The mOTU profiler is a computational tool that estimates relative taxonomic abundance of known and currently unknown microbial community members using metagenomic shotgun sequencing data.
Check the wiki for more information.
If you are using mOTUs, please cite:
Alessio Milanese, Daniel R Mende, Lucas Paoli, Guillem Salazar, Hans-Joachim Ruscheweyh, Miguelangel Cuenca, Pascal Hingamp, Renato Alves, Paul I Costea, Luis Pedro Coelho, Thomas S B Schmidt, Alexandre Almeida, Alex L Mitchell, Robert D Finn, Jaime Huerta-Cepas, Peer Bork, Georg Zeller & Shinichi Sunagawa. Microbial abundance, activity and population genomic profiling with mOTUs2; Nature Communications 10, Article number: 1014 (2019). PMID: 30833550; doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08844-4
The mOTU profiler requires:
- Python 3 (or higher)
- the Burrow-Wheeler Aligner v0.7.15 or higher (bwa)
- SAMtools v1.5 or higher (link)
In order to use the command snv_call you need:
- metaSNV v1.0.3, available also on bioconda (we assume metaSNV.py to be in the system path)
Check installation wiki to see how to install the dependencies with conda.
mOTUs can be installed either by using pip or via conda.
Installation with conda has the advantage that it will also download and install dependencies:
# Install in the base environment
conda install motus
# OR, create a new environment
conda create -n motu-env motus
conda activate motu-envInstallation with pip:
# Download and install mOTUs
pip install motu-profiler
# Download the mOTUs database
motus downloadDBYou can test that motus is intalled correctly with:
motus profile --test
Here is a simple example on how to obtain a taxonomic profiling from a raw read file:
motus profile -s metagenomic_sample.fastq > taxonomy_profile.txtYou can separate the previous call as:
motus map_tax -s metagenomic_sample.fastq -o mapped_reads.sam
motus calc_mgc -i mapped_reads.sam -o mgc_ab_table.count
motus calc_motu -i mgc_ab_table.count > taxonomy_profile.txt
rm mapped_reads.sam mgc_ab_table.countThe use of multiple threads (-t) is recommended, since bwa will finish faster. Here is an example with Paired-End reads:
motus profile -f for_sample.fastq -r rev_sample.fastq -s no_pair.fastq -t 6 > taxonomy_profile.txtYou can merge taxonomy files from different samples with mOTU merge:
motus profile -s metagenomic_sample_1.fastq -o taxonomy_profile_1.txt
motus profile -s metagenomic_sample_2.fastq -o taxonomy_profile_2.txt
motus merge -i taxonomy_profile_1.txt,taxonomy_profile_2.txt > all_sample_profiles.txtYou can profile samples that have been sequenced through different runs:
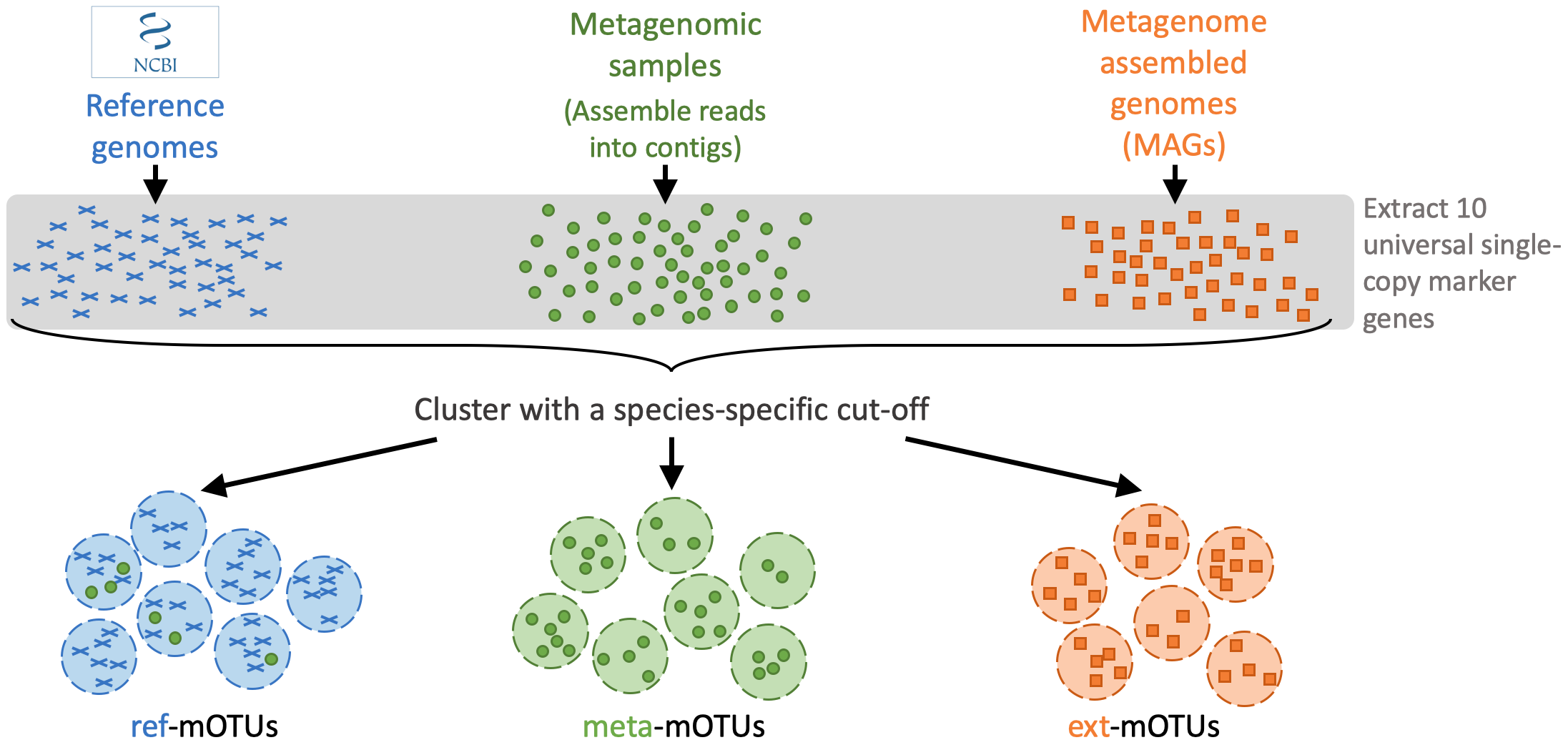
motus profile -f sample1_run1_for.fastq,sample1_run2_for.fastq -r sample1_run1_rev.fastq,sample1_run2_rev.fastq -s sample1_run1_single.fastq > taxonomy_profile.txtThe mOTUs tool performs taxonomic profiling of metagenomics and metatrancriptomics samples, i.e. it identifies species and their relative abundance present in a sample. It is based on a set of mOTUs (~species) contained in the mOTUs database. The mOTUs database is created from reference genomes, metagenomic samples and metagenome assembled genomes (MAGs):
A mOTUs database is composed of three types of mOTUs:
- ref-mOTUs, which represent known species,
- meta-mOTUs, which represent unknown species obtained from metagenomic samples,
- ext-mOTUs, which represent unknown species obtained from MAGs.
Note that meta- and ext-mOTUs will not have a species level annotation.
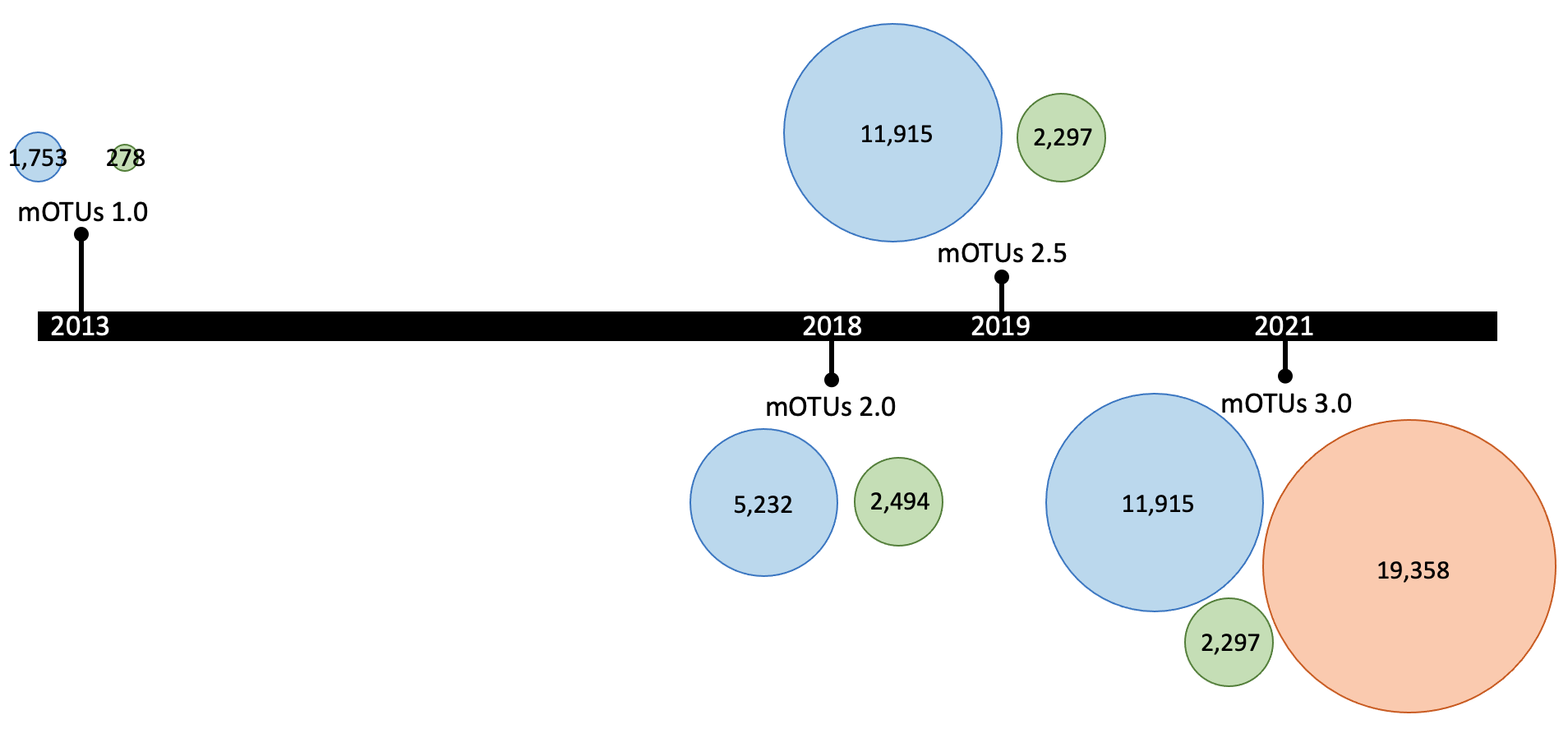
The mOTUs database is updated periodically, e.g the latest version (3.0.3), which doubles the number of profilable species by including ~600,000 draft genomes. Major releases are represented in the following graph (where the numbers represents the number of mOTUs for each of the three groups, with the same color-code as the previous graph):
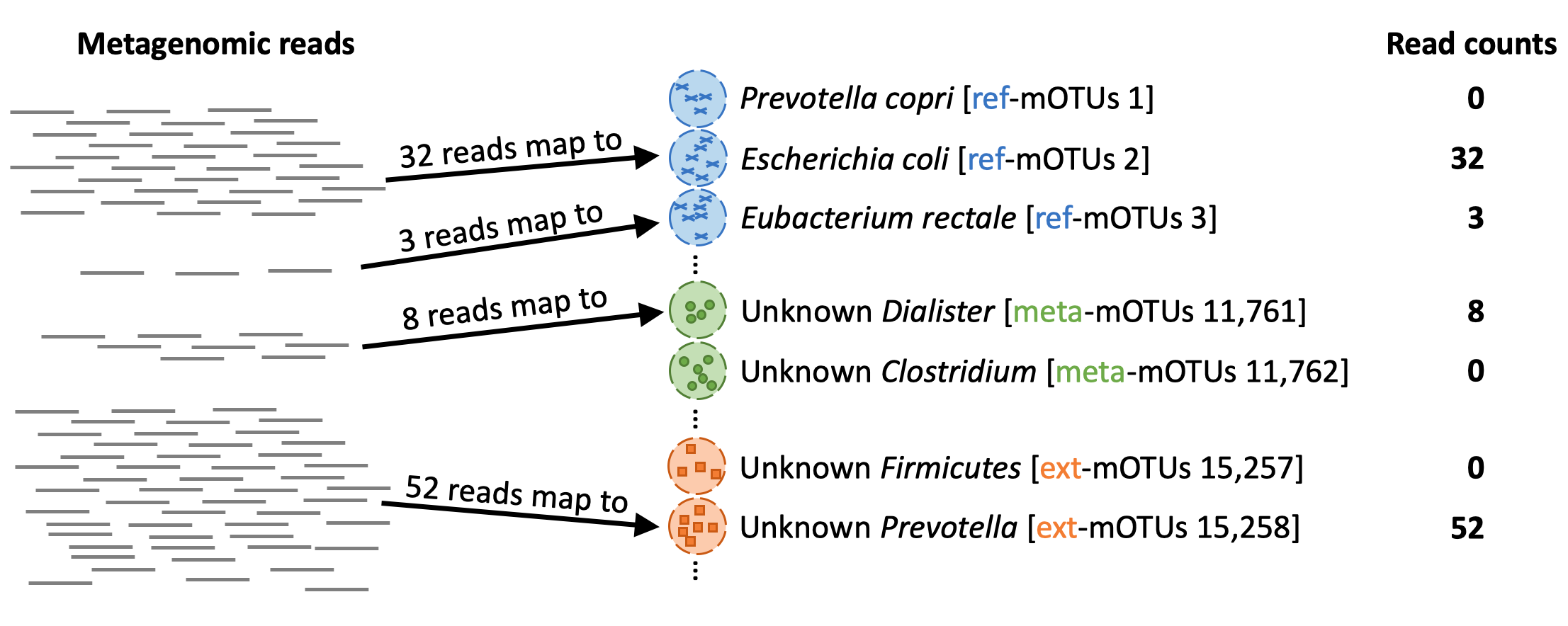
When profiling (motus profile) a metagenomic sample, the mOTUs tool maps the reads from the sample to the genes in the different mOTUs:
Version 3.0.3 2022-07-13 by AlessioMilanese
- Add command
prep_longto allow the profiling of long reads (more information here).
Version 3.0.2 2022-01-31 by AlessioMilanese
- Convert the repository to a python package and submit to PyPI
Version 3.0.1 2021-07-27 by AlessioMilanese
- Improve ref-mOTUs taxonomy according to #76
- Solve bug with
-Aoption
Version 3.0.0 2021-06-22 by AlessioMilanese
- Improve code base
- Minor bug fixes
Version 2.6.1 2021-04-27 by AlessioMilanese
- Minor bug fixes
- Improved the taxonomy of 32 ref-mOTUs (#45)
Version 2.6.0 2021-03-08 by AlessioMilanese
- Add 19,358 new mOTUs
- Add taxonomic profiles of > 11k metagenomic and metatranscriptomic samples. The updated merge function can integrate those in to the users results.
- Minor bug fixes
- Change
-1tounassigned
Version 2.5.1 2019-08-17 by AlessioMilanese
- Update the taxonomy to participate to the CAMI 2 challenge
Version 2.5.0 2019-08-09 by AlessioMilanese
- Add -db option to use a database from another directory
- Add -A to print all taxonomy levels together
- Update the database with more than 60k new reference genomes. There are 11,915 ref-mOTUs and 2,297 meta-mOTUs.
Version 2.1.1 2019-03-04 by AlessioMilanese
- Correct problem with samtools when installing with conda
Version 2.1.0 2019-03-03 by AlessioMilanese
- Correct error '\t\t' when printing -C recall
- Update database (gene coordinates)
Version 2.0.1 2018-08-23 by AlessioMilanese
- Add -C to print the result in CAMI format (BioBoxes format 0.9.1)
- Add -K to snv_call command to keep all the directories produced by metaSNV
Version 2.0.0 2018-06-12 by AlessioMilanese
- Set relative abundances as default (instead of counts)
- Add -B to print the result in BIOM format
- Add test directory
- Python2 is not supported anymore
- Minor bug fixes
Version 2.0.0-rc1 2018-05-10 by AlessioMilanese
- First release supporting all basic functionality.