday. All posts are collected in the #FlavonoidFriday github repository.
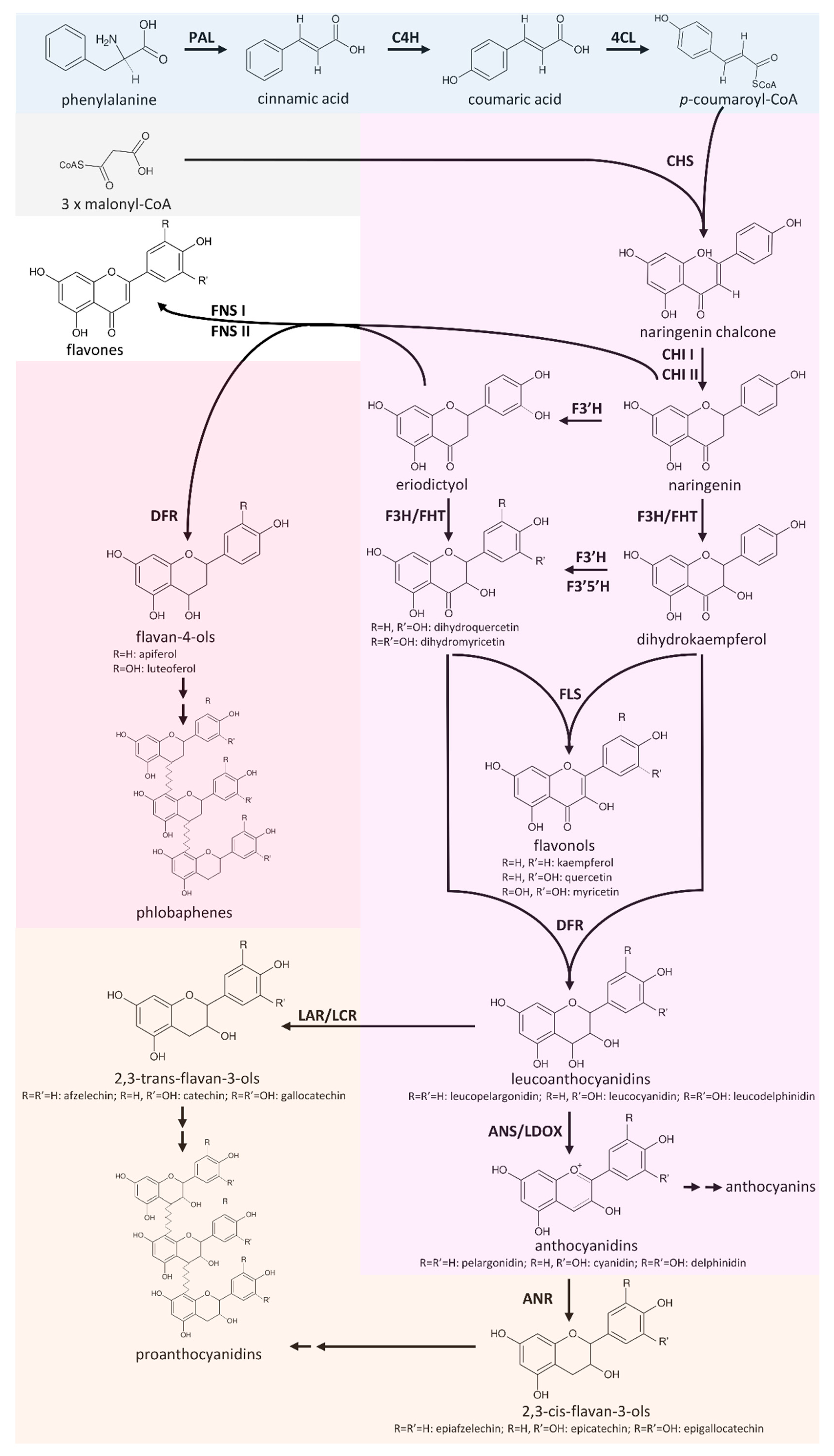
Knowledge-based Identification of Pathway Enzymes (KIPEs) performs an automatic annotation of the flavonoid biosynthesis steps in a new transcriptome of genome sequence assembly. Scripts and datasets are availabe in the KIPEs repository. KIPEs is also available on our web server. This enables all scientists to use KIPEs in their research projects. Please find additional details in the corresponding publication 'Automatic Identification of Players in the Flavonoid Biosynthesis with Application on the Biomedicinal Plant Croton tiglium'. Recently, we updated KIPEs with additional features and data sets as described in our preprint 'KIPEs3: Automatic annotation of biosynthesis pathways'.

This tool performs an automatic identification, annotation, and analysis of the MYB gene family in plants. It can be applied to new transcriptome of genome assemblies. Please find the scripts and data sets in the MYB_annotator repository. The MYB_annotator is also available on our web server. This enables all scientists to use the bHLH_annotator in their research projects. Please find additional details in the corresponding publication 'Automatic identification and annotation of MYB gene family members in plants'.

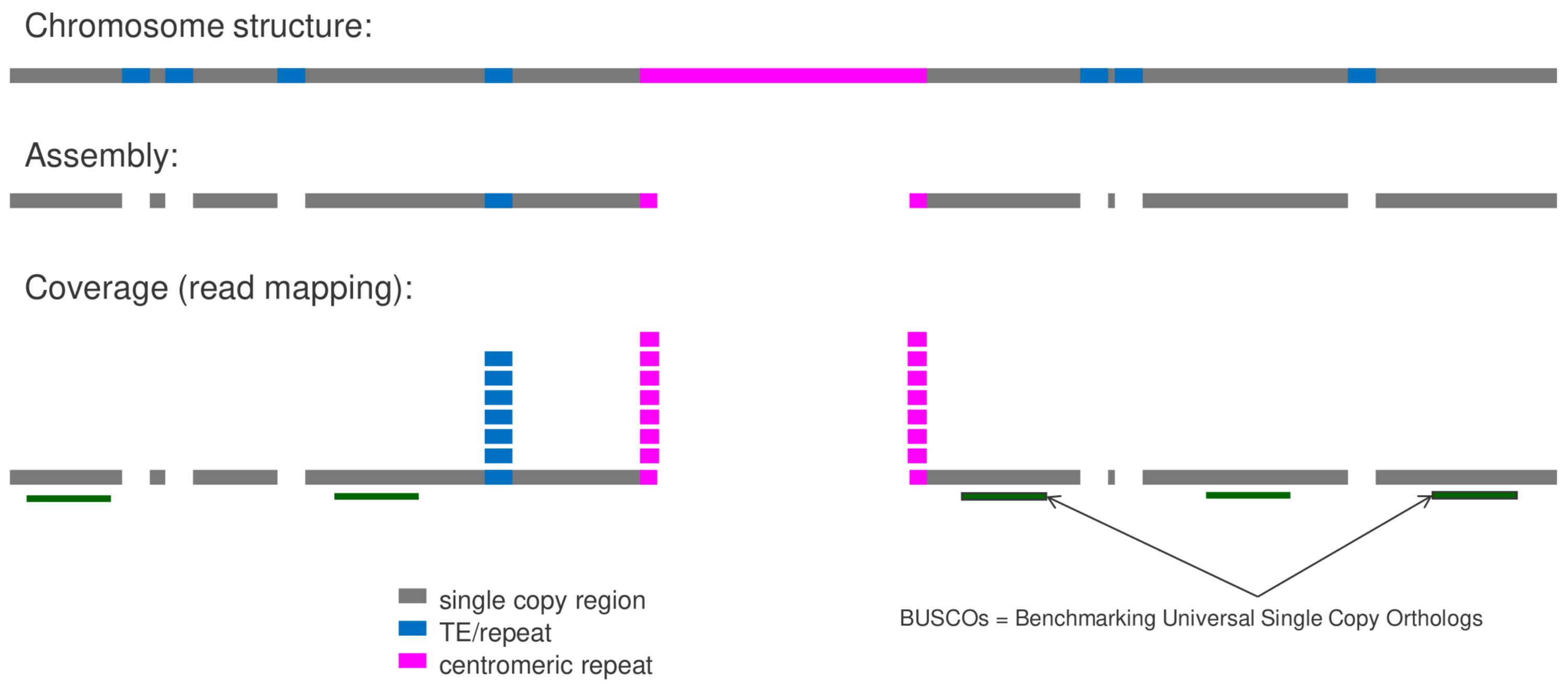
Mapping-based Genome Size Estimation (MGSE) performs an estimation of a genome size based on a read mapping to an existing genome sequence assembly. Please find the script and detailed instructions in the MGSE repository. Additional details are described in the corresponding publication 'Mapping-based genome size estimation'.
Prediction of the functional consequences of sequence variants listed in a VCF file. Please find scripts and detailed instructions in the NAVIP repository. We are currently working to make NAVIP available through our web server. Please find additional details in the corresponding publication 'Influence of neighboring small sequence variants on functional impact prediction'.

This tool performs an automatic identification, annotation, and analysis of the bHLH transcription factor gene family in plants. It can be applied to new transcriptome assemblies or to the annotation derived from genome sequences. Please find the scripts and data sets in the bHLH_annotator repository. The bHLH_annotator is also available on our web server. This enables all scientists to use the bHLH_annotator in their research projects. Please find additional details in the corresponding publication 'Automatic annotation of the bHLH gene family in plants'.

This course enables life scientists to learn Python basics to address their specific research questions. The APPLS repository contains the materials of this course.

This course provides a comprehensive introduction to the analysis of next generation sequencing (NGS) data sets. All materials are available in the AGR repository.

This course introduces molecular biologists to wet lab methods of genome research. Please find the materials in the MMGR repository.

Material used in this course can be found here.

Material used in this course can be found here. Scripts and instructions of the bioinformatics component are available here.
Material used in this course can be found here. Scripts and instructions of the bioinformatics component are available here.
iGEM (international Genetically Engineered Machine) is the largest synthetic biology competition with over 300 international teams participating each year. PuckerLab was/is hosting the TU Braunschweig iGEM2022 and TU Braunschweig iGEM2023 teams.

Material used in this course can be found here.
Material used in this course can be found here. Additional data sets are available here.
Material used in this course can be found here.
Material used in this course can be found here.
Scripts associated with our analysis of the FNS I evolution in the Apiaceae are available in the ApiaceaeFNS1 repository. Please find additional details in our preprint Apiaceae FNS I originated from F3H through tandem gene duplication.
The CoExp repository contains several scripts associated with a co-expression analysis. This includes the preparation of count tables with kallisto. The actual co-expression analysis is also available through our webserver.
The scripts in the pitaya repository were developed and applied to refute two publications about pigments in this Caryophyllales plant species. Please find additional details in our publication The report of anthocyanins in the betalain-pigmented genus Hylocereus is not well evidenced and is not a strong basis to refute the mutual exclusion paradigm and preprint The evidence for anthocyanins in the betalain-pigmented genus Hylocereus is weak.
The LongReadWalker allows to close gaps between contigs of long read assemblies. All reads are screened for overlaps with the flanking contigs. Matches are used to extend contigs. An iterative approach is similar to the walking strategy deployed in the early days of genome sequencing when primers were placed at the border of known sequences to 'walk' into unknown sequences. The LongReadWalker tries to close a gap starting at both flanking contigs. The resulting sequences should match to fully support the gap replacing sequence.
The GKseq repository contains some scripts used for the analysis described in our paper Large scale genomic rearrangements in selected Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA lines are caused by T-DNA insertion mutagenesis. Please find loreta in this separate repository.
Please find NAVIP in the corresponding repository. Detailed explanations can be found in our preprint Influence of neighboring small sequence variants on functional impact prediction.
Please find scripts associated with our benchmarking study Comparison of Read Mapping and Variant Calling Tools for the Analysis of Plant NGS Data in the variant calling repository.
The yam repository contains several analysis scripts associated with the investigation of the yam genome sequence High Contiguity de novo Genome Sequence Assembly of Trifoliate Yam (Dioscorea dumetorum) Using Long Read Sequencing.
The ncss repository contains scripts required for the systematic analysis of non-canonical splice sites. Please find additional details in the corresponding publications Genome-wide analyses supported by RNA-Seq reveal non-canonical splice sites in plant genomes and Animal, Fungi, and Plant Genome Sequences Harbor Different Non-Canonical Splice Sites.
The At7 repository contains several scripts associated with the coverage analyses performed on the At7 genome sequencing data sets. Please find additional details in the corresponding publicaton Twenty-Five Years of Propagation in Suspension Cell Culture Results in Substantial Alterations of the Arabidopsis Thaliana Genome.
The Nd-1 repository contains scripts developed for the PacBio sequencing of the Arabidopsis thaliana Nd-1 genome sequence. Please find additional details in the corresponding publication A chromosome-level sequence assembly reveals the structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana Nd-1 genome and its gene set.
The PEPD repository contains scripts and instructions associated with the analysis of the PEPD structure. Please find additional details about the analysis results in our preprint Harnessing natural diversity to identify key amino acid residues in prolidase.
https://github.com/bpucker/CaryoAnthoBlock (under review)
All tools developed by the Plant Biotechnology and Bioinformatics group @ TU braunschweig are available in the PBBtools repository. Many of these tools are available via our BioinfToolServer.
Please find a full list of our publications on the @PuckerLab website.
Do you have questions or are you interested in a collaboration? Please get in touch via email.